When searching for alien life, it’s not unusual to use Earth as a test bed for theories and even practice runs. Perhaps one of the most tantalising places in the Solar System to look for life is Saturn’s moon Enceladus. It has a liquid water interior and it is here that life may just be possible. A team of researchers want to test techniques for searching for life on Enceledaus by exploring the oceans of Earth. They have collected water and ice samples and hope to find chemicals like methane and hydrogen.
Continue reading “Researchers Practice Searching for Life on Enceladus, in the Arctic Ocean”There are Places on Earth Which Could Have Life, but Don’t. What Can We Learn?
Don’t know about you but when I think of Earth my mind is filled with the diversity of life and the rich flora and fauna. In reality, about 99% of Earth is uninhabitable; deep underground places with high pressure and temperature where even the toughest bacteria cannot survive. There are places though where life thrives from tiniest toughest bacteria to the largest elephant. Then there are places that are habitable but devoid of life; lava flows are a great example and the space between microbes. A paper recently released looks at these uninhabited, habitable areas and wonders what we may learn as we search for life in the Universe.
Continue reading “There are Places on Earth Which Could Have Life, but Don’t. What Can We Learn?”Toxic Perchlorate on Mars Could Make Life More Interesting
The search for life in the Universe has fascinated humans for centuries. Mars has of course been high on the list of potential habitats for alien existence but since the numerous spacecraft images that have come back showing a barren landscape, it seems Mars may not be so habitable after all. That is, until recently. The Martian regolith, the top layer of dust upon the surface has been found to be full of perchlorate salts. These chemicals are poisonous to most life on Earth but a new study suggests that some extremophile protein enzymes and RNA may just be able to survive!
Continue reading “Toxic Perchlorate on Mars Could Make Life More Interesting”Did Earth’s Multicellular Life Depend on Plate Tectonics?

How did complex life emerge and evolve on the Earth and what does this mean for finding life beyond Earth? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a pair of researchers investigated how plate tectonics, oceans, and continents are responsible for the emergence and evolution of complex life across our planet and how this could address the Fermi Paradox while attempting to improve the Drake Equation regarding why we haven’t found life in the universe and the parameters for finding life, respectively. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the criterion for finding life beyond Earth, specifically pertaining to the geological processes exhibited on Earth.
Continue reading “Did Earth’s Multicellular Life Depend on Plate Tectonics?”Astrobiology: Why study it? How to study it? What are the challenges?
Universe Today has proudly examined the importance of studying impact craters, planetary surfaces, and exoplanets, and what they can teach scientists and the public about finding life beyond Earth. Impact craters both shape these planetary surfaces and hold the power to create or destroy life, and we learned how exoplanets are changing our views of planetary formation and evolution, including how and where we might find life in the cosmos. Here, we will discuss how these disciplines contribute to the field responsible for finding life beyond Earth, known as astrobiology. We will discuss why scientists study astrobiology, also known as astrobiologists, challenges of studying astrobiology, and how students can pursue studying astrobiology, as well. So, why is it so important to study astrobiology?
Continue reading “Astrobiology: Why study it? How to study it? What are the challenges?”Even Tiny Amounts of DNA on Mars Will Be Detectable

The Search for Life is focused on the search for biosignatures. Planetary life leaves a chemical fingerprint on a planet’s atmosphere, and scientists are trying to work out which chemicals in what combinations and amounts are a surefire indicator of life. Martian methane is one they’re puzzling over right now.
But new evidence suggests that super-tiny amounts of DNA can be detected in Martian rocks if it’s there. And though it requires physical samples rather than remote sensing, it’s still an intriguing development.
Continue reading “Even Tiny Amounts of DNA on Mars Will Be Detectable”The JWST Just Found Carbon on Europa, Boosting the Moon’s Potential Habitability
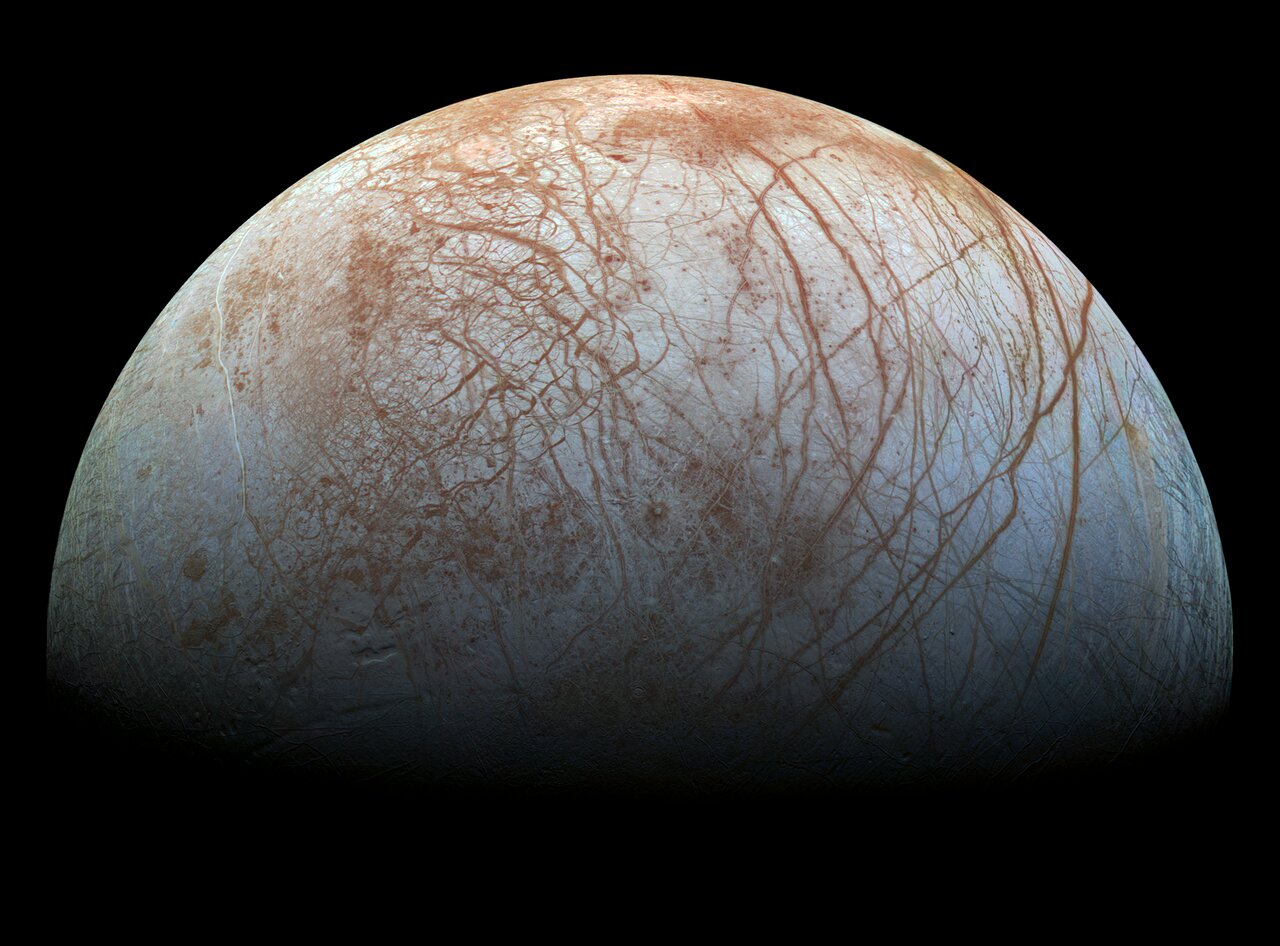

Most planets and moons in the Solar System are clearly dead and totally unsuitable for life. Earth is the only exception. But there are a few worlds where there are intriguing possibilities of life.
Chief among them is Jupiter’s moon Europa, and the JWST just discovered carbon there. That makes the moon and its subsurface ocean an even more desirable target in the search for life.
Continue reading “The JWST Just Found Carbon on Europa, Boosting the Moon’s Potential Habitability”The Clouds of Venus Could Support Life
A recent study published in Astrobiology examines the likelihood of the planet Venus being able to support life within the thick cloud layer that envelopes it. This study holds the potential to help us better understand how life could exist under the intense Venusian conditions, as discussions within the scientific community about whether life exists on the second planet from the Sun continue to burn hotter than Venus itself.
Continue reading “The Clouds of Venus Could Support Life”JWST is Powerful Enough to See a Variety of Biosignatures in Exoplanets
The best hope for finding life on another world isn’t listening for coded messages or traveling to distant stars, it’s detecting the chemical signs of life in exoplanet atmospheres. This long hoped-for achievement is often thought to be beyond our current observatories, but a new study argues that the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) could pull it off.
Continue reading “JWST is Powerful Enough to See a Variety of Biosignatures in Exoplanets”A Lack of Alien Signals Actually Tells Us a Lot
In a recent study published in The Astronomical Journal, a researcher from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) discusses the potential reasons why we haven’t received technoemission, also called technosignatures, from an extraterrestrial intelligence during the 60 years that SETI has been searching, along with recommending additional methods as to how we can continue to search for such emissions.
Continue reading “A Lack of Alien Signals Actually Tells Us a Lot”