Over the 50-plus years since President John F. Kennedy’s Rice University speech, spaceflight has proven to be hard. It doesn’t take much to wreck a good day to fly.
Befitting a Halloween story, rocket launches, orbital insertions, and landings are what make for sleepless nights. These make-or-break events of space missions can be things that go bump in the night: sometimes you get second chances and sometimes not. Here’s a look at some of the past mission failures that occurred at launch. Consider this a first installment in an ongoing series of articles – “Not Because They Are Easy.”

The evening of October 28, 2014, was another of those hard moments in the quest to explore and expand humanity’s presence in space. Ten years ago, Orbital Sciences Corporation sought an engine to fit performance requirements for a new launch vehicle. Their choice was a Soviet-era liquid fuel engine, one considered cost-effective, meeting requirements, and proving good margins for performance and safety. The failure of the Antares rocket this week could be due to a flaw in the AJ-26 or it could be from a myriad of other rocket parts. Was it decisions inside NASA that cancelled or delayed engine development programs and led OSC and Lockheed-Martin to choose “made in Russia” rather than America?
Here are other unmanned launch failures of the past 25 years:
Falcon 1, Flight 2, March 21, 2007. Fairings are hard. There are fairings that surround the upper stage engines and a fairing covering payloads. Fairings must not only separate but also not cause collateral damage. The second flight of the Falcon 1 is an example of a 1st stage separation and fairing that swiped the second stage nozzle. Later, overcompensation by the control system traceable to the staging led to loss of attitude control; however, the launch achieved most of its goals and the mission was considered a success. (View: 3:35)
Proton M Launch, Baikonur Aerodrome, July 2, 2013. The Proton M is the Russian Space program’s workhorse for unmanned payloads. On this day, the Navigation, Guidance, and Control System failed moments after launch. Angular velocity sensors of the guidance control system were installed backwards. Fortunately, the Proton M veered away from its launch pad sparing it damage.
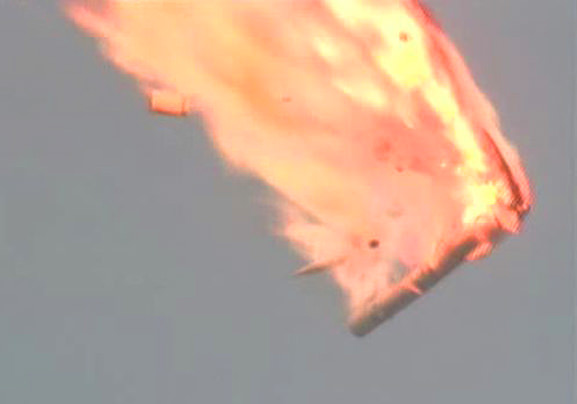
Ariane V Maiden Flight, June 4, 1996. The Ariane V was carrying an ambitious ESA mission called Cluster – a set of four satellites to fly in tetrahedral formation to study dynamic phenomena in the Earth’s magnetosphere. The ESA launch vehicle reused flight software from the successful Ariane IV. Due to differences in the flight path of the Ariane V, data processing led to a data overflow – a 64 floating point variable overflowing a 16 bit integer. The fault remained undetected and flight control reacted in error. The vehicle veered off-course, the structure was stressed and disintegrated 37 seconds into flight. Fallout from the explosion caused scientists and engineers to don protective gas masks. (View: 0:50)
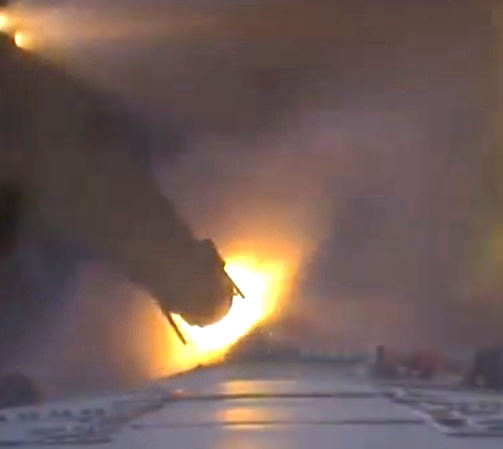
Delta II, January 17, 1997. The Delta II is one of the most successful rockets in the history of space flight, but not on this day. Varied configurations change up the number of solid rocket motors strapped to the first stage. The US Air Force satellite GPS IIR-1 was to be lifted to Earth orbit, but a Castor 4A solid rocket booster failed seconds after launch. A hairline fracture in the rocket casing was the fault. Both unspent liquid and solid fuel rained down on the Cape, destroying launch equipment, buildings, and even parked automobiles. This is one of the most well documented launch failures in history.
Compilation of Early Launch Failures. Beginning with several of the early failures of Von Braun’s V2, this video compiles many failures over a 70 year period. The early US space program endured multiple launch failures as they worked at a breakneck speed to catch up with the Soviets after Sputnik. NASA did not yet exist. The Air Force and Army had competing designs, and it was the Army with the German rocket scientists, including Von Braun, that launched the Juno 1 rocket carrying Explorer 1 on January 31, 1958.
One must always realize that while spectacular to launch viewers, a rocket launch has involved years of development, lessons learned, and multiple revisions. The payloads carried involve many hundreds of thousands of work-hours. Launch vehicle and payloads become quite personal. NASA and ESA have offered grief counseling to their engineers after failures.
“We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard, because that goal will serve to organize and measure the best of our energies and skills, because that challenge is one that we are willing to accept, one we are unwilling to postpone, and one which we intend to win, and the others, too.”