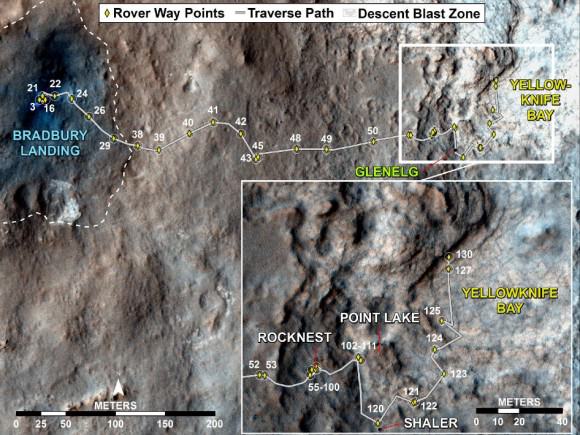
Image caption: Opportunity Celebrates 9 Years and 3200 Sols on Mars snapping this panoramic view from her current location on ‘Matijevic Hill’ at Endeavour Crater. The rover discovered phyllosilicate clay minerals and calcium sulfate veins at the bright outcrops of ‘Whitewater Lake’, at right, imaged by the Navcam camera on Sol 3197 (Jan. 20, 2013). “Copper Cliff” is the dark outcrop, at top center. Darker “Kirkwood” outcrop, at left, is site of mysterious “newberries” concretions. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer
9 Years ago, NASA’s pair of identical twin sister rovers – christened Spirit & Opportunity- bounced to daunting airbag-cushioned landings on opposite sides of the Red Planet for what was supposed to be merely 90 day missions, or maybe a little bit longer scientists hoped.
Today, Opportunity celebrates a truly unfathomable achievement, starting Year 10 on Mars since she rolled to a bumpy stop on January 24, 2004 inside tiny Eagle crater. And she’s now at a super sweet spot for science (see our photo mosaic above) loaded with clays and veined minerals and making the most remarkable findings yet about the planets watery past – thus building upon a long string of previously unthinkable discoveries due to her totally unforeseen longevity.
“Regarding achieving nine years, I never thought we’d achieve nine months!” Principal Investigator Prof. Steve Squyres of Cornell University told Universe Today for this article commemorating Opportunity’s 9th anniversary.
Opportunity reached 3200 Sols, or Martian days, and counting , by her 9th birthday. She is now 108 months into the 3 month primary mission – that’s 36 times longer than the 3 month “warranty.”
“Every sol is a gift,” Squyres told me. He always refers to the rovers as our “Priceless assets on Mars”, that have to be taken good care of to wring out the maximum science data possible and for as long as humanly, or more aptly, robotically possible.

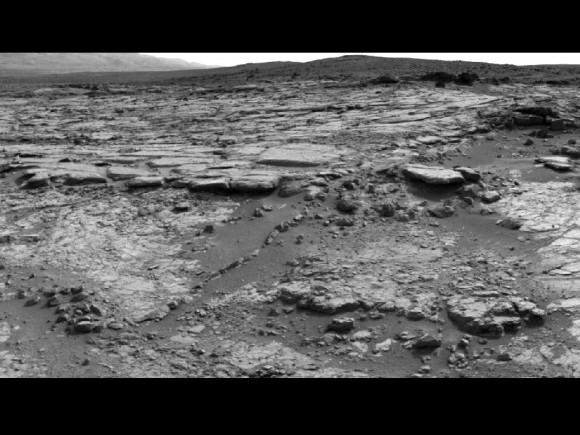
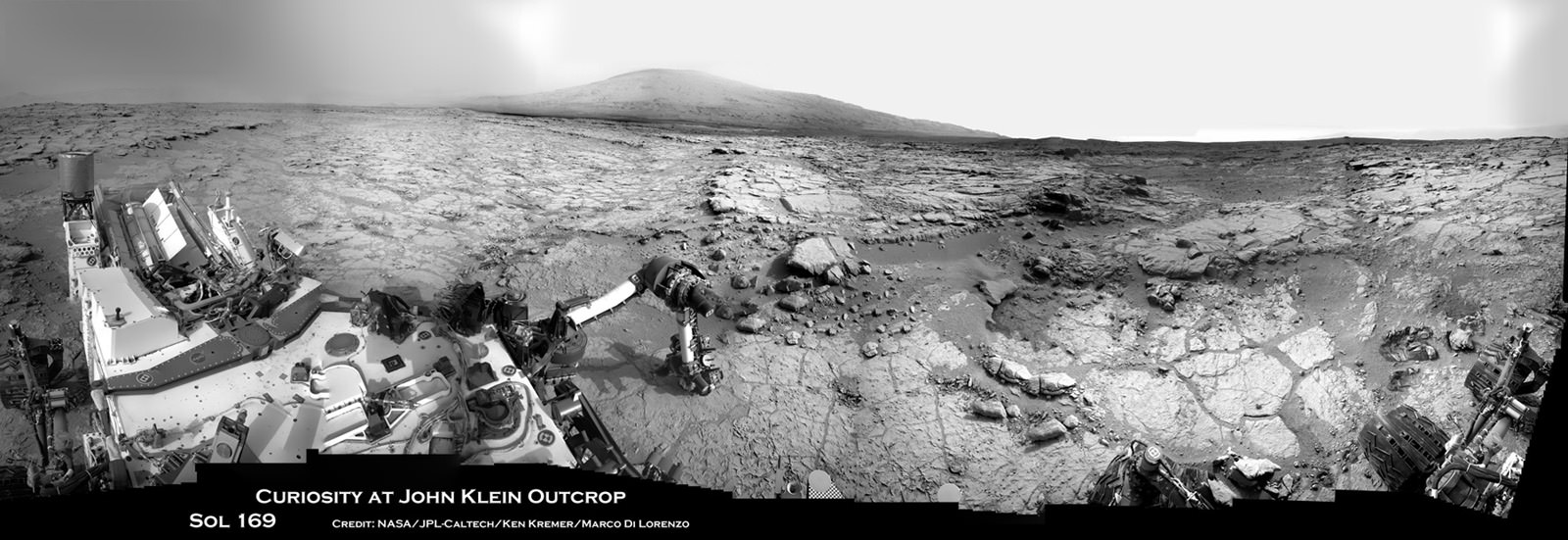
Image Caption: ‘Matijevic Hill’ Panorama for Rover’s Ninth Anniversary. As Opportunity neared the ninth anniversary of its landing on Mars, the rover was working in the ‘Matijevic Hill’ area seen in this view from Opportunity’s panoramic camera (Pancam). Two of the features investigated at Matijevic Hill are “Copper Cliff,” the dark outcrop in the left center of the image, and “Whitewater Lake,” the bright outcrop on the far right. The component images for this mosaic were taken from Sol 3137 (Nov. 19, 2012) through Sol 3150 (Dec. 3, 2012). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/Arizona State Univ.
The resilient, solar powered Opportunity robot begins her 10th year roving around beautifully Earth-like Martian terrain where where she proved that potentially life sustaining liquid water once flowed billions of years ago when the planet was warmer and wetter.
Opportunity is healthy and has driven over 22 miles (35 kilometers )- marking the first overland expedition on another planet. See our photo mosaics and route map by Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo.
She is now working at the inboard edge of “Cape York” – a hilly segment of the eroded rim of 14 mile (22 km) wide Endeavour Crater, featuring terrain with older rocks than previously inspected and unlike anything studied before. It’s a place no one ever dared dream of reaching prior to launch in the summer of 2003 and landing on the Meridiani Planum region of Mars.
“It’s like a whole new mission since we arrived at Cape York,” says Squyres.

Image caption: Opportunity Celebrates 9 Years on Mars snapping this panoramic view of the vast expanse of 14 mile (22 km) wide Endeavour Crater from atop ‘Matijevic Hill’ on Sol 3182 (Jan. 5, 2013). The rover then drove 43 feet to arrive at ‘Whitewater Lake’ and investigate clay minerals. Photo mosaic was stitched from Navcam images and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
Today Opportunity is poised for breakthrough science at deposits of phyllosilicates – clay minerals which stem from an earlier epoch when liquid water flowed on Mars eons ago and perhaps may have been more favorable to sustaining microbial life because they form in more neutral pH water. Endeavour Crater is more than 3 Billion years old.
I asked Squyres to discuss the discovery of the phyllosilicates – which have never before been analyzed up close on the Martian surface and are actually a main target of NASA’s new Curiosity rover at Gale Crater.
“We have found the phyllosilicates at Cape York: they’re in the Whitewater Lake materials,” Squyres explained. Spectral data collected from Mars orbit by the CRISM spectrometer aboard NASA’s MRO circling spacecraft allowed the researchers to direct Opportunity to this exact spot.
“Whitewater Lake” is an area of bright local outcrops currently being investigated and providing information about a different and apparently less acidic environment compared to other areas and craters visited earlier in the mission – and potentially more conducive to life.
Opportunity also discovered more mineral veins at “Whitewater Lake”, in addition to those hydrated mineral veins discovered earlier at Cape York at a spot named “Homestake” – see our mosaic below.
“We have investigated the veins in these materials, and we have determined that they are calcium sulfate,” Squyres confirmed to me.

Image caption: Opportunity discovers hydrated Mineral Vein at Endeavour Crater – November 2011. Opportunity determined that the ‘Homestake’ mineral vein was composed of calcium sulfate,or gypsum, while exploring around the base of Cape York ridge at the western rim of Endeavour Crater. The vein discovery indicates the ancient flow of liquid water at this spot on Mars. This panoramic mosaic of images was taken on Sol 2761, November 2011, and illustrates the exact spot of the mineral vein discovery. Featured on NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) on 12 Dec 2011. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Kenneth Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo.
How do the new mineral veins compare to those at ‘Homestake’ and those just found by Curiosity at Yellowknife Bay inside Gale crater? I asked Sqyures.
“Much narrower, and possibly older,” he said compared to the Homestake calcium sulfate veins .
“It’s too early to say how they compare to the veins at Gale, though.”
The local area at “Cape York” is called “Matijevic Hill” – in honor of a recently deceased team member who played a key role on NASA’s Mars rovers.
The rover has already spent a few months at “Matijevic Hill” on a ‘walk about’ scouting survey and also found concretions dubbed “newberries” that are different from the “blueberry” concretions found earlier in the mission.
How widespread are the phyllosilicates ?
“Matijevic Hill is the only exposure of phyllosilicates we know of at Cape York, so in order to find more we’re going to have to go elsewhere,” Squyres replied. “We haven’t figured out what the “newberries” are yet, but attempting to do that will be our next task.”
It is likely to take many more weeks and even months to “figure out” what this all means for science.
Therefore, no one should expect the robot to move much in the near future. Since the rover made landfall at the western rim of Endeavour crater at Spirit Point in August 2011, she has been circling around Cape York ever since.

Image caption: Opportunity rover first arrived at the western rim of Endeavour Crater (14 miles, 22 km wide) in August 2011. This photo mosaic of navcam images shows portions of the segmented rim of Endeavour crater on Sol 2678. Large ejecta blocks from a smaller nearby crater are visible in the middle. At Endeavour, Opportunity will investigate the oldest minerals deposits she has ever visited from billions of years ago and which may hold clues to environments that were potentially habitable for microbial life. The rover may eventually drive to Cape Tribulation at right if she survives. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer (kenkremer.com)
What is the next destination for Opportunity?
“Once we’re done at Cape York, our next destination will be Solander Point [to the south],” Squyres confirmed. It’s the next rim segment south of Cape York (see map).
Eventually, if Opportunity continues to function and survives the next Martian winter, she may be directed several miles even further south, along the crater rim to a spot called Cape Tribulation – because it also harbors caches of phyllosilicate clay minerals. But there is no telling when that might be.
“One step at a time,” said Squyres as always. He is not making any guesses or predictions. The mission is totally discovery driven.
Well after so many great science discoveries over the past 9 years, I asked Squyres to describe the context and significance of the phyllosilicates discovery?
“Impossible to say, I’m afraid… we’re still figuring this place out; I can’t put it in context yet,” Squyres concluded.
Thus, there is still so much more bountiful science research still to be done by Opportunity – and nobody is making any forecasts on how long she might yet survive.
So just keep praying to the Martian weather gods for occasional winds and “dust devils” to clean off those life giving solar panels – and to the US Congress to provide the essential funding.
Ken Kremer

Image caption: Opportunity Phones Home – Dusty Self Portrait from Endeavour Crater on Mars on Sol 2852, February 2012. NASA’s rover Opportunity snaps self-portrait where she endured 5th frigid Martian winter at Greeley Haven. Opportunity is currently investigating Cape York ridge and Matijevic Hill at right. Vast expanse of Endeavour Crater and rim in background with dusty solar panels and full on view of the High Gain Antenna (HGA) in the foreground. Mosaic: NASA/JPL/Cornell/ASU/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer

Image caption: Endeavour Crater Panorama from Opportunity, Sol 2681, August 2011 on arrival at the rim of Endeavour and Cape York ridge. Odyssey crater visible at left. Mineral veins were later found to surround Cape York. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer
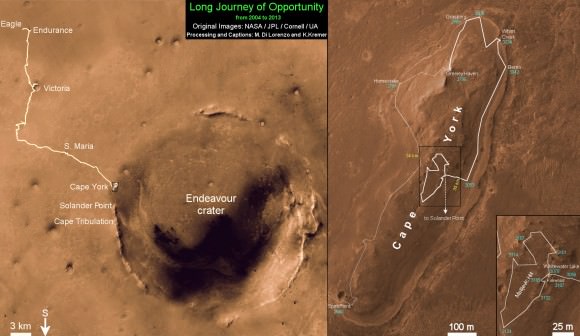
Image caption: Traverse Map for NASA’s Opportunity rover from 2004 to 2013 – shows the entire path the rover has driven over 9 years, 3200 Sols and more than 22 miles (35 km) from Eagle Crater landing site to current location at Cape York ridge at Endeavour Crater. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/ASU/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer (kenkremer.com)






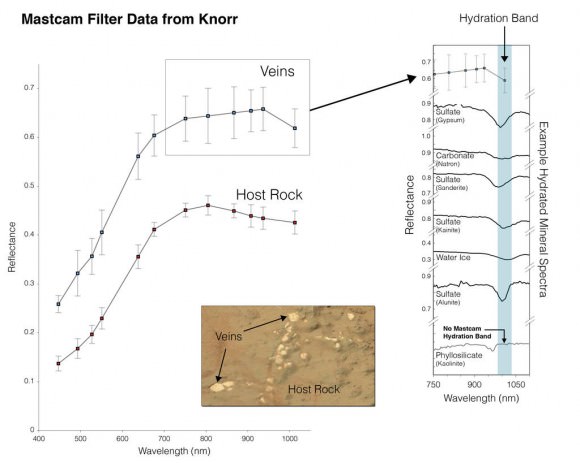
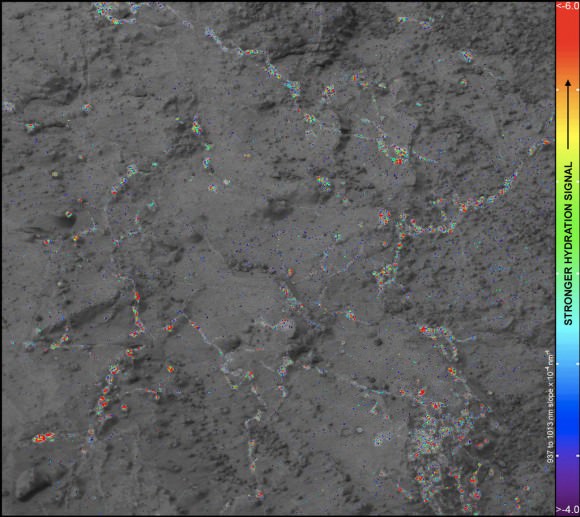










![PIA16716_ip[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/PIA16716_ip1-580x580.jpg)