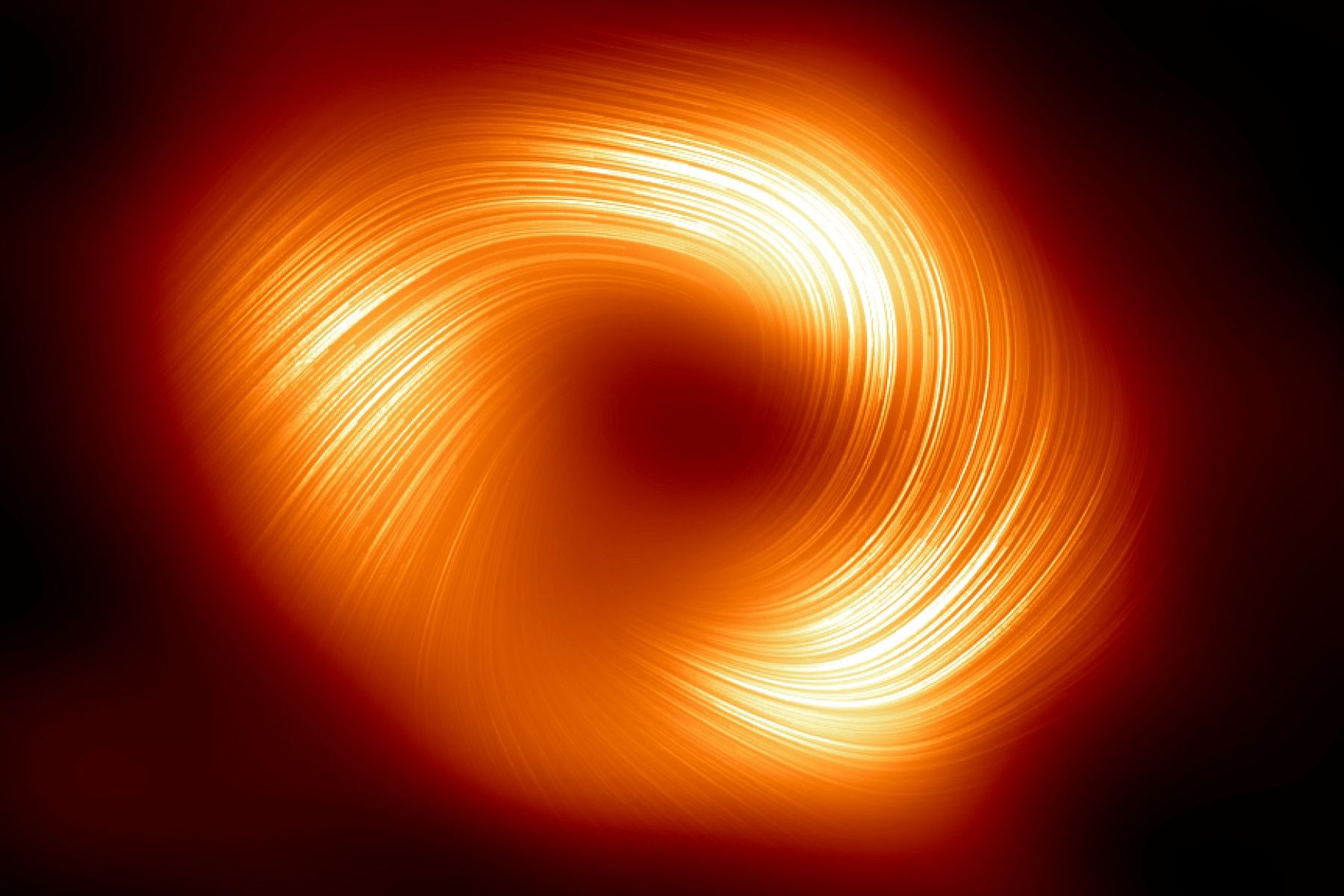
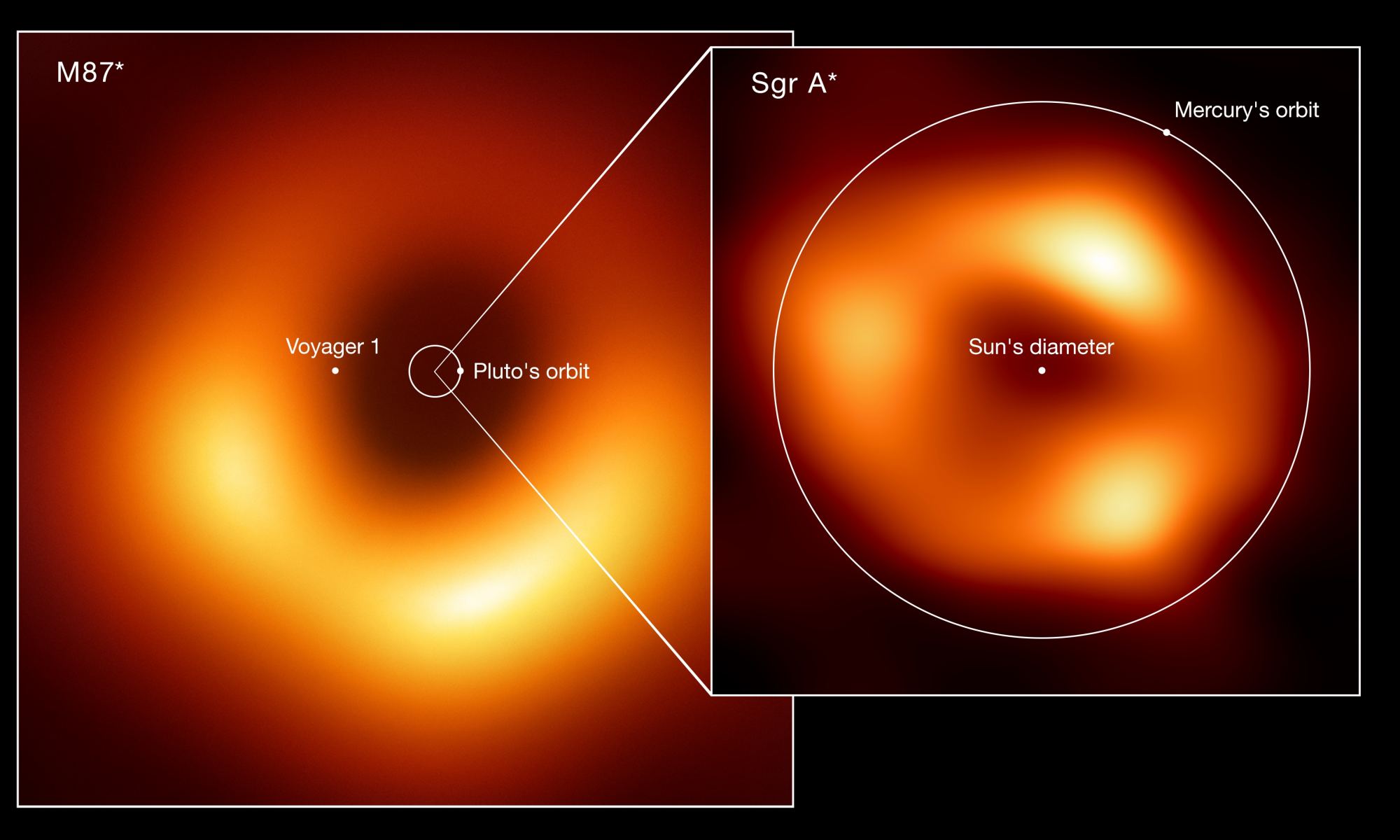
The prospect of actually resolving the event horizon of black holes feels like the stuff of science fiction yet it is a reality. Already the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) has resolved the horizon of the black holes at the centre of the Milky Way and M87. A team of astronomers are now looking to the next generation of the EHT which will work at multiple frequencies with more telescopes than EHT. A new paper suggests it may even be possible to capture the ring where light goes into orbit around the black hole at the centre of the Milky Way.
Continue reading “Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope To Unlock Mysteries of Black Holes”Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope To Unlock Mysteries of Black Holes