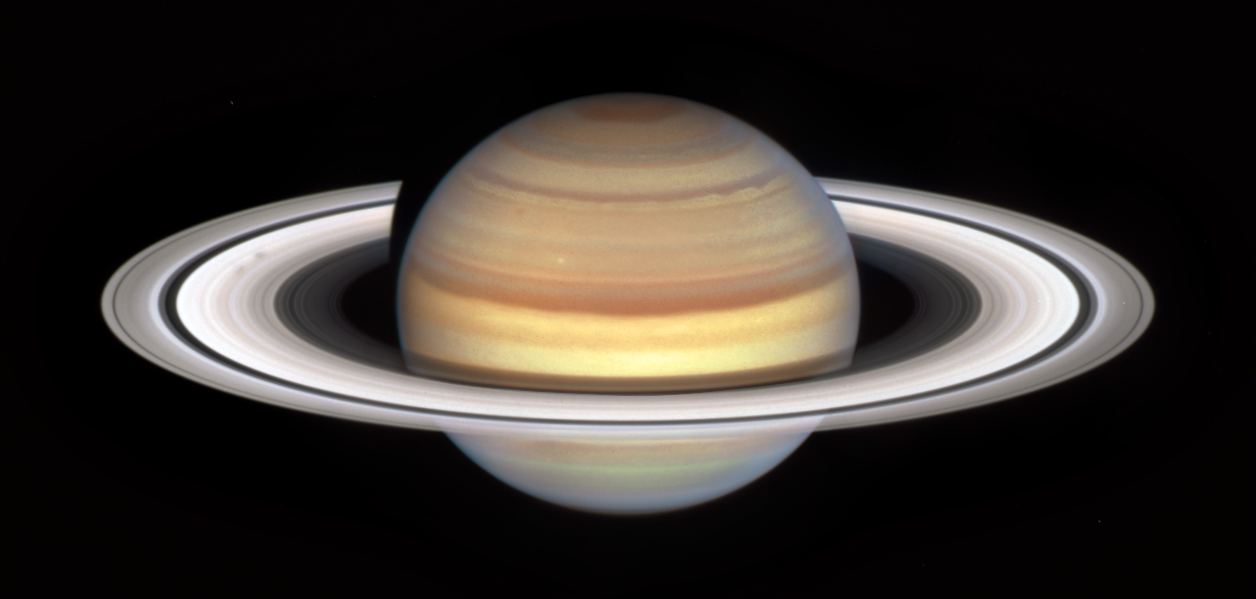
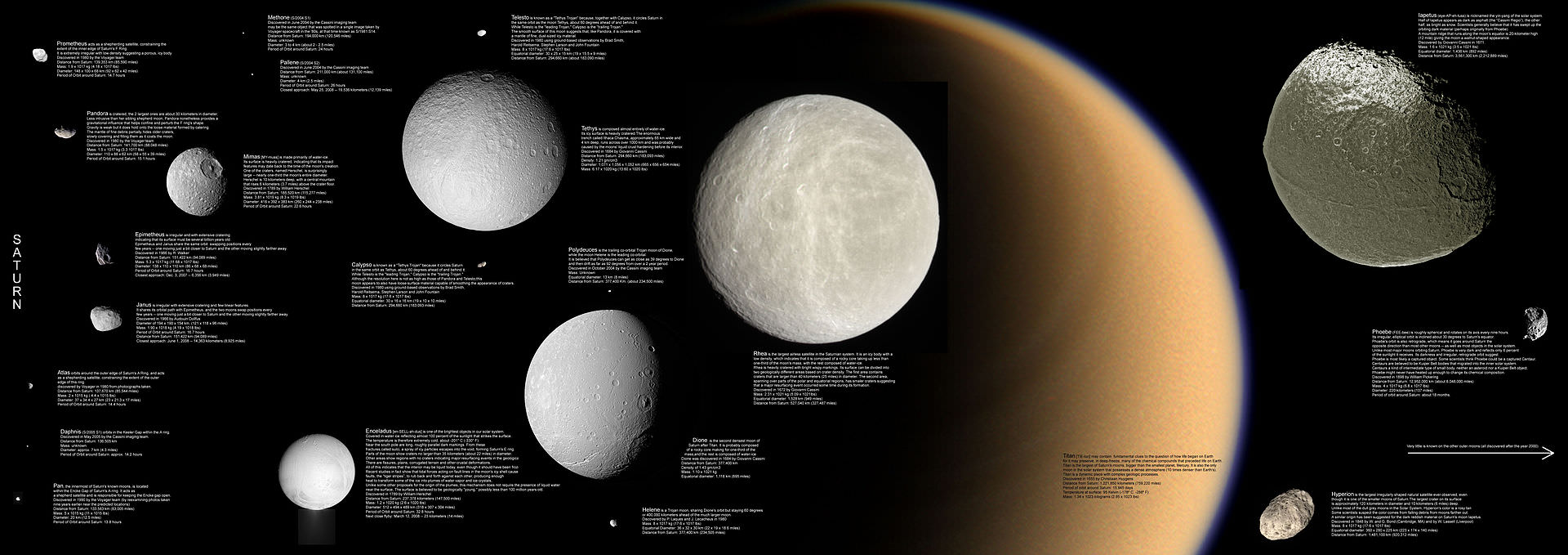
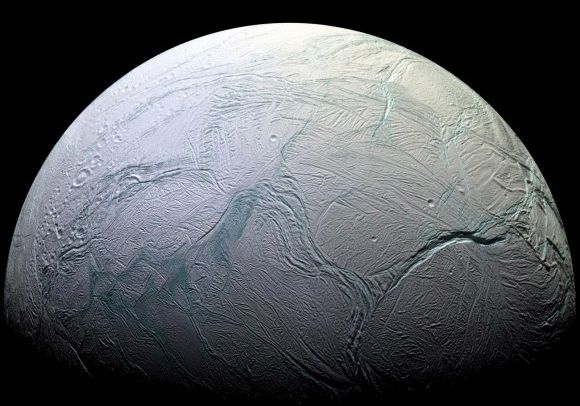
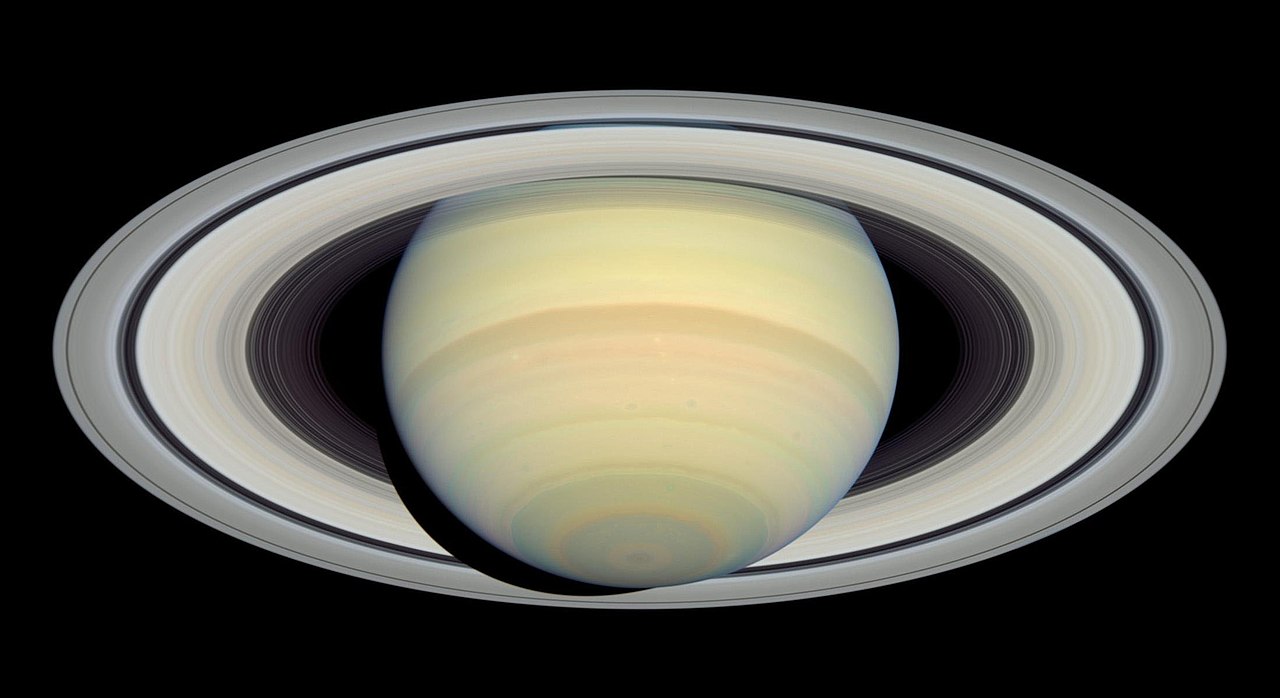
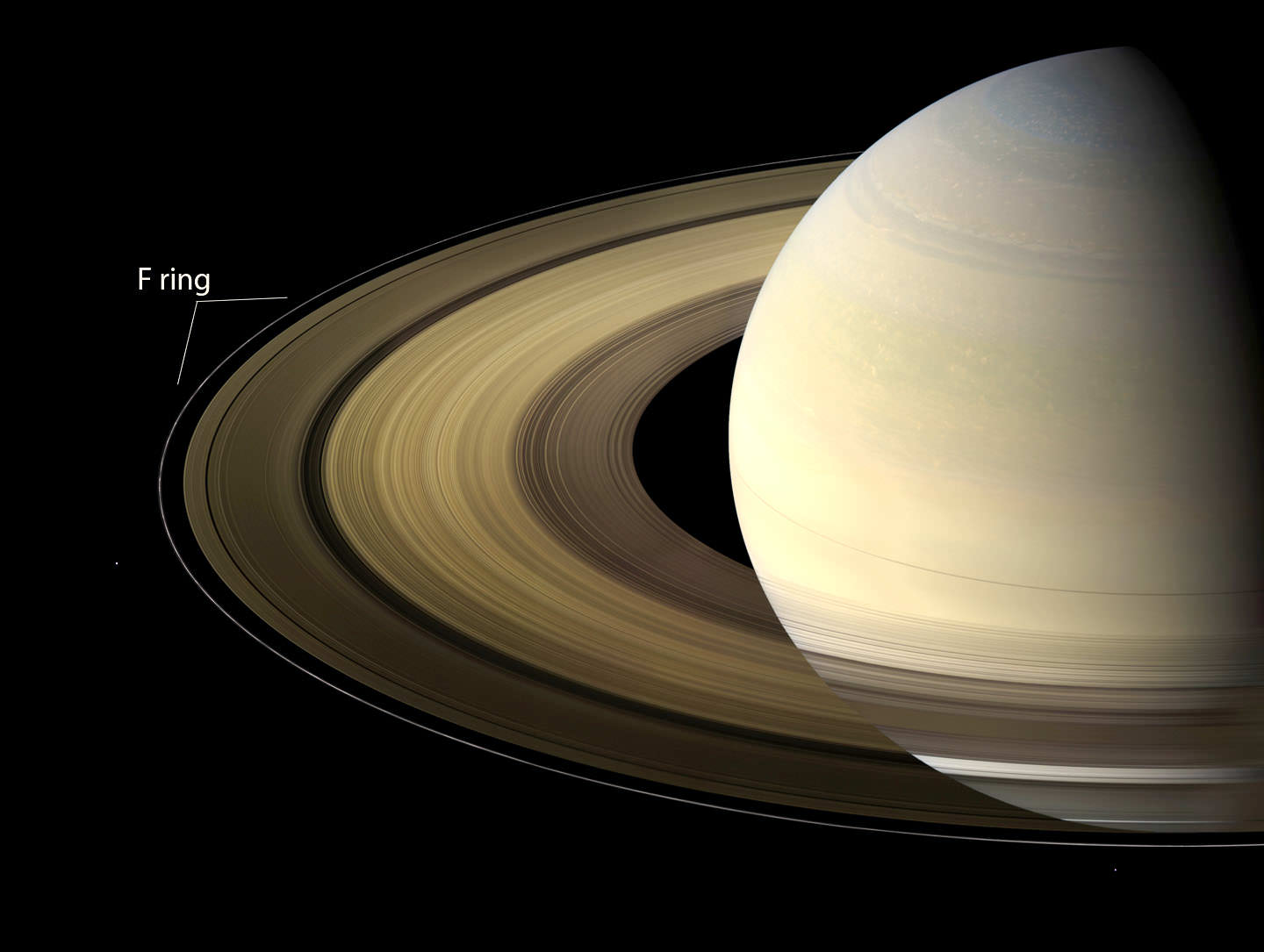
Saturn is best known for two things: its iconic ring structures and its large system of natural satellites. Currently, 146 moons and moonlets have been discovered orbiting the ringed giant, 24 of which are regular satellites. These include the seven largest moons, Titan, Rhea, Iapetus, Dione, Tethys, Enceladus, and Mimas, which are icy bodies believed to have interior oceans. In addition, there are unresolved questions about the age of these satellites, with some suspecting that they formed more recently (like Saturn’s rings, which are a few hundred million years old).
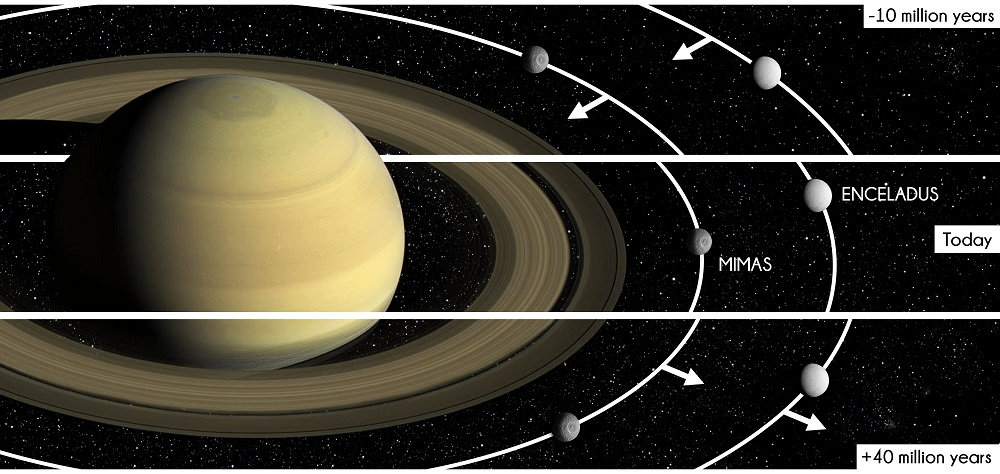
To address these questions, an international team of astronomers created a series of high-resolution simulations coupled with improved estimates of Trans-Neptunian Object (TNO) populations. This allowed them to construct a chronology of impacts for Saturn’s most heavily cratered regular satellites – Mimas, Enceladus, Tethys, Dione, and Rhea. This established age limits of 4.1 and 4.4 billion years for all five, with the two innermost moons appearing more youthful than the outer three. These results could have significant implications for our understanding of the formation and tidal evolution of moons in the outer Solar System.
Continue reading “Whether Saturn's Rings are Young or Old, its Moons are as Ancient as the Planet Itself”