NASA has some high hopes for the James Webb Space Telescope, which finished the “cold” phase of its construction at the end of November 2016. The result of 20 years of engineering and construction, this telescope is seen as Hubble’s natural successor. Once it is deployed in October of 2018, it will use a 6.5 meter (21 ft 4 in) primary mirror to examine the Universe in the visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared wavelengths.
All told, the JWST will be 100 times more powerful than its predecessor and will be capable of looking over 13 billion years in time. To honor the completion of the telescope, Northrop Grumman – the company contracted by NASA to build it – and Crazy Boat Pictures teamed up to produce a short film about it. Titled “Into the Unknown – the Story of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope“, the video chronicles the project from inception to completion.
The film (which you can watch at the bottom of the page) shows the construction of the telescope’s large mirrors, its instrument package, and its framework. It also features conversations with the scientists and engineers who were involved and some stunning visuals. In addition to detailing the creation process, the film also delves into the telescope’s mission and all the cosmological questions it will address.
In addressing the nature of James Webb’s mission, the film also pays homage to the Hubble Space Telescope and its many accomplishments. Over the course of its 26 years of operation, it has revealed auroras and supernovas and discovered billions of stars, galaxies, and exoplanets, some of which were shown to orbit within their star’s respective habitable zones.
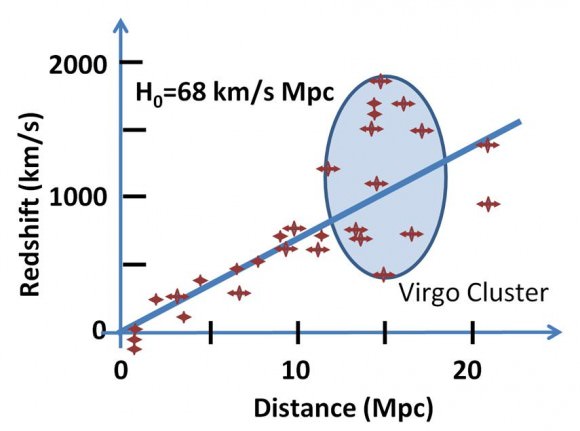
On top of that, Hubble was used to determine the age of the Universe (13.8 billion years) and confirmed the existence of the supermassive black hole (SMBH) – Sagittarius A* – at the center of our galaxy, not to mention many others. It was also responsible for measuring the rate at which the Universe is expanding – in other words, measuring the Hubble Constant.
This played a pivotal role in helping scientists to develop the theory of Dark Energy, one of the most profound discoveries since Edwin Hubble (the telescope’s namesake) proposed that the Universe is in a state of expansion back in 1929. So it goes without saying that the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope led to some of the greatest discoveries in modern astronomy.
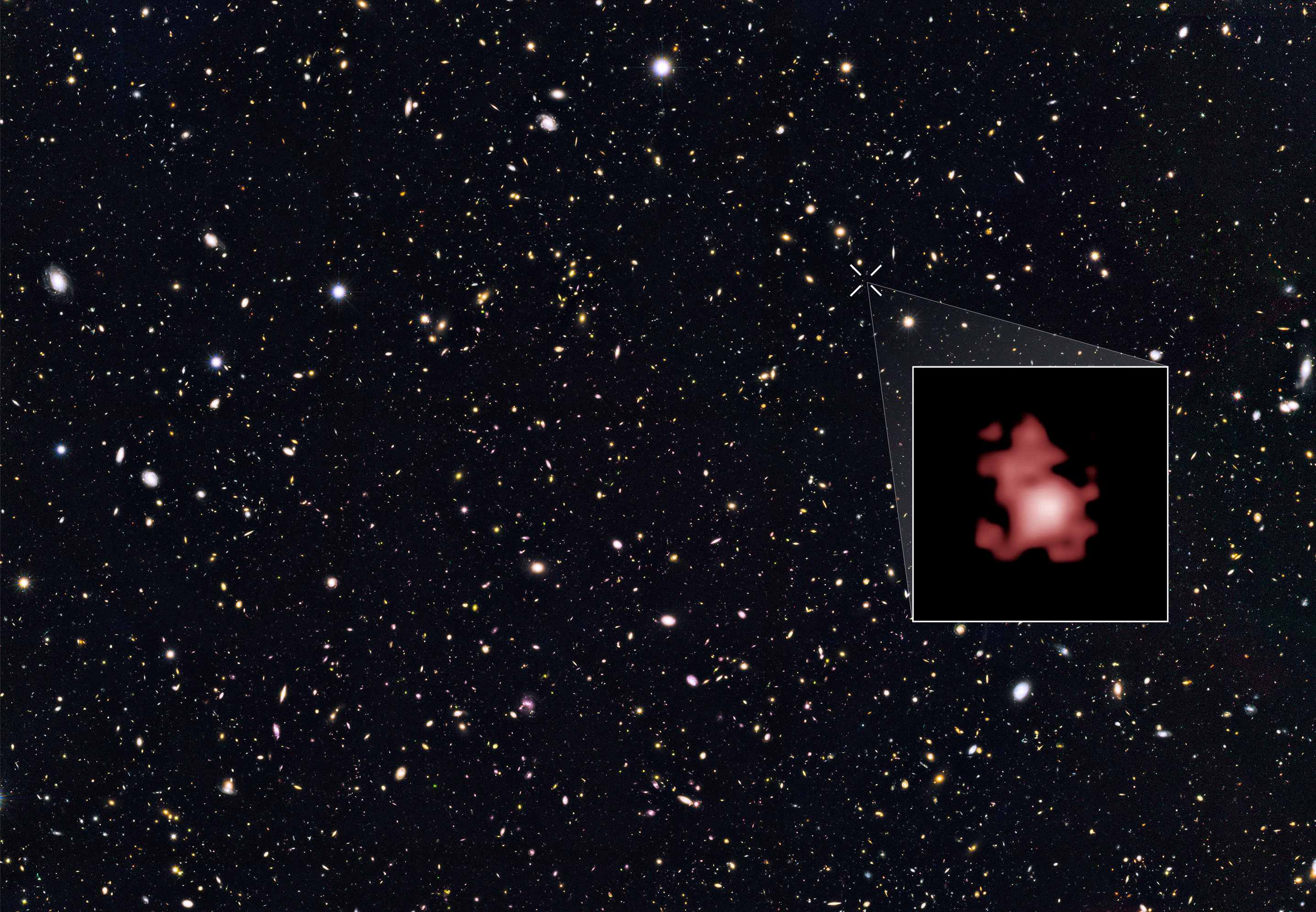
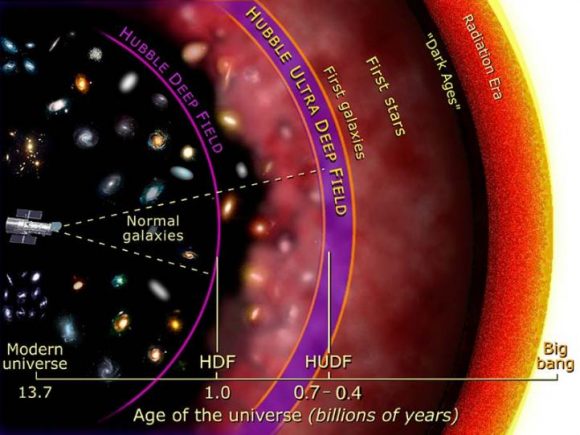
That being said, Hubble is still subject to limitations, which astronomers are now hoping to push past. For one, its instruments are not able to pick up the most distant (and hence, dimmest) galaxies in the Universe, which date to just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. Even with “The Deep Fields” initiative, Hubble is still limited to seeing back to about half a billion years after the Big Bang.
As Dr. John Mather, the project scientist for the James Webb Telescope, told Universe Today via email:
“Hubble showed us that we could not see the first galaxies being born, because they’re too far away, too faint, and too red. JWST is bigger, colder, and observes infrared light to see those first galaxies. Hubble showed us there’s a black hole in the center of almost every galaxy. JWST will look as far back in time as possible to see when and how that happened: did the galaxy form the black hole, or did the galaxy grow around a pre-existing black hole? Hubble showed us great clouds of glowing gas and dust where stars are being born. JWST will look through the dust clouds to see the stars themselves as they form in the cloud. Hubble showed us that we can see some planets around other stars, and that we can get chemical information about other planets that happen to pass directly in front of their stars. JWST will extend this to longer wavelengths with a bigger telescope, with a possibility of detecting water on a super-Earth exoplanet. Hubble showed us details of planets and asteroids close to home, and JWST will give a closer look, though it’s still better to send a visiting robot if we can.”
With its much larger set of segmented mirrors, it will observe the Universe as it captures light from the first galaxies and stars. Its extremely-sensitive suite of optics will also be able to gather information in the long-wavelength (orange-red) and infrared wavelengths with greater accuracy, measuring the redshift of distant galaxies and even helping in the hunt for extra-solar planets.

With the assembly of its major components now complete, the telescope will spend the next two years undergoing tests before its scheduled launch date in October 2018. These will include stress tests that will subject the telescope to the types of intense vibrations, sounds, and g forces (ten times Earth’s gravity) it will experience inside the Ariane 5 rocket that will take it into space.
Six months before its deployment, NASA also plans to send the JWST to the Johnson Space Center, where it will be subjected to the kinds of conditions it will experience in space. This will consist of scientists placing the telescope in a chamber where temperatures will be lowered to 53 K (-220 °C; -370 °F), which will simulate its operating conditions at the L2 Lagrange Point.
Once all of that is complete, and the JWST checks out, it will be launched aboard an Ariane 5 rocket from Arianespace’s ELA-3 launch pad in French Guayana. And thanks to experience gained from Hubble and updated algorithms, the telescope will be focused and gathering information shortly after it is launched. And as Dr. Mather explained, the big cosmological questions it is expected to address are numerous:
“Where did we come from? The Big Bang gave us hydrogen and helium spread out almost uniformly across the universe. But something, presumably gravity, stopped the expansion of the material and turned it into galaxies and stars and black holes. JWST will look at all these processes: how did the first luminous objects form, and what were they? How and where did the black holes form, and what did they do to the growing galaxies? How did the galaxies cluster together, and how did galaxies like the Milky Way grow and develop their beautiful spiral structure? Where is the cosmic dark matter and how does it affect ordinary matter? How much dark energy is there, and how does it change with time?”
Needless to say, NASA and the astronomical community are quite excited that the James Webb Telescope is finished construction, and can’t wait until it is deployed and begins to send back data. One can only imagine the kinds of things it will see deep in the cosmic field. But in the meantime, be sure to check out the film and see how this effort all came together:
Further Reading: NASA – JWST, Northrop Grumman