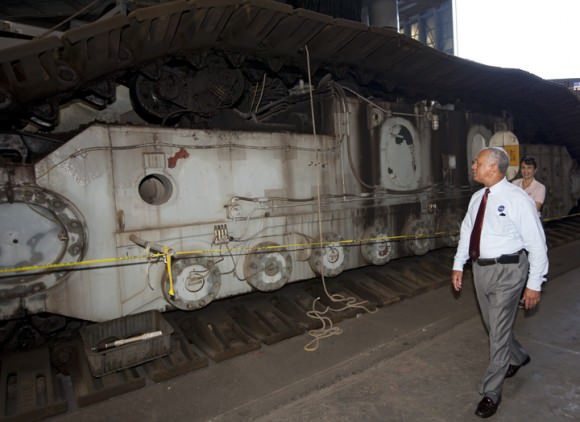
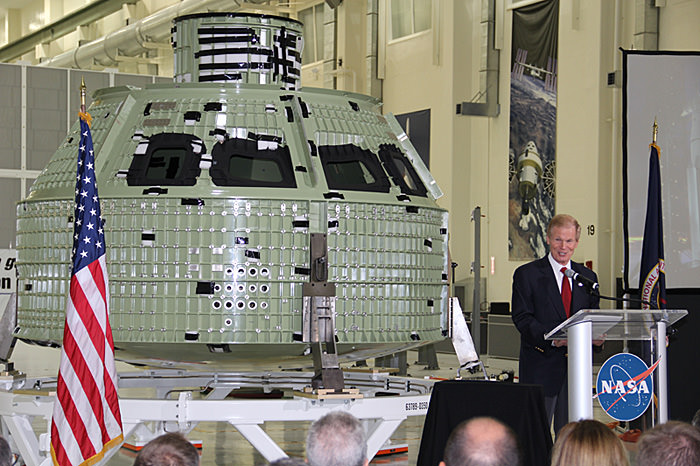
Image caption: Sen. Bill Nelson of Florida welcomes the newly arrived Orion crew capsule at a Kennedy Space Center unveiling ceremony on July 2, 2012 and proclaims Mars is NASA’s long term goal for human exploration. Credit: Ken Kremer
NASA’s first space-bound Orion crew capsule was officially unveiled at a welcoming ceremony at the Kennedy Space Center on Monday (July 2) to initiate a process that the agency hopes will finally put Americans back on a path to exciting destinations of exploration beyond low Earth orbit for the first time in 40 years since Apollo and spawn a new era in deep space exploration by humans – starting with an initial uncrewed test flight in 2014.
Over 450 invited guests and dignitaries attended the Orion arrival ceremony at Kennedy’s Operations and Checkout Building (O & C) to mark this watershed moment meant to reignite human exploration of the cosmos.
“This starts a new, exciting chapter in this nation’s great space exploration story,” said Lori Garver, NASA deputy administrator. “Today we are lifting our spirits to new heights.”

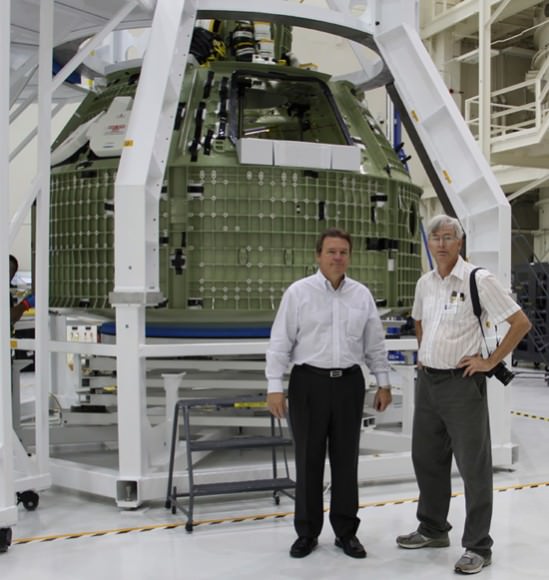
Image caption: Posing in front of NASA’s 1st Orion crew module set for 2014 liftoff are; KSC Director Bob Cabana, Mark Geyer, NASA Orion Program manager, Sen. Bill Nelson (FL), Lori Garver, NASA Deputy Administrator. Credit: Ken Kremer
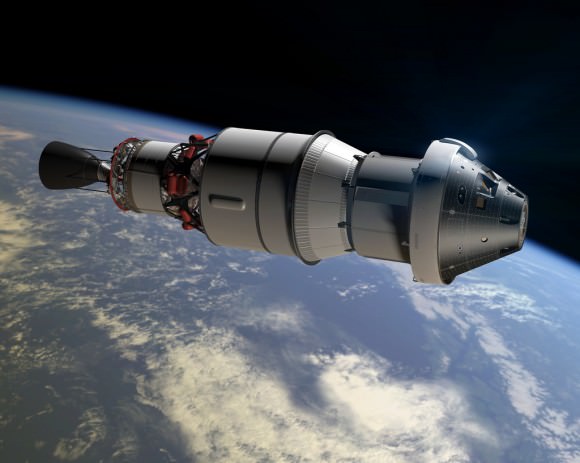
This Orion capsule is due to lift off on a critical unmanned test flight in 2014 atop a powerful Delta 4 Heavy booster – like the Delta rocket just launched on June 29.
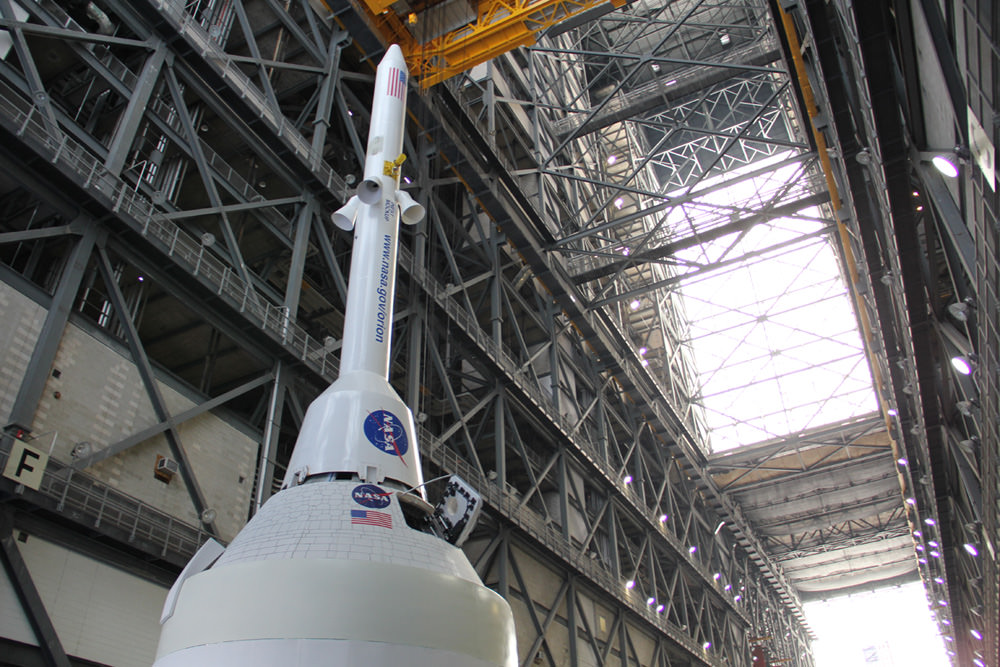
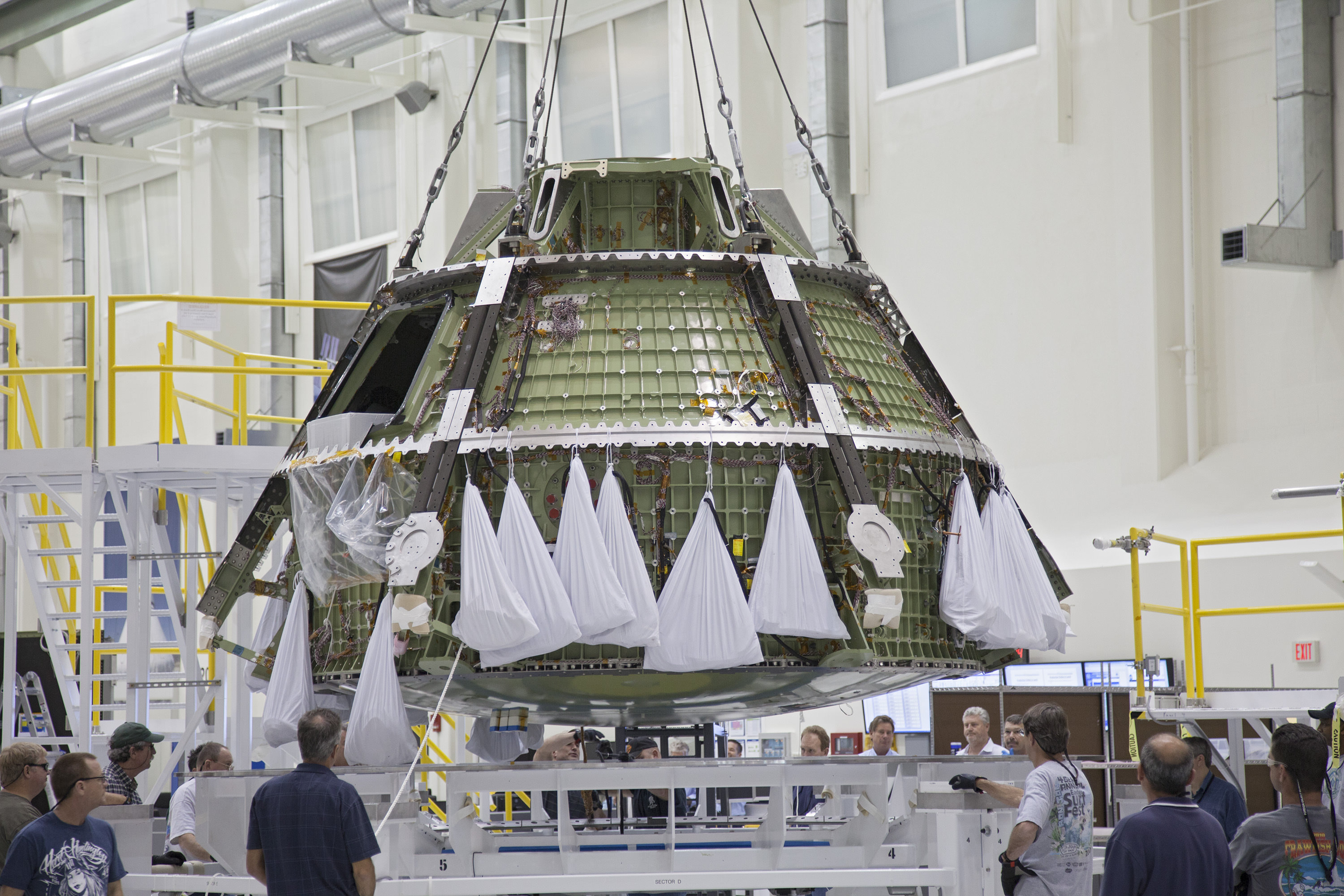
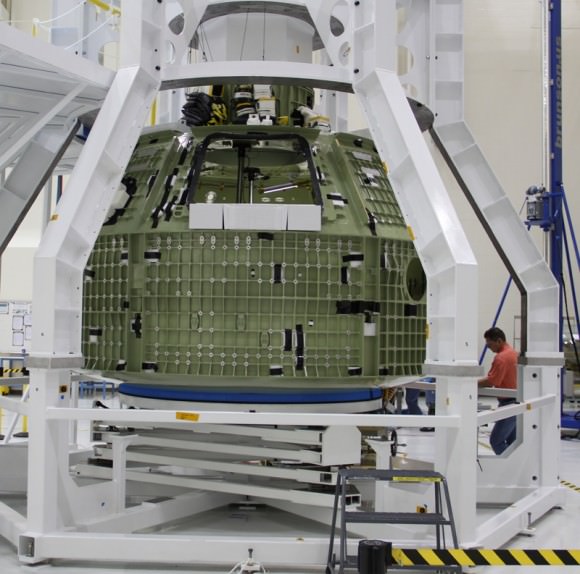
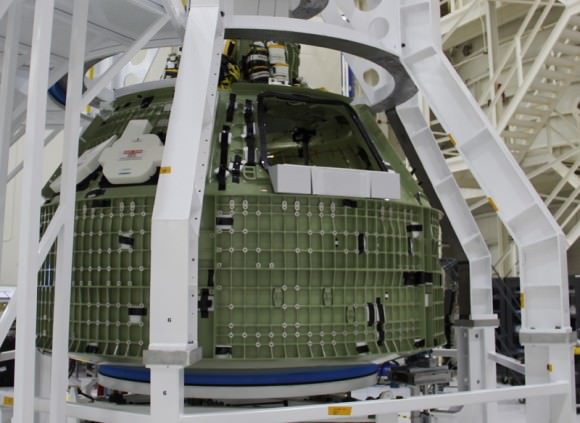
The bare bones, olive green colored aluminum alloy pressure shell arrived at KSC last week from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility where the vessel was assembled and the final welds to shape it into a capsule were just completed. Every space shuttle External Tank was built at Michoud in New Orleans.
U.S. Senator Bill Nelson of Florida has spearheaded the effort in Congress to give NASA the goal and the funding to build the Orion Multipurpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) and the means to launch it atop the most powerful rocket ever built – a Saturn V class booster dubbed the SLS or Space Launch System – to destinations in deep space that have never been explored before.
“Isn’t this beautiful?” said Nelson as he stood in front of the incomplete vessel, motioned to the crowd and aimed his sights high. “I know there are a lot of people here who can’t wait to get their hands and their fingers on this hardware.
“And ladies and gentlemen, we’re going to Mars!” proclaimed Nelson.
“Without question, the long-term goal of our space program, human space program right now is the goal of going to Mars in the decade of the 2030s.”
“We still need to refine how we’re going to go there, we’ve got to develop a lot of technologies, we’ve got to figure out how and where we’re going to stop along the way. The president’s goal is an asteroid in 2025. But we know the Orion capsule is a critical part of the system that is going to take us there.”
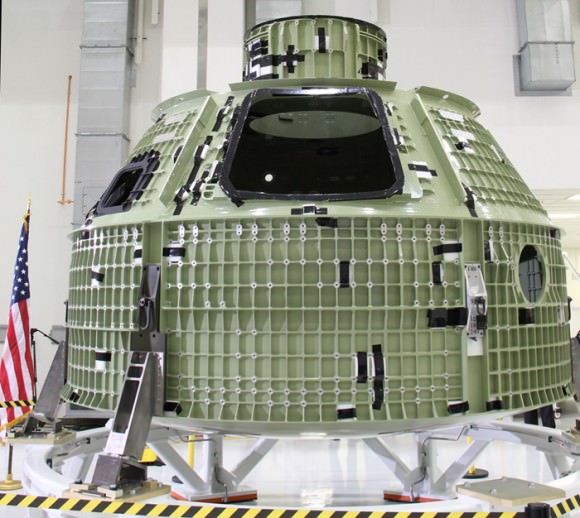

Image caption: The green colored aluminum alloy pressure vessel arrived at KSC last week and will be outfitted with all the instrumentation required for spaceflight. Launch is slated for 2014 atop Delta 4 Heavy booster from pad 37 on Cape Canaveral. Crew hatch and tunnel visible at center. Credit: Ken Kremer
Orion is the most advanced spacecraft ever designed.
Over about the next 18 months, engineers and technicians at KSC will install all the systems and gear – such as avionics, instrumentation, flight computers and the heat shield – required to transform this empty shell into a functioning spacecraft.
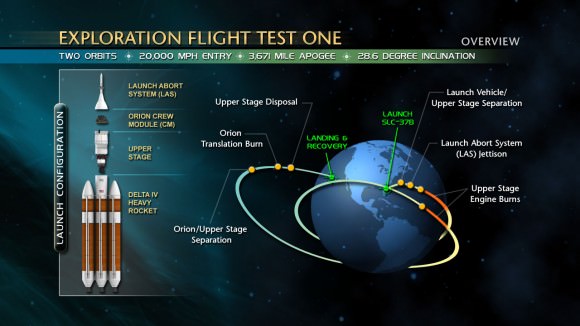
The 2014 uncrewed flight, called Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1, will be loaded with a wide variety of instruments to evaluate how the spacecraft behaves during launch, in space and then through the searing heat of reentry.
The 2 orbit flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station. Although the mission will only last a few hours it will be able high enough to send the vehicle plunging back into the atmosphere at over 20.000 MPH to test the craft and its heat shield at deep-space re-entry speeds approaching those of the Apollo moon landing missions.

Image caption: Sen. Bill Nelson of Florida discusses the new arrived Orion capsule with NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver while surrounded by a horde of reporters at the Kennedy Space Center unveiling ceremony on July 2, 2012. Credit: Ken Kremer
Orion arrived at Kennedy on nearly the same day that the center opened its door 50 years ago.
“As KSC celebrates its 50th anniversary this month, I can’t think of a more appropriate way to celebrate than by having the very first Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle here at KSC,” said KSC Center Director Robert Cabana, a former shuttle commander, at the O & C ceremony.
“The future is here, now, and the vehicle we see here today is not a Powerpoint chart. It’s a real spacecraft, moving toward a test flight in 2014.”
In 2017, an Orion capsule will lift off on the first SLS flight. The first crewed Orion will launch around 2021 and orbit the moon, Lori Garver told me in an interview at KSC.
But the entire schedule and construction of the hardware is fully dependent on funding from the federal government.
In these lean times, there is no guarantee of future funding and NASA’s budget has already been significantly chopped – forcing numerous delays and outright mission cancellations on many NASA projects; including the outright termination of NASA next Mars rover and multi-year delays to the commercial crew program and prior plans to launch a crewed Orion to orbit as early as 2013.

Image caption: Veteran NASA Astronaut Rex Walheim discusses Orion with Universe Today. Walheim flew on the last space shuttle mission (STS-135). Credit: Ken Kremer
Astronaut Rex Walheim, who flew on the final space shuttle mission (STS-135) and has had key role in developing Orion, said the Orion capsule can be the principal spacecraft for the next 30 years of human exploration of the solar system.
“It’s the first in a line of vehicles that can take us where we’ve never gone before,” Walheim said. “It’ll be a building block approach, we’ll have to have a lander and a habitation module, but we can get there.”

Image caption: John Karas, Lockheed Martin Vice President for Human Space Flight poses with Orion and discusses the upcoming 2014 EFT-1 test flight with Universe Today. Lockheed is the prime contractor for Orion. Credit: Ken Kremer
“Personally I am thrilled to be working on the next vehicle that will take us beyond low Earth orbit, said John Karas, Lockheed Martin Vice President for Human Space Flight. Lockheed Martin is the prime contractor to build Orion.
“Orion will carry humans to destinations never explored before and change human’s perspectives”
“Folks here are ready to start working on the EFT-1 mission. In about 18 months, EFT-1 will fly on the next Delta 4 Heavy flight.
“I can’t wait to go deeper into the cosmos!” Karas exclaimed.
Ken Kremer
…..
July 13/14: Free Public Lectures about NASA’s Mars and Planetary Exploration, the Space Shuttle, SpaceX , Orion and more by Ken Kremer at the Adirondack Public Observatory in Tupper Lake, NY.