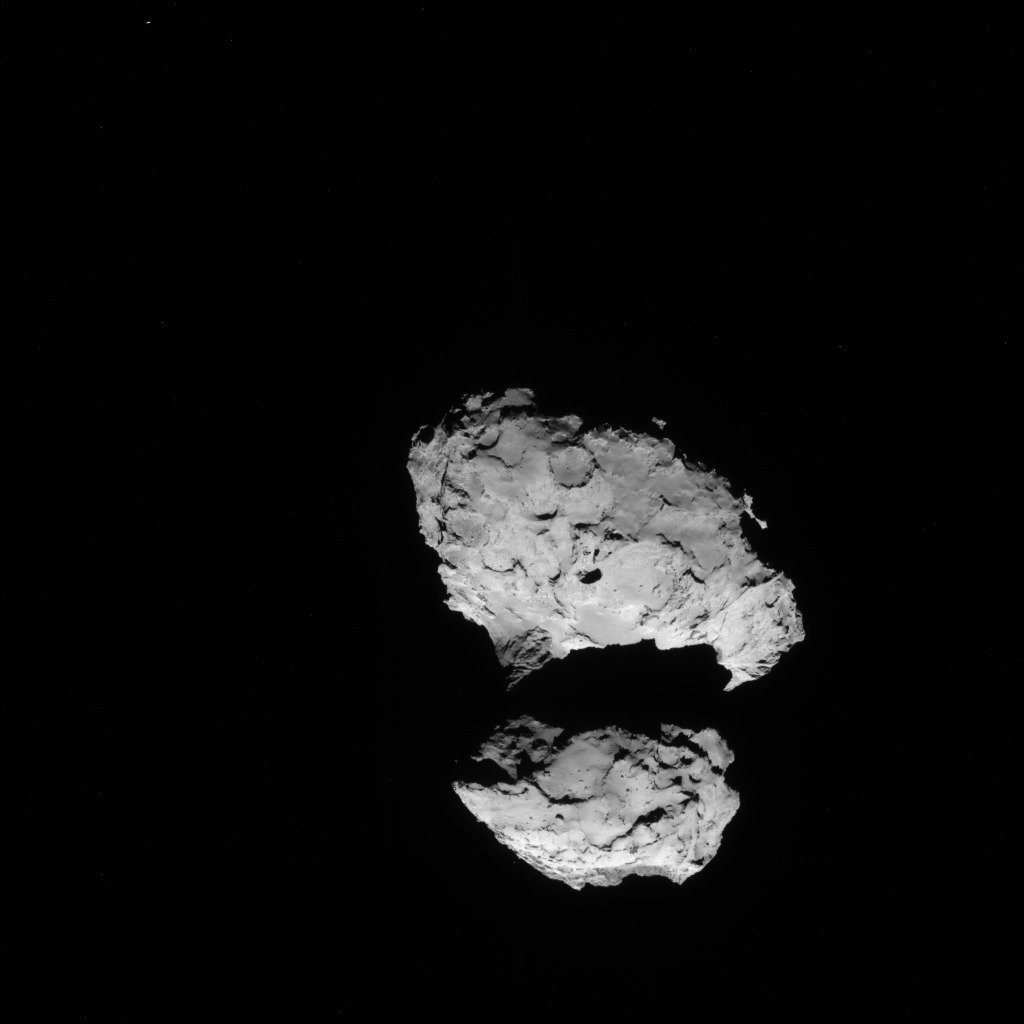
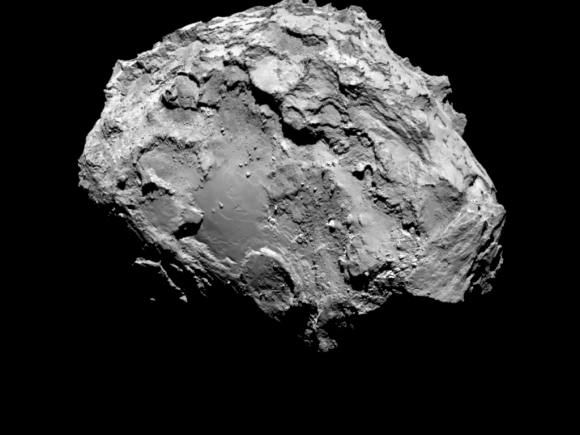
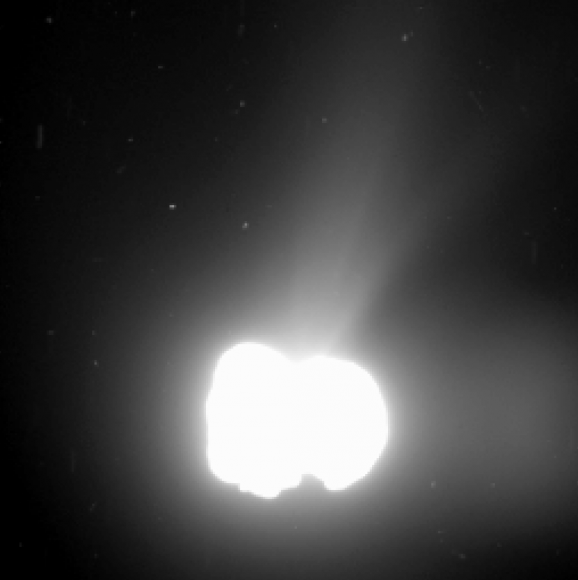
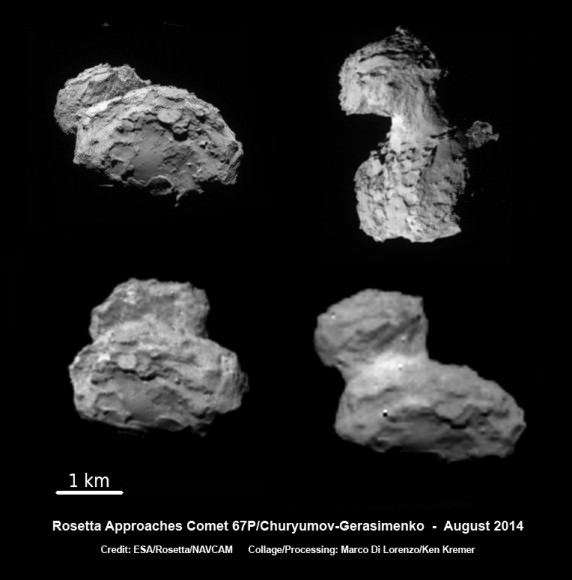
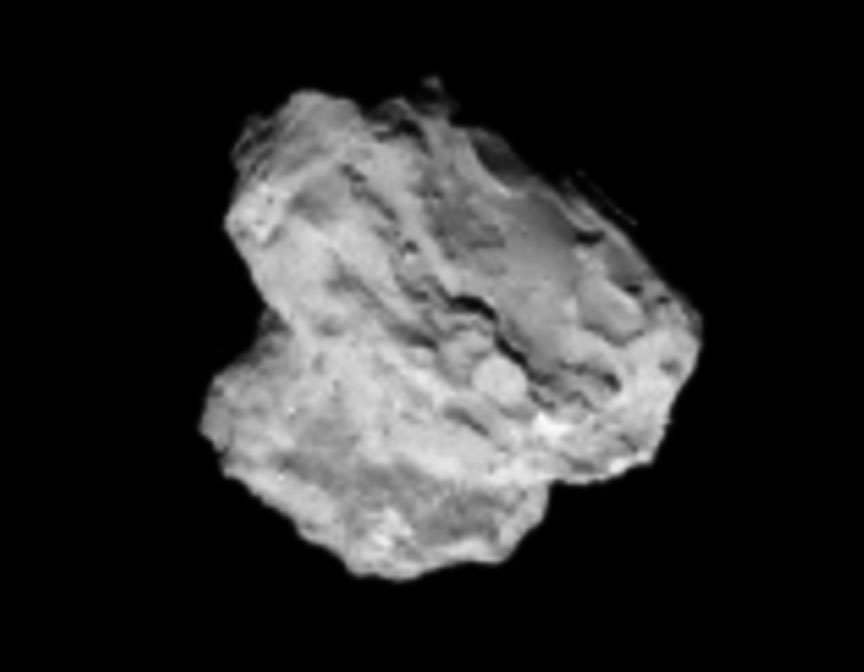
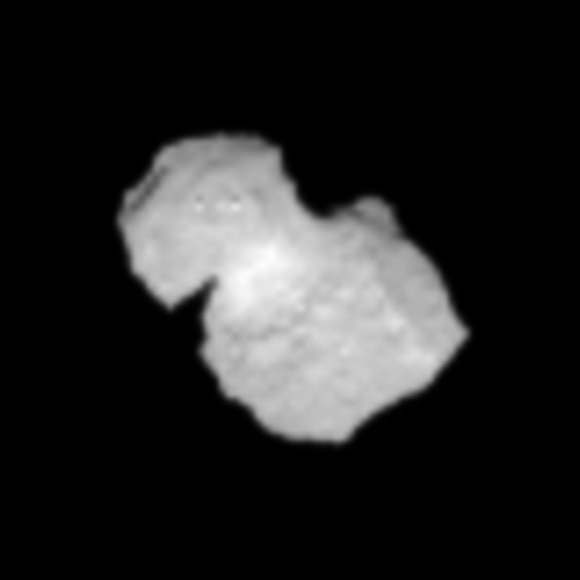
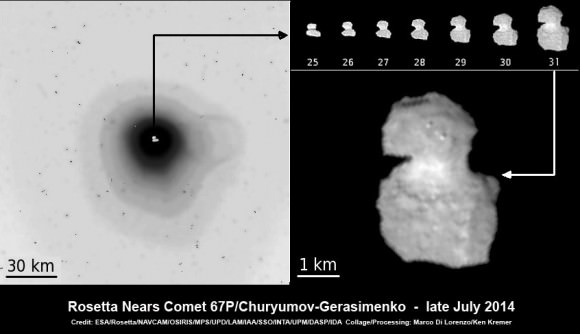
The ‘head’ of the bizarre comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko has been selected as the primary landing site for the Rosetta spacecraft’s attached Philae lander, attempting mankind’s first ever landing on a comet in mid-November.
Scientists leading the European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission announced the primary landing site at a media briefing today, Sept. 15, at ESA headquarters.
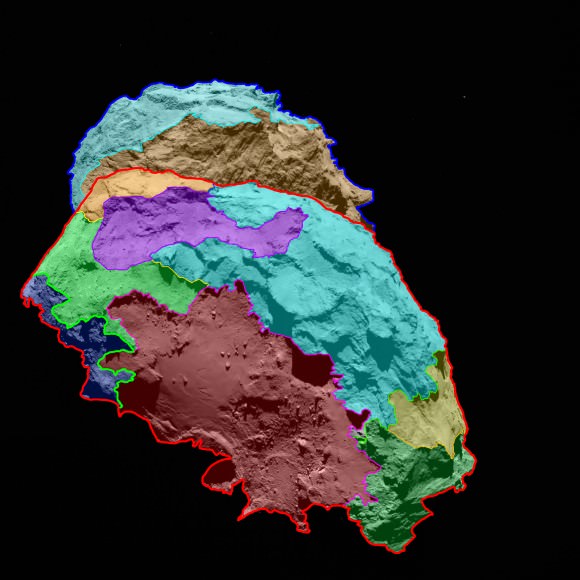
After weeks of detailed study and debate focused on balancing scientific interest with finding a ‘technically feasible’ and safe Philae touchdown site, the team chose a target dubbed Site J as the primary landing site from among a list of five initially selected sites, said Stephan Ulamec, Philae Lander Manager at the DLR German Aerospace Center, at the briefing.
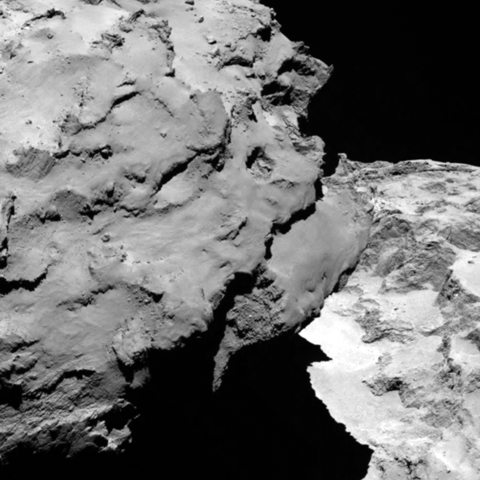
“Site J is the primary landing site around the head of the comet,” Ulamec announced.
“Site C is the backup site on the body [near the bottom of the comet].”
“This was not an easy task. Site J is a mix of flat areas and rough terrain. It’s not a perfectly flat area. There is still risk with high slope areas.”
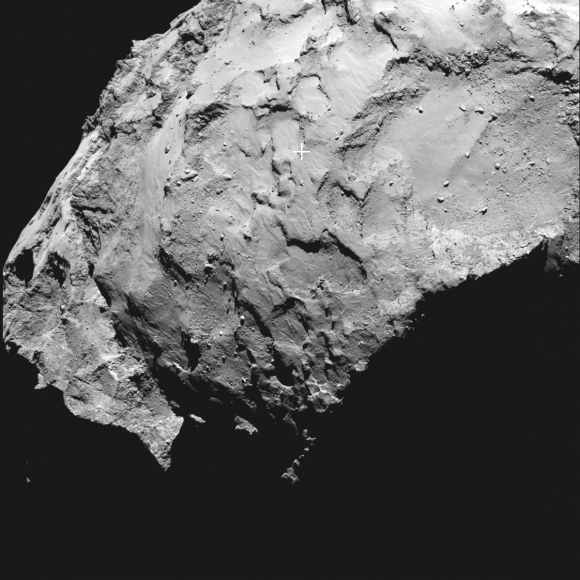

He also made clear that there is still some landing uncertainty with the targeting of the lander onto the comet.
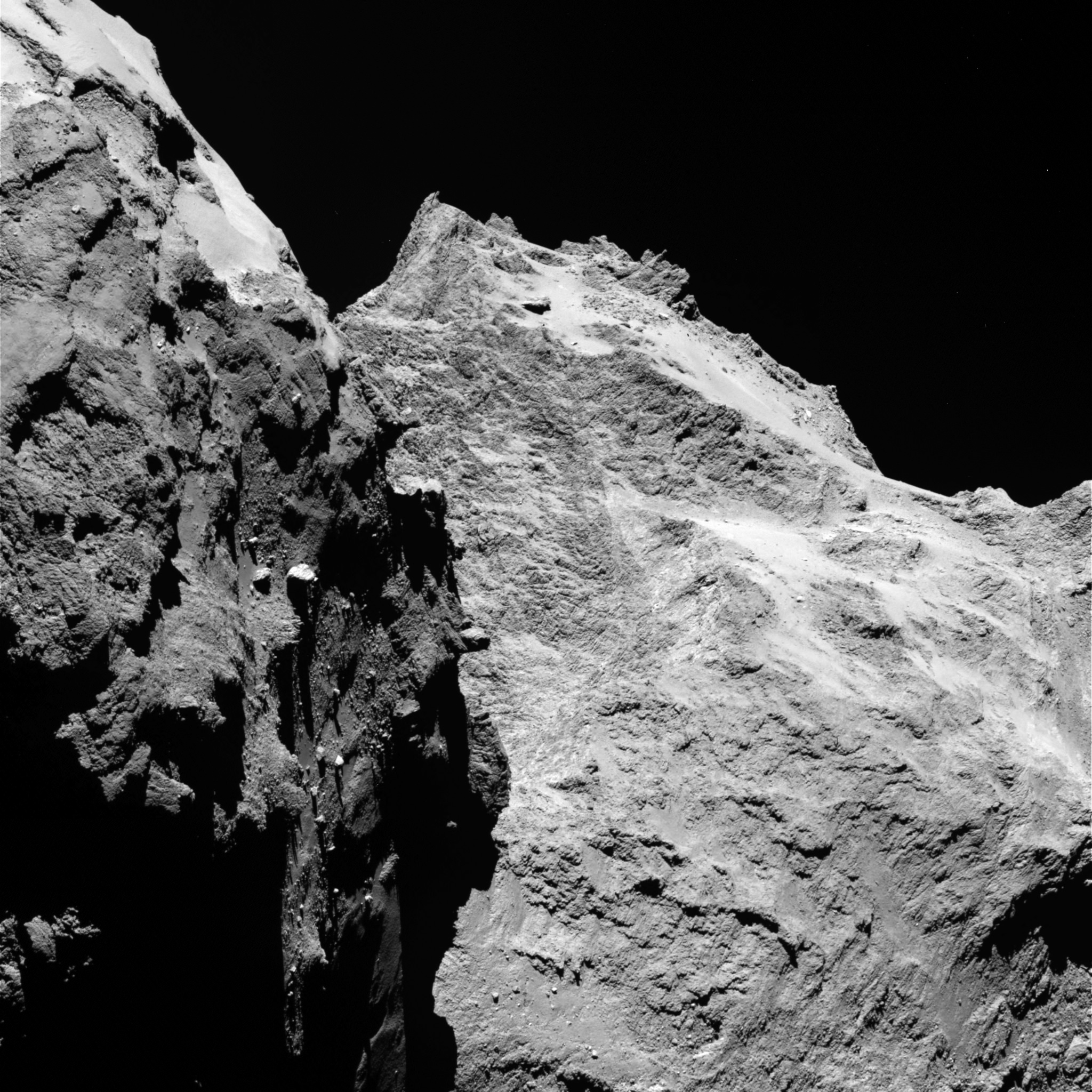
Site J is an intriguing region on Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko that offers unique scientific potential, with hints of activity nearby, and minimum risk to the lander compared to the other candidate sites, according to ESA.
“As we have seen from recent close-up images, the comet is a beautiful but dramatic world – it is scientifically exciting, but its shape makes it operationally challenging,” says Ulamec.
“None of the candidate landing sites met all of the operational criteria at the 100% level, but Site J is clearly the best solution.”
Philae’s history-making landing on comet 67P is currently scheduled for around Nov. 11, 2014, and will be entirely automatic. The 100 kg lander is equipped with 10 science instruments.
“All of Rosetta’s instruments are supporting the landing site selection,” said Holger Sierks, principal investigator for Rosetta’s OSIRIS camera from the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Gottingen, Germany.
“Site J is just 500-600 meters away from some pits and an area of comet outgassing activity. They will become more active as we get closer to the sun.
The team is in a race against time to select a suitable landing zone quickly and develop the complex landing sequence since the comet warms up and the surface becomes ever more active as it swings in closer to the sun and makes the landing ever more hazardous.
Since the descent to the comet is passive it is only possible to predict that the landing point will place within a ‘landing ellipse’ typically a few hundred metres in size, the team elaborated.
The three-legged lander will fire two harpoons and use ice screws to anchor itself to the 4 kilometer (2.5 mile) wide comet’s surface. Philae will collect stereo and panoramic images and also drill 20 to 30 centimeters into and sample its incredibly varied surface.
“We will make the first ever in situ analysis of a comet at this site, giving us an unparalleled insight into the composition, structure and evolution of a comet,” says Jean-Pierre Bibring, a lead lander scientist and principal investigator of the CIVA instrument at the IAS in Orsay, France.
“Site J in particular offers us the chance to analyse pristine material, characterise the properties of the nucleus, and study the processes that drive its activity.”
“It’s amazing how much we have learned so far.”
“We are in a true revolution of how we think Planets form and evolve,” Bibring elaborated at the briefing.
“We will make many types of scientific measurements of the comet from the surface. We will get a complete panoramic view of the comet on the macroscopic and microscopic scale.”
Rosetta is currently orbiting the comet from a distance of 30 km, said ESA Rosetta flight director Andrea Accomazzo. He said it will likely go even closer to 20 km and perhaps 10 km.

“Now that we’re closer to the comet, continued science and mapping operations will help us improve the analysis of the primary and backup landing sites,” says ESA Rosetta flight director Andrea Accomazzo.
“Of course, we cannot predict the activity of the comet between now and landing, and on landing day itself. A sudden increase in activity could affect the position of Rosetta in its orbit at the moment of deployment and in turn the exact location where Philae will land, and that’s what makes this a risky operation.”
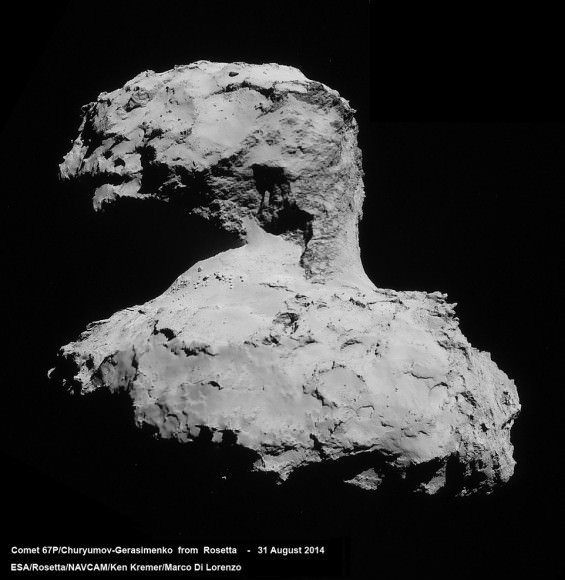

The final landing site selections were made at a meeting being held this weekend on 13 and 14 September 2014 between the Rosetta Lander Team and the Rosetta orbiter team at CNES in Toulouse, France.
“No one has ever attempted to land on a comet before, so it is a real challenge,” says Fred Jansen, ESA Rosetta mission manager.
“The complicated ‘double’ structure of the comet has had a considerable impact on the overall risks related to landing, but they are risks worth taking to have the chance of making the first ever soft landing on a comet.”

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Rosetta, Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.