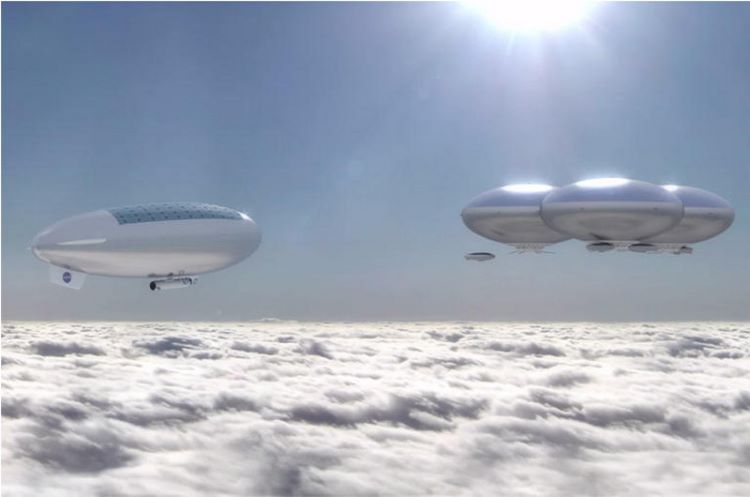
NASA is preparing to send humans back to the Moon with the Artemis missions in the next few years as part of the agency’s Moon to Mars Architecture with the long-term goal of landing humans on the Red Planet sometime in the 2030s or 2040s. But what about sending humans to other worlds of the Solar System? And, why not Venus? It’s closer to Earth than Mars by several tens of millions of kilometers, and despite its extremely harsh surface conditions, previous studies have suggested that life could exist in its clouds. In contrast, we have yet to find any signs of life anywhere on the Red Planet or in its thin atmosphere. So, should we send humans to Venus?
Continue reading “Should We Send Humans to Venus?”Should We Send Humans to Venus?