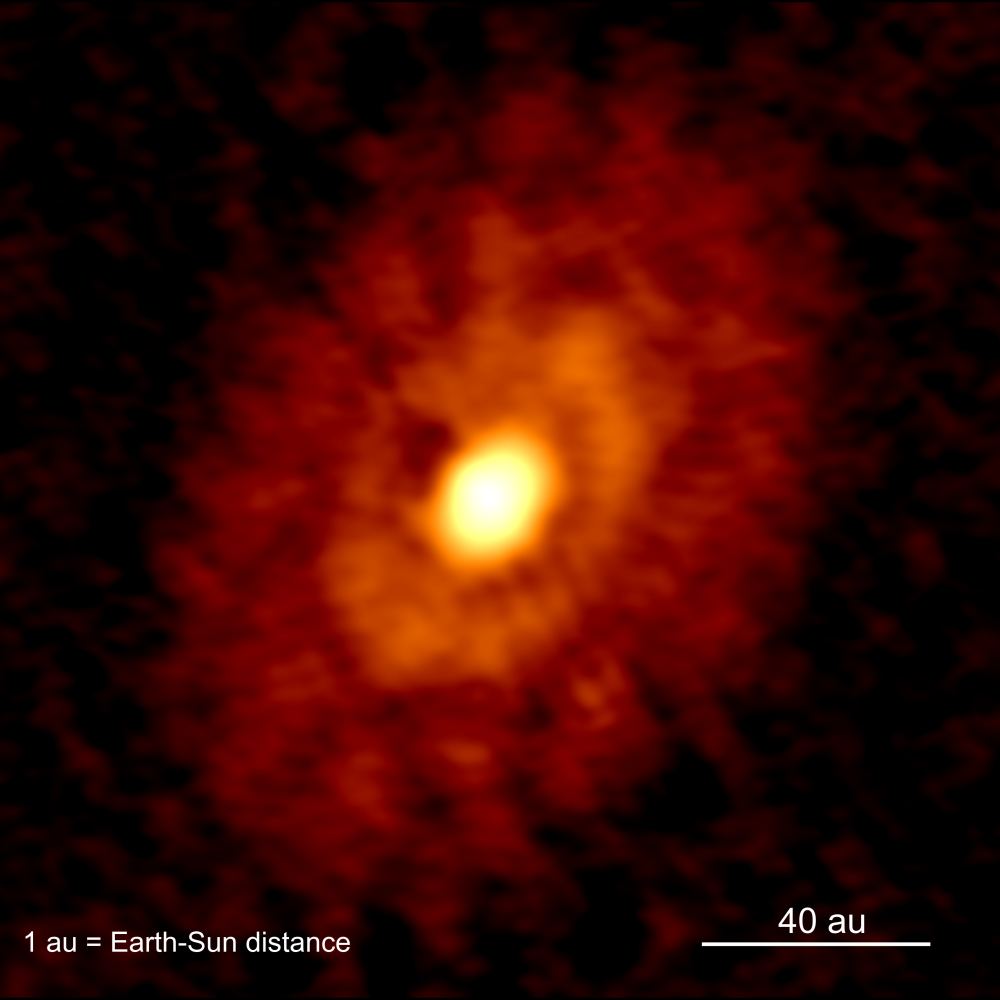
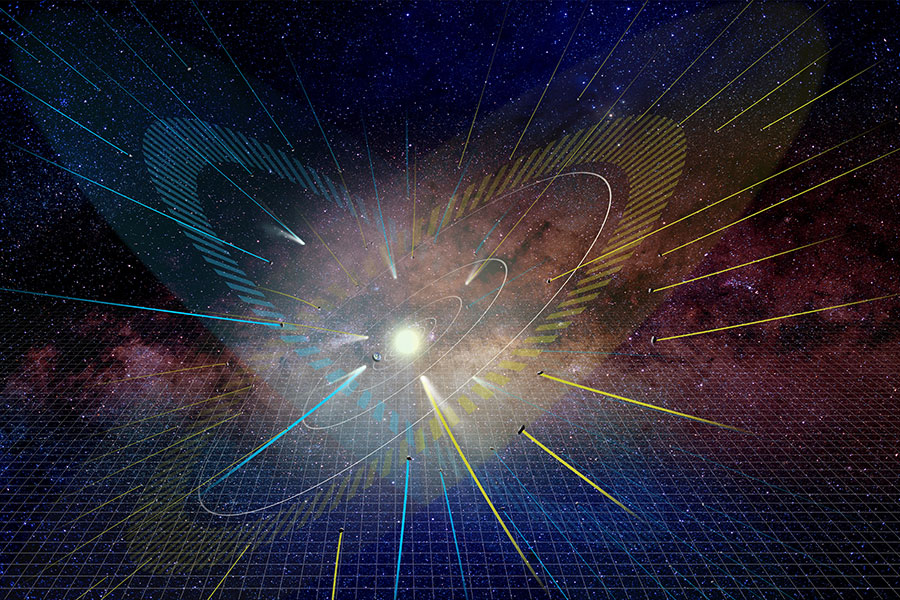
Almost all the objects orbiting the sun live in a particular plane, called the ecliptic plane. But a recent analysis of long-period comets reveals a second home, a so-called “empty ecliptic”. And it may be populated with comets dragged there by none other than the gravity of the Milky Way galaxy.
Continue reading “The Solar System has a second plane where objects orbit the Sun”The Solar System has a second plane where objects orbit the Sun