[/caption]
From a NASA Press Release:
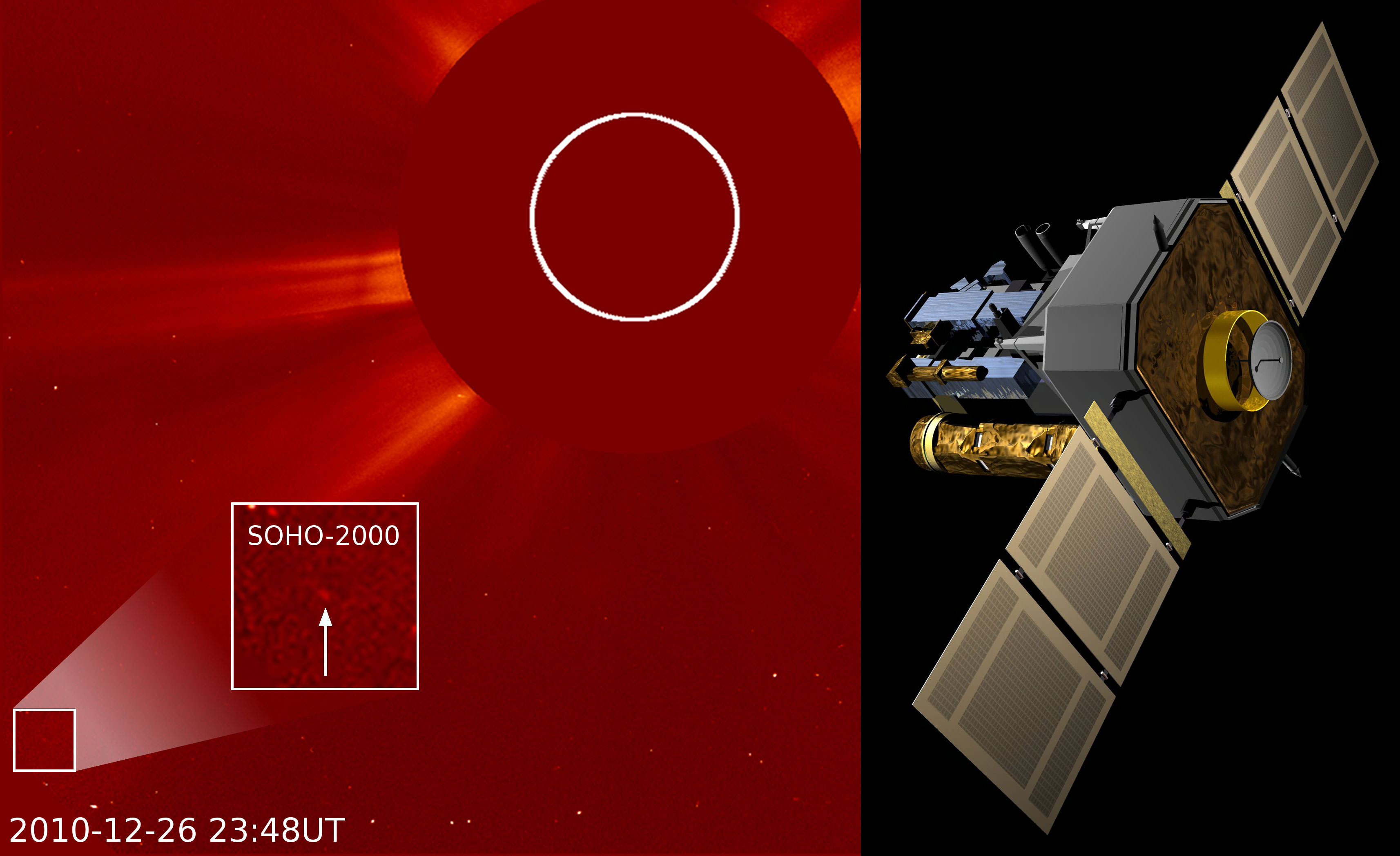
As people on Earth celebrate the holidays and prepare to ring in the New Year, an ESA/NASA spacecraft has quietly reached its own milestone: on December 26, the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) discovered its 2000th comet.
Drawing on help from citizen scientists around the world, SOHO has become the single greatest comet finder of all time. This is all the more impressive since SOHO was not specifically designed to find comets, but to monitor the sun.
“Since it launched on December 2, 1995 to observe the sun, SOHO has more than doubled the number of comets for which orbits have been determined over the last three hundred years,” says Joe Gurman, the U.S. project scientist for SOHO at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Of course, it is not SOHO itself that discovers the comets — that is the province of the dozens of amateur astronomer volunteers who daily pore over the fuzzy lights dancing across the pictures produced by SOHO’s LASCO (or Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph) cameras. Over 70 people representing 18 different countries have helped spot comets over the last 15 years by searching through the publicly available SOHO images online.
The 1999th and 2000th comet were both discovered on December 26 by Michal Kusiak, an astronomy student at Jagiellonian University in Krakow, Poland. Kusiak found his first SOHO comet in November 2007 and has since found more than 100.
“There are a lot of people who do it,” says Karl Battams who has been in charge of running the SOHO comet-sighting website since 2003 for the Naval Research Lab in Washington, where he also does computer processing for LASCO. “They do it for free, they’re extremely thorough, and if it wasn’t for these people, most of this stuff would never see the light of day.”
Battams receives reports from people who think that one of the spots in SOHO’s LASCO images looks to be the correct size and brightness and headed for the sun – characteristics typical of the comets SOHO finds. He confirms the finding, gives each comet an unofficial number, and then sends the information off to the Minor Planet Center in Cambridge, Mass, which categorizes small astronomical bodies and their orbits.
It took SOHO ten years to spot its first thousand comets, but only five more to find the next thousand. That’s due partly to increased participation from comet hunters and work done to optimize the images for comet-sighting, but also due to an unexplained systematic increase in the number of comets around the sun. Indeed, December alone has seen an unprecedented 37 new comets spotted so far, a number high enough to qualify as a “comet storm.”
LASCO was not designed primarily to spot comets. The LASCO camera blocks out the brightest part of the sun in order to better watch emissions in the sun’s much fainter outer atmosphere, or corona. LASCO’s comet finding skills are a natural side effect — with the sun blocked, it’s also much easier to see dimmer objects such as comets.
“But there is definitely a lot of science that comes with these comets,” says Battams. “First, now we know there are far more comets in the inner solar system than we were previously aware of, and that can tell us a lot about where such things come from and how they’re formed originally and break up. We can tell that a lot of these comets all have a common origin.” Indeed, says Battams, a full 85% of the comets discovered with LASCO are thought to come from a single group known as the Kreutz family, believed to be the remnants of a single large comet that broke up several hundred years ago.
The Kreutz family comets are “sungrazers” – bodies whose orbits approach so near the Sun that most are vaporized within hours of discovery – but many of the other LASCO comets boomerang around the sun and return periodically. One frequent visitor is comet 96P Machholz. Orbiting the sun approximately every six years, this comet has now been seen by SOHO three times.
SOHO is a cooperative project between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA. The spacecraft was built in Europe for ESA and equipped with instruments by teams of scientists in Europe and the USA.
For more information see the SOHO website. .
See SOHO realtime data.