Space-based solar power (SBSP) has been in the news recently, with the successful test of a solar power demonstrator in space taking place last summer. While the concept is fundamentally sound, there are plenty of hurdles to overcome if the technology is to be widely adopted – not the least of which is cost. NASA is no stranger to costly projects, though, and they recently commissioned a study from their internal Office of Technology, Policy, and Strategy that suggests how NASA could continue to support this budding idea. Most interestingly, if the technological cards are played right, SBSP could be the most carbon-efficient, lowest-cost power source for humanity by 2050.
Continue reading “New NASA Report Suggests We Could See Space-Based Power After 2050”Does Beaming Power in Space Make Sense at the Moon?
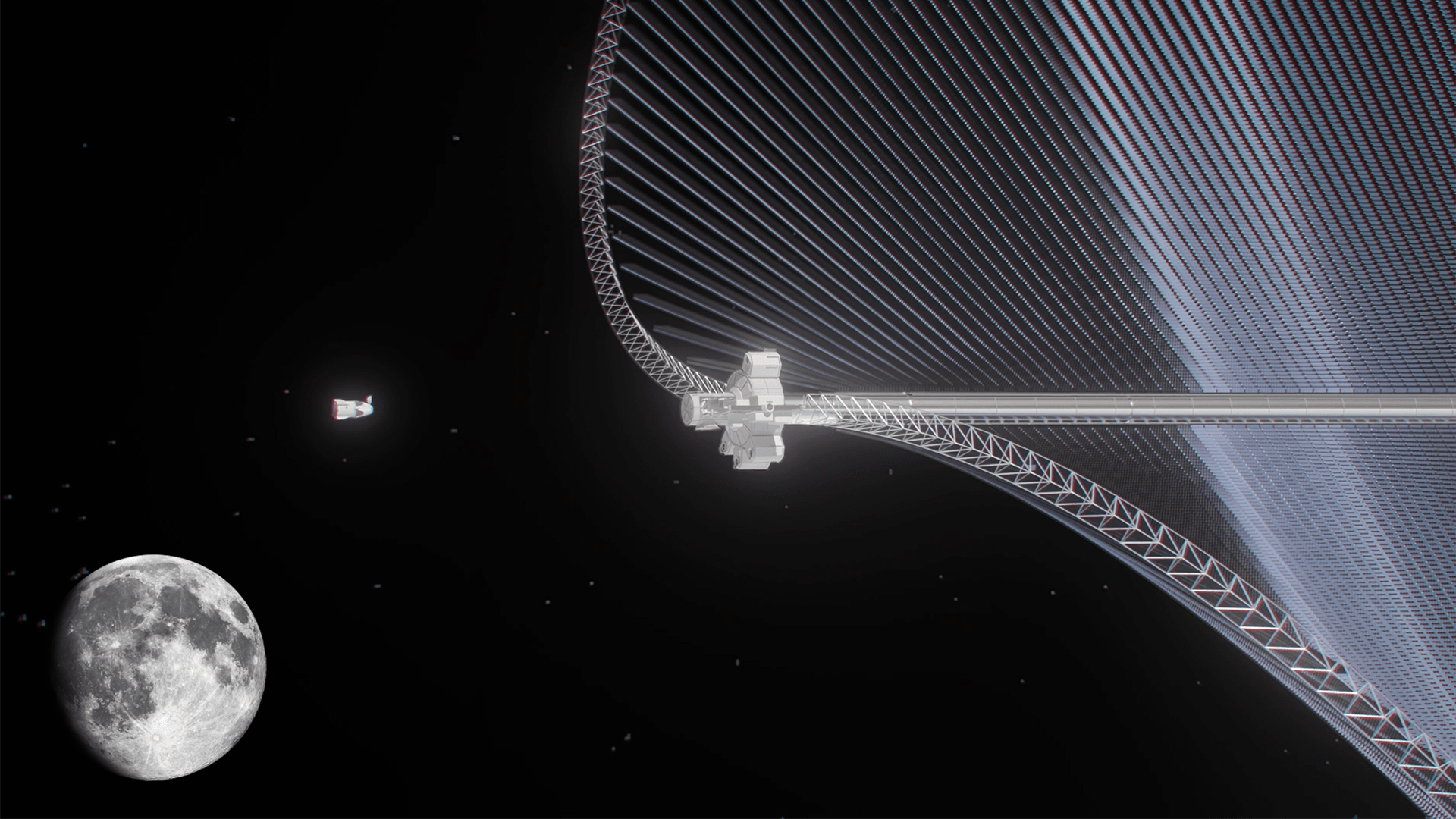
Space-based solar power (SBSP) is considered one of the most promising technologies for addressing Climate Change. The concept calls for satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) to collect power without interruption and beam it to receiving stations on Earth. This technology circumvents the main limiting factor of solar energy, which is how it is subject to the planet’s diurnal cycle and weather. While the prospect of SBSP has been considered promising for decades, it’s only in recent years that it has become practical, thanks to the declining costs of sending payloads to space.
However, the technology has applications beyond providing Earth with abundant clean energy. The European Space Agency (ESA) is also investigating it as a means of proving power on the Moon through the “Clean Energy – New Ideas for Solar Power from Space” study, which recently yielded a technology demonstrator known as the Greater Earth Lunar Power Station (GEO-LPS). This technology could provide a steady supply of power for future operations on the Moon, which include creating a permanent lunar base like the ESA’s proposed Moon Village.
Continue reading “Does Beaming Power in Space Make Sense at the Moon?”New Satellite Successfully Beams Power From Space

Solar power is the fastest-growing form of renewable energy and currently accounts for 3.6% of global electricity production today. This makes it the third largest source of the renewable energy market, followed by hydroelectric power and wind. These three methods are expected to grow exponentially in the coming decades, reaching 40% by 2035 and 45% by 2050. Altogether, renewables are expected to account for 90% of the energy market by mid-century, with solar accounting for roughly half. However, several technical challenges and issues need to be overcome for this transition to occur.
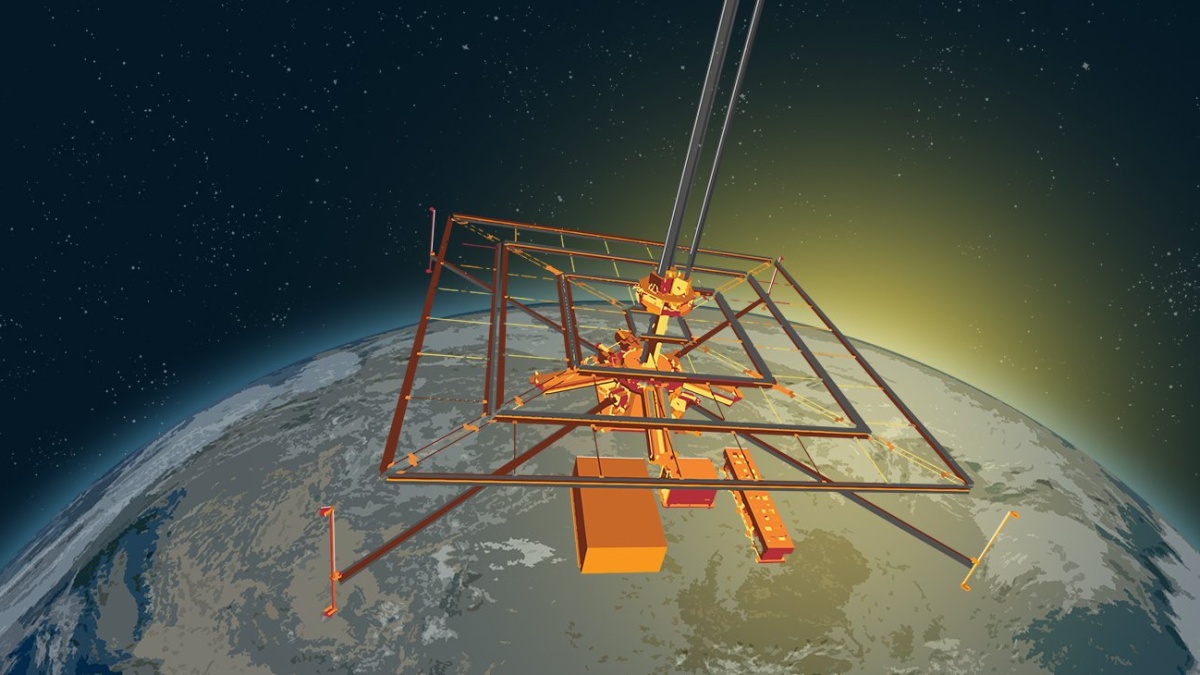
The main limiting factor for solar power is intermittency, meaning it can only collect power when sufficient sunlight is available. To address this, scientists have spent decades researching space-based solar power (SBSP), where satellites in orbit would collect power 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, without interruption. To develop the technology, researchers with the Space Solar Power Project (SSPP) at Caltech recently completed the first successful wireless power transfer using the Microwave Array for Power-transfer Low-orbit Experiment (MAPLE).
Continue reading “New Satellite Successfully Beams Power From Space”Is Space Power a Good Idea? A New Spacecraft is Going to Find Out!
Solar power, long considered the leading contender among renewable energy sources, has advanced significantly over the past few decades. The cost of manufacturing and installing solar panels has dropped considerably, and efficiency has increased, making it price competitive with coal, oil, and fossil fuels. However, some barriers, like distribution and storage, still prevent solar power from being adopted more aggressively. In addition, there’s the ever-present issue of intermittency, where arrays cannot collect power in bad weather and during evenings.
These issues have led to the concept of space-based solar power (SBSP), where satellites equipped with solar arrays could gather solar energy twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, three-hundred and sixty-five days a year. To test this method, researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) recently launched a technology demonstrator to space. It’s called the Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD), which will test several key components of SBSP and evaluate the method’s ability to harvest clean energy and beam it back to Earth.
Continue reading “Is Space Power a Good Idea? A New Spacecraft is Going to Find Out!”