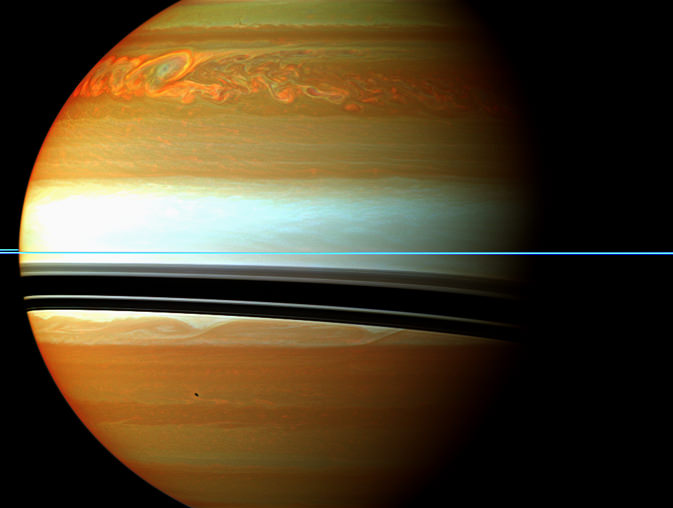
Earth releases about as much energy out into space as it absorbs, arriving at a thermal equilibrium. This means it will reach an average temperature as is the case with most planets. Saturn however, is a little different as recent observations show the planet’s energy is out of balance. It seems that in addition to the energy it receives from the Sun, there must also be an internal source of heat, perhaps driven by its highly elliptical orbit.
Continue reading “Saturn’s Energy is Out of Balance”New Saturn Storm Emerging?


Are you following the planets this season? The planetary action is about to heat up, as Jupiter, Saturn and Mars all head towards fine oppositions over the next few months.
Spying the Storms of Saturn
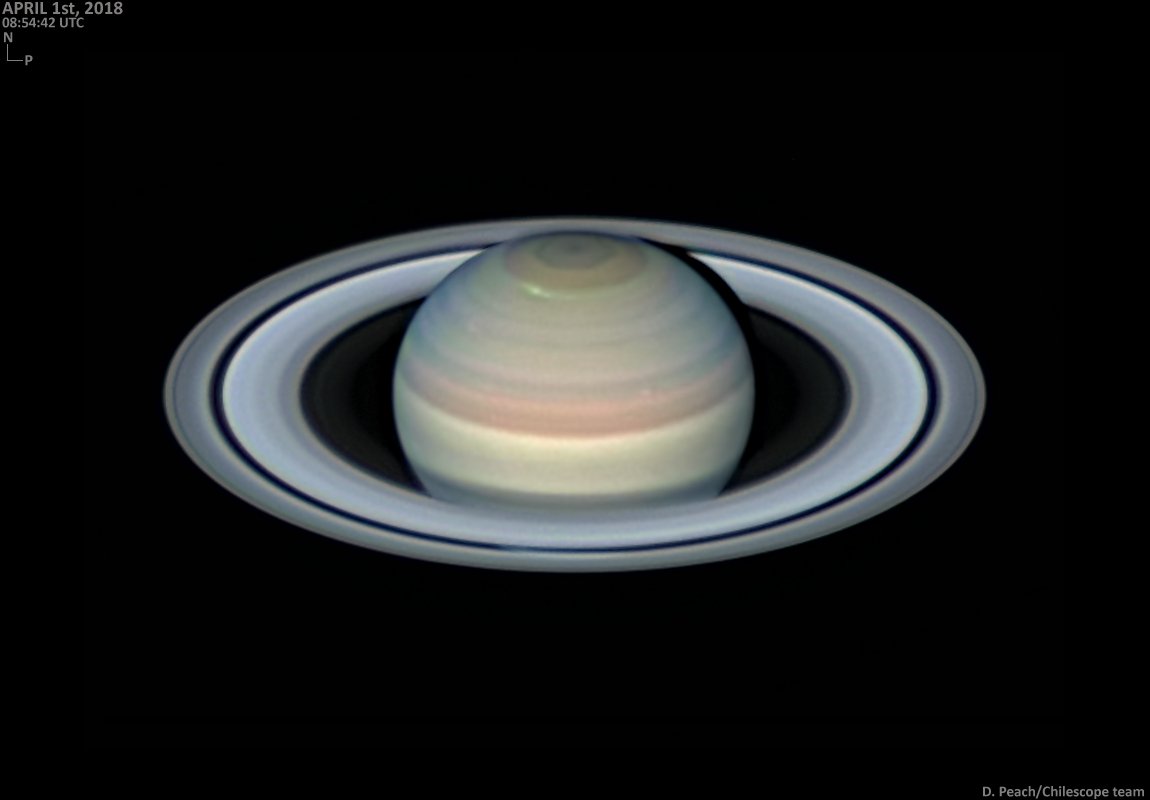
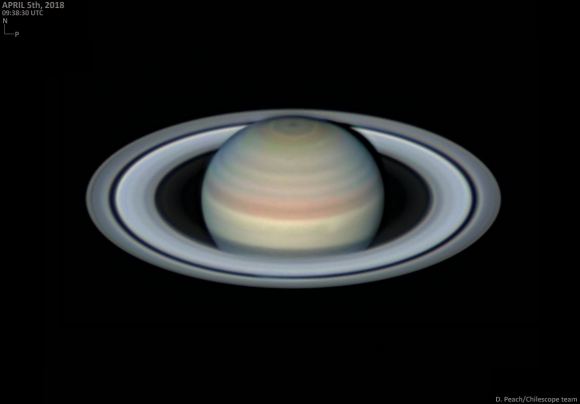
Astrophotographer Damian Peach raised the alarm on Twitter this past week of a possible bright storm emerging of the planet Saturn. The spot was noticeable even with the naked eye and in the raw video Peach captured, a sure sign that the storm was a biggie.
Though outbursts of clusters of white spots on the surface of Saturn aren’t uncommon, it’s rare to see one emerge at such a high latitude. The storm had faded considerably the next observing session Peach performed on April 5th, though observers should remain vigilant.

It’s sad to think: Cassini and our eyes in the outer solar system are no more… and the situation will probably remain this way for some years to come. Juno also wraps up its mission at Jupiter (pending extension) this year, and New Horizons visits its final destination Ultima Thule (neé 2014 MU69) on New Year’s Day 2019, though it’ll likely continue to chronicle its journey through the outer realms of the solar system, much like the Voyager 1, 2 and Pioneer 10, 11 missions, also bound to orbit the galaxy, mute testaments to human civilization. But even though proposals for Europa Clipper, a nuclear-powered quad-copter for Saturn’s moon Titan, and a Uranus and/or Neptune Orbiter are all on the drawing board, the “gap decade” of outer solar system exploration will indeed come to pass and soon.

But dedicated amateur astronomers continue to monitor the outer solar system for changes. This month sees Saturn rising around 1:30 AM local and transiting highest to the south for northern hemisphere observers at 6:00 AM local, just before sunrise. Saturn crosses the constellation Sagittarius in 2018, bottoming out at its most southerly point this year for its 29 year path around the Sun. Saturn currently shines at +0.4 magnitude, extending 40” across (including rings) as it heads towards a fine opposition on June 27th. After opposition, Saturn formally crosses into the dusk sky. The amazing rings are an automatic draw, but last week’s storm admonishes us not to forget to check out the saffron-colored disk of Saturn itself as well. For example, I’ve always wondered: why didn’t we see the hexagon before? It’s right there festooning the northern hemisphere cap, plain as day in modern amateur images… to be sure, we’re in a modern renaissance of planetary astrophotography today, what with image stacking and processing, but surely eagle-eyed observers of yore could’ve easily picked this feature out.
And the view is changing as well, as Saturn’s rings reached a maximum tilt in respect to our line of sight of 27 degrees in 2017, and now head back towards edge-on again in 2025. And be sure to check out Saturn’s retinue of moons, half a dozen of which are easily visible in a telescope at even low power.
Finally, here’s another elemental mystery poised by Saturn related to the current storm, one that Cassini sought to solve in its final days: how fast does Saturn rotate, exactly? The usual rough guesstimate quoted is usually around 10.5 hours, but we’ve yet to pin down this fundamental value with any degree of precession.
One thing’s definitely for sure: we need to go back. In the meantime, we can enjoy the early morning views of the most glorious of the planets in our Solar System.
Weekly Space Hangout – April 17, 2015: Amy Shira Teitel and “Breaking the Chains of Gravity”
Host: Fraser Cain (@fcain)
Special Guest: Amy Shira Teitel (@astVintageSpace) discussing space history and her new book Breaking the Chains of Gravity
Guests:
Morgan Rehnberg (cosmicchatter.org / @MorganRehnberg )
This Week’s Stories:
Falcon 9 launch and (almost!) landing
NASA Invites ESA to Build Europa Piggyback Probe
Bouncing Philae Reveals Comet is Not Magnetised
Astronomers Watch Starbirth in Real Time
SpaceX Conducts Tanking Test on In-Flight Abort Falcon 9
Rosetta Team Completely Rethinking Comet Close Encounter Strategy
Apollo 13 Custom LEGO Minifigures Mark Mission’s 45th Anniversary
LEGO Launching Awesome Spaceport Shuttle Sets in August
New Horizons Closes in on Pluto
Work Platform to be Installed in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Watching the Sunsets of Mars Through Robot Eyes: Photos
NASA Invites ESA to Build Europa Piggyback Probe
ULA Plans to Introduce New Rocket One Piece at a Time
Two Mysterious Bright Spots on Dwarf Planet Ceres Are Not Alike
18 Image Montage Show Off Comet 67/P Activity
ULA’s Next Rocket To Be Named Vulcan
NASA Posts Huge Library of Space Sounds And You’re Free to Use Them
Explaining the Great 2011 Saturn Storm
Liquid Salt Water May Exist on Mars
Color Map Suggests a Once-Active Ceres
Diverse Destinations Considered for New Interplanetary Probe
Paul Allen Asserts Rights to “Vulcan” Trademark, Challenging Name of New Rocket
First New Horizons Color Picture of Pluto and Charon
NASA’s Spitzer Spots Planet Deep Within Our Galaxy
Icy Tendrils Reaching into Saturn Ring Traced to Their Source
First Signs of Self-Interacting Dark Matter?
Anomaly Delays Launch of THOR 7 and SICRAL 2
Nearby Exoplanet’s Hellish Atmosphere Measured
The Universe Isn’t Accelerating As Fast As We Thought
Glitter Cloud May Serve As Space Mirror
Cassini Spots the Sombrero Galaxy from Saturn
EM-1 Orion Crew Module Set for First Weld Milestone in May
Special Delivery: NASA Marshall Receives 3D-Printed Tools from Space
The Roomba for Lawns is Really Pissing Off Astronomers
Giant Galaxies Die from the Inside Out
ALMA Reveals Intense Magnetic Field Close to Supermassive Black Hole
Dawn Glimpses Ceres’ North Pole
Lapcat A2 Concept Sup-Orbital Spaceplane SABRE Engine Passed Feasibility Test by USAF Research Lab
50 Years Since the First Full Saturn V Test Fire
ULA CEO Outlines BE-4 Engine Reuse Economic Case
Certification Process Begins for Vulcan to Carry Military Payloads
Major Advance in Artificial Photosynthesis Poses Win/Win for the Environment
45th Anniversary [TODAY] of Apollo 13’s Safe Return to Earth
Hubble’s Having A Party in Washington Next Week (25th Anniversary of Hubble)
Don’t forget, the Cosmoquest Hangoutathon is coming soon!
We record the Weekly Space Hangout every Friday at 12:00 pm Pacific / 3:00 pm Eastern. You can watch us live on Google+, Universe Today, or the Universe Today YouTube page.
You can join in the discussion between episodes over at our Weekly Space Hangout Crew group in G+, and suggest your ideas for stories we can discuss each week!
Giant “Invisible” Vortex Still Remains on Saturn Following Huge Storm
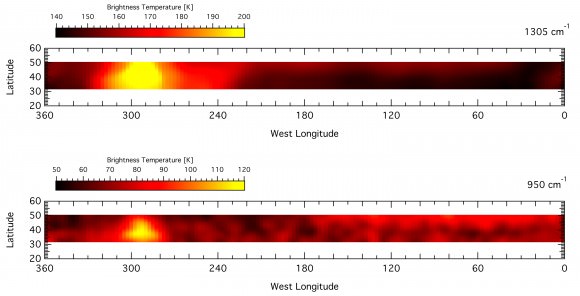
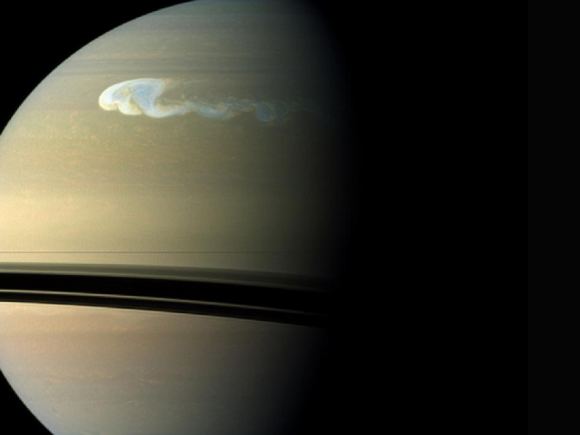
In 2010, a small, bright white storm emerged on Saturn’s northern hemisphere. This storm grew until it wrapped around the planet in curly cloud structures, creating a colossal atmospheric disturbance that endured into the early part of 2012, becoming the largest storm seen on the planet since 1990. Being in orbit around the ringed planet, the Cassini spacecraft had a front row seat to watch the disturbance unfold, allowing planetary scientists an unprecedented look at this monster storm. While the storm was visible even to amateur astronomers on Earth, much of its activity took place beyond the reach of visible-light cameras and telescopes, astronomers say. Not only did huge “beacons” of hot air chase each other around the planet, but infrared observations show a giant oval vortex is still persisting as a side effect from the storm.
“It’s the first time we’ve seen anything like it on any planet in the Solar System,” said Leigh Fletcher from the University of Oxford, UK, lead author of a paper describing the unprecedented storm. “It’s extremely unusual, as we can only see the vortex at infrared wavelengths – we can’t tell that it is there simply by looking at the cloud cover.”
Fletcher and her team also used ground-based observations with the Very Large Telescope of the European Southern Observatory in Chile, and NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility at the summit of Mauna Kea in Hawaii.
As the visible storm erupted in the roiling cloud deck of Saturn’s troposphere, waves of energy rippled hundreds of kilometers upwards, depositing their energy as the two vast ‘beacons’ of hot air in the stratosphere.
Data from Cassini’s composite infrared spectrometer (CIRS) instrument revealed the storm’s powerful discharge sent the temperature in Saturn’s stratosphere soaring 65 degrees C (150 degrees Fahrenheit, 83 kelvins) above normal.
Researchers described in a complimentary paper that will be published in the Nov. 20 issue of the Astrophysical Journal this as a “belch” of energy, as they observed a huge increase in the amount of ethylene gas in Saturn’s atmosphere, the origin of which is a mystery. Ethylene, an odorless, colorless gas, isn’t typically observed on Saturn. On Earth, it is created by natural and man-made sources.
Researchers are still is exploring the origin of the ethylene, but they have ruled out a large reservoir deep in the atmosphere.
“We’ve really never been able to see ethylene on Saturn before, so this was a complete surprise,” said Goddard’s Michael Flasar, the CIRS team lead.
The beacons were expected to cool down and dissipate, but by late April 2011 – by which time bright cloud material had encircled the entire planet – the hot spots had merged to create an enormous vortex that for a brief period exceeded even the size of Jupiter’s famous Great Red Spot.
The forceful storm generated unprecedented spikes in temperature and increased amounts of ethylene. In these two sets of measurements taken by Cassini’s composite infrared spectrometer, yellow represents the highest temperatures. Each strip maps a single molecule (top: methane, bottom: ethylene), with temperature measurements taken in the northern hemisphere, all the way around the planet. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/GSFC
Although comparisons to Jupiter’s Red Spot have been made to this storm, Saturn’s storm was much higher in the atmosphere while Jupiter’s vortex is embedded deep down in the turbulent ‘weather zone’, Fletcher said.
Also, Jupiter’s famous vortex has raged for at least 300 years. But after traversing the planet once every 120 days since May 2011, Saturn’s large beacon is cooling and shrinking. Scientists expect it to fade away completely by the end of 2013.
The question now remains as to whether Saturn’s storm-generating energy has been sapped or if there will be a repeat performance, the team said.
The outburst already caught observers by surprise by arriving during the planet’s northern hemisphere spring, years ahead of the predictably stormy summer season.
“The beauty is that Cassini will be operating until the Saturn system reaches its summer solstice in 2017, so if there is another global event like this, we’ll be there to see it,” says ESA’s Cassini project scientist Nicolas Altobelli.