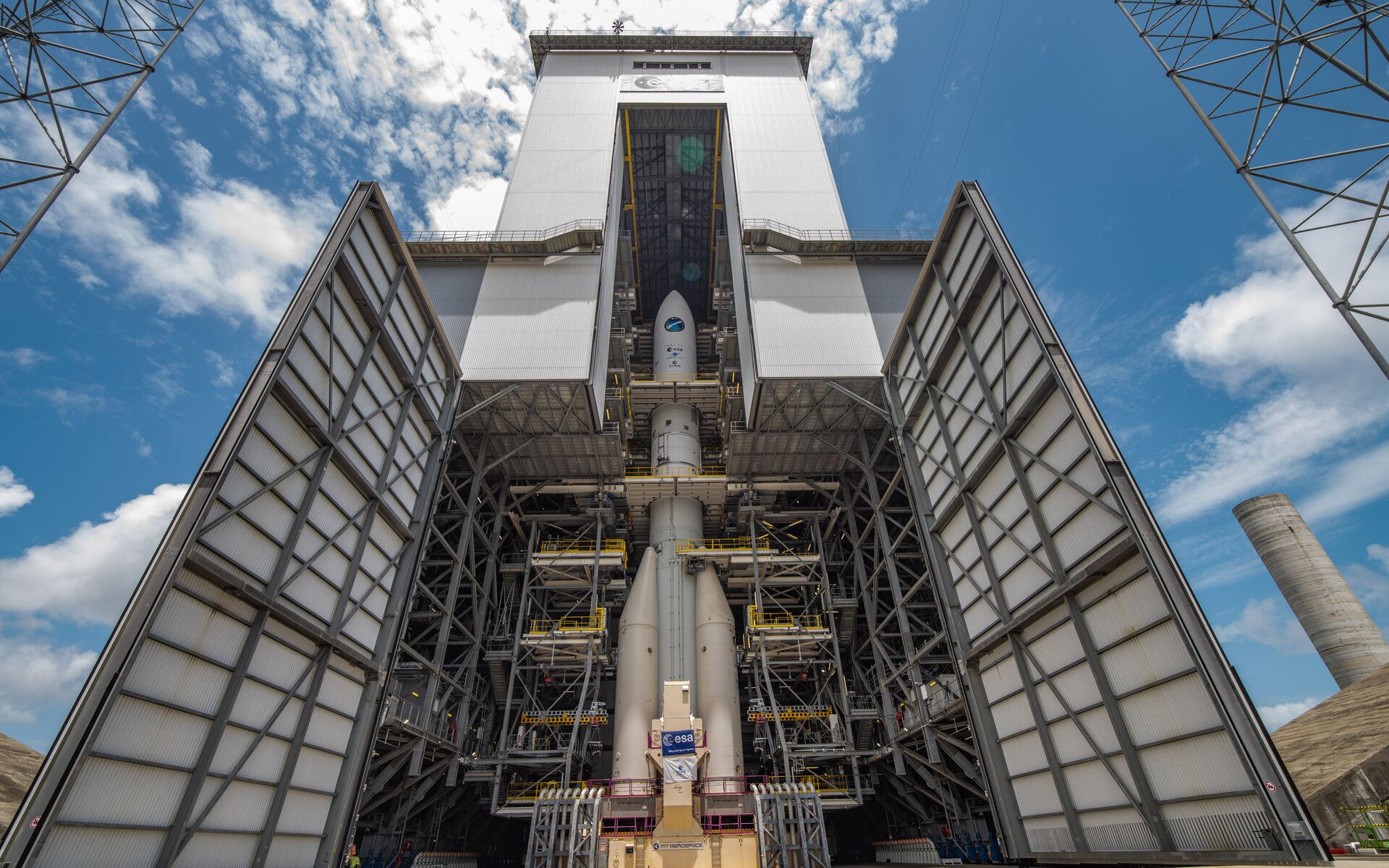
The European Space Agency has retired its Ariane 5 rocket, and all eyes are on its next generation, Ariane 6. The rocket’s pieces have been arriving at the Kourou facility in French Guiana and are now assembled. ESA has now announced they’ll attempt a test launch on July 9th and hope to complete a second flight before the end of 2024. This new heavy-life rocket has a re-ignitable upper stage, allowing it to launch multiple payloads into different orbits.
Continue reading “ESA Sets the Launch Date for Ariane 6: July 9th”ESA Sets the Launch Date for Ariane 6: July 9th