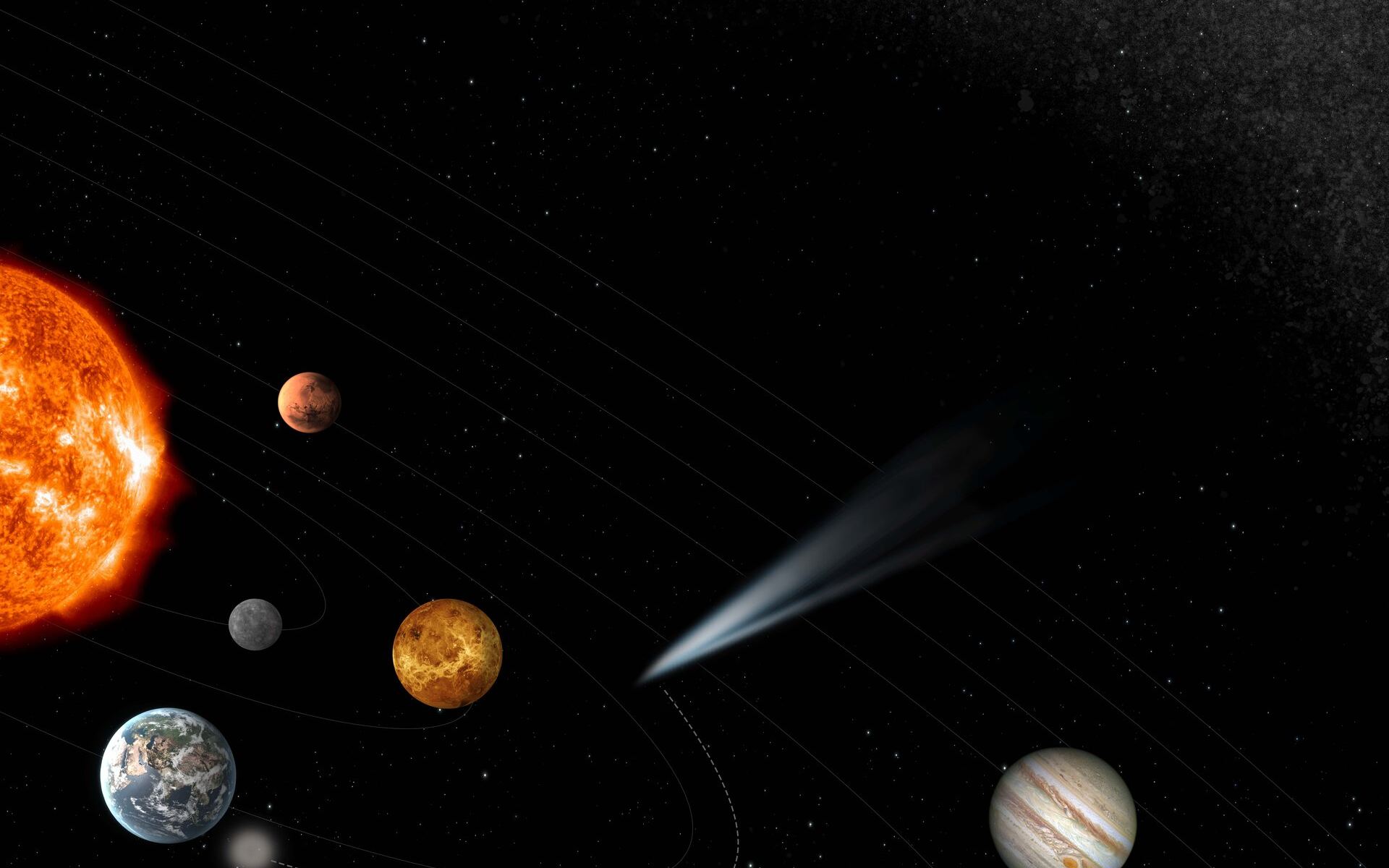
Comets, with their long, beautiful, bright tails of ice, are some of the most spectacular sightings in the night sky. This was most apparent when Comet NEOWISE passed by Earth in the summer of 2020, dazzling viewers from all over the planet while being mainly visible in the northern hemisphere. Even though the sky might look the same night after night, comets are a humble reminder that the universe is a very active and beautiful place.
Continue reading “ESA Gives Green Light on its Comet Interceptor Mission”Traveling the Solar System with Pulsar Navigation

A team of researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have found a way for travelers through the Solar System to work out exactly where they are, without needing help from ground-based observers on Earth. They have refined the pulsar navigation technique, which uses X-ray signals from distant pulsars, in a way similar to how GPS uses signals from a constellation of specialized satellites, to calculate an exact position .
Continue reading “Traveling the Solar System with Pulsar Navigation”The Sun is Slowly Tearing This Comet Apart
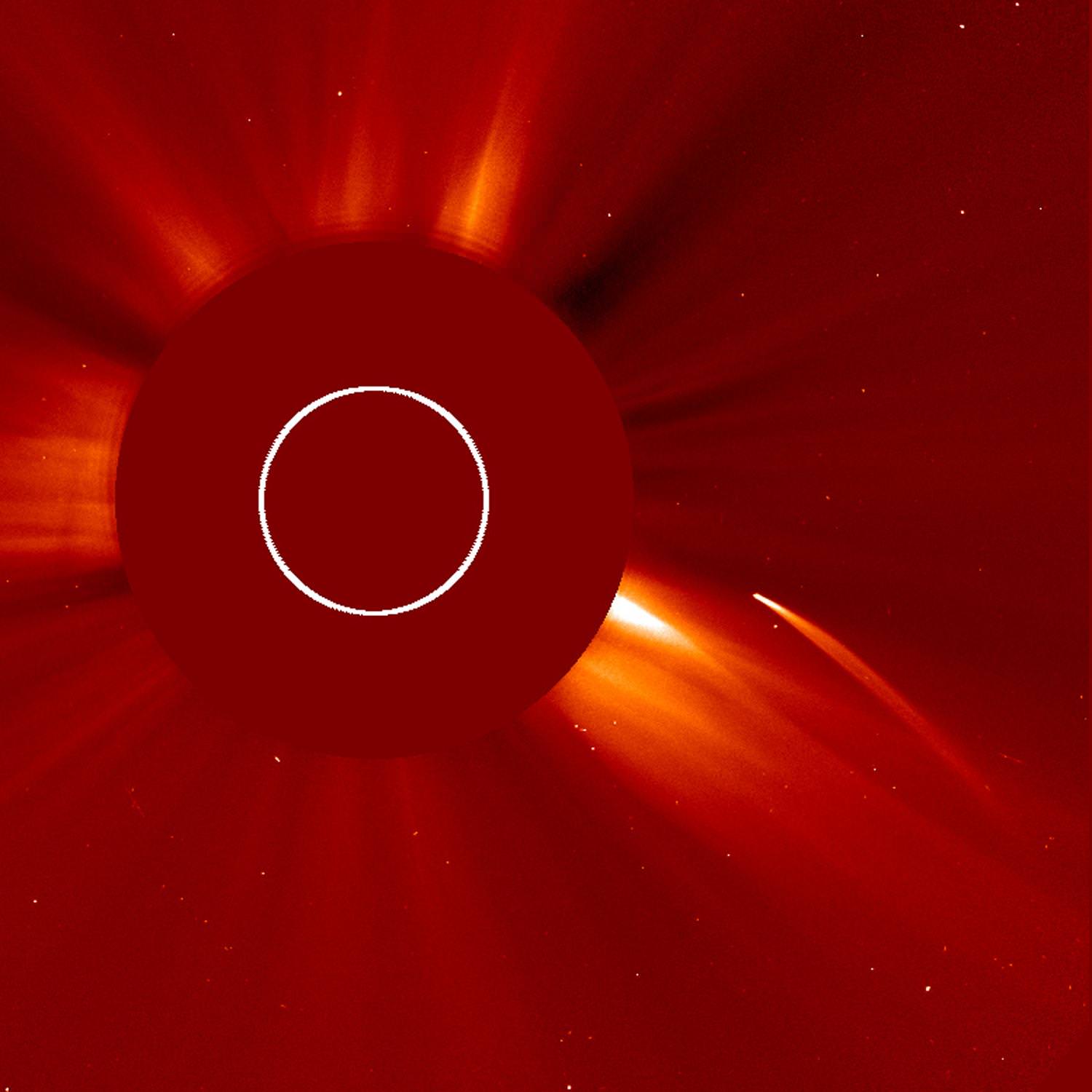
Using ground-based and space-based observations, a team of researchers has been monitoring a difficult-to-see comet carefully. It’s called Comet 323P/SOHO, and it was discovered over 20 years ago in 1999. But it’s difficult to observe due to its proximity to the Sun.
They’ve found that the Sun is slowly tearing the comet to pieces.
Continue reading “The Sun is Slowly Tearing This Comet Apart”Mini-Neptunes can Lose gas and Turn Into Super-Earths

Can one type of planet become another? Can a mini-Neptune lose its atmosphere and become a super-Earth? Astronomers have found two examples of mini-Neptunes transitioning to super-Earths, and the discovery might help explain a noted “gap” in the size distribution of exoplanets.
Continue reading “Mini-Neptunes can Lose gas and Turn Into Super-Earths”Here are Hubble’s 2021 Photos of the Outer Solar System
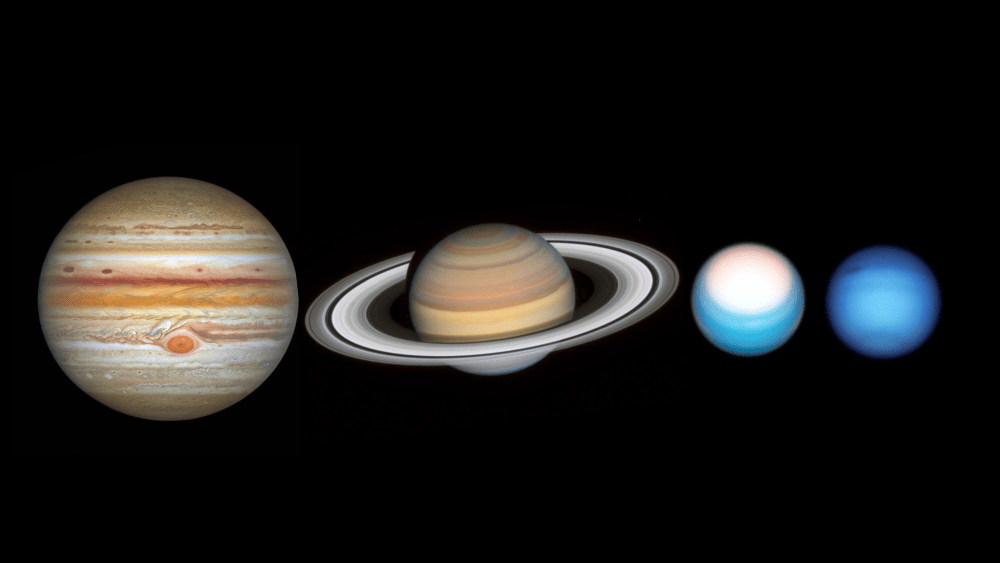
If we had to rely solely on spacecraft to learn about the outer planets, we wouldn’t be making great progress. It takes a massive effort to get a spacecraft to the outer Solar System. But thanks to the Hubble Space Telescope, we can keep tabs on the gas giants without leaving Earth’s orbit.
Continue reading “Here are Hubble’s 2021 Photos of the Outer Solar System”The Early Solar System Had a Gap Where the Asteroid Belt is Today
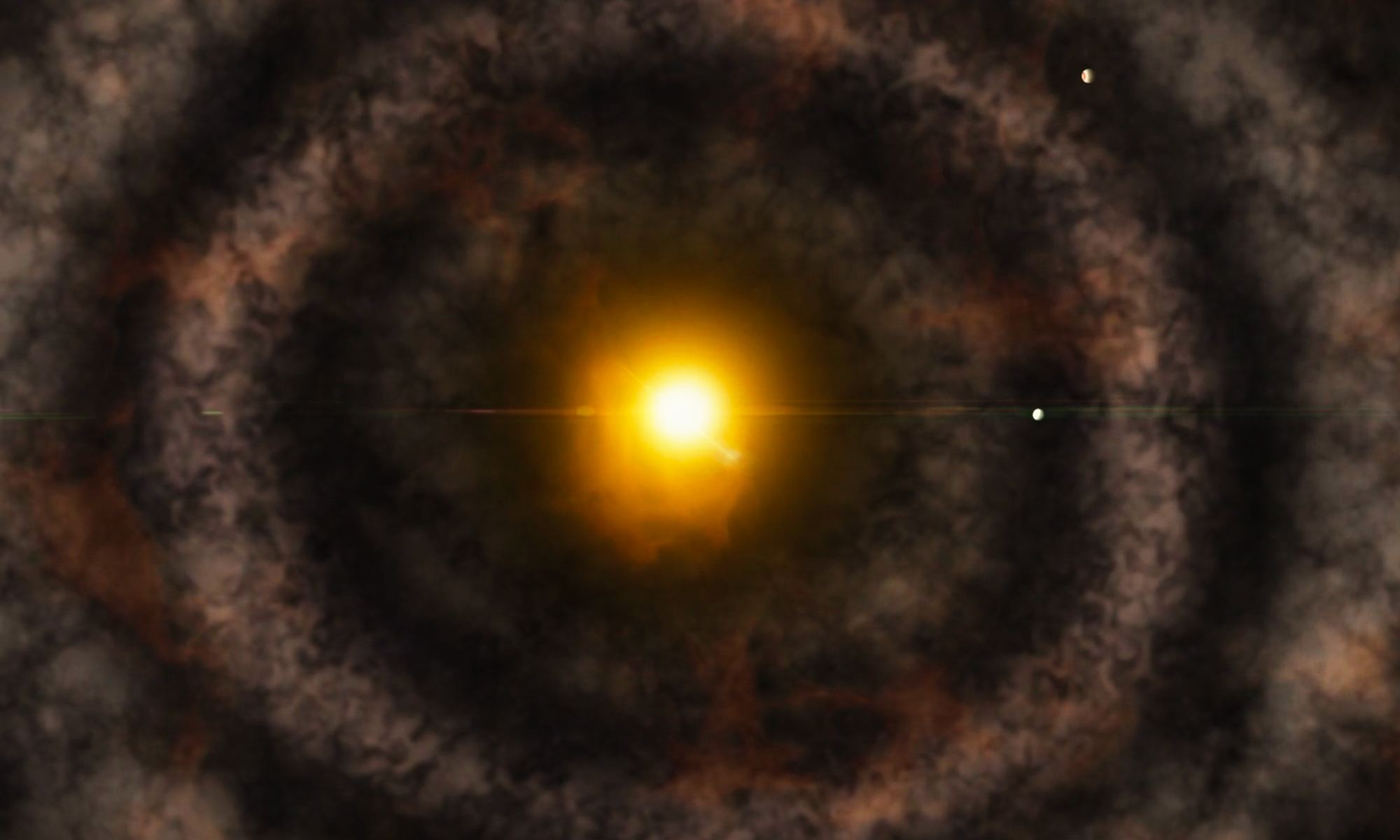

Wind the cosmic clock back a few billion years and our Solar System looked much different than it does today. About 4.5 billion years ago, the young Sun shone much like it does now, though it was a little smaller. Instead of being surrounded by planets, it was ensconced in a swirling disk of gas and dust. That disk is called a protoplanetary disk and it’s where the planets eventually formed.
There was a conspicuous gap in the early Solar System’s protoplanetary disk, between where Mars and Jupiter are now, and where the modern-day asteroid belt sits. What exactly caused the gap is a mystery, but astronomers think it’s a sign of the processes that governed planet formation.
Continue reading “The Early Solar System Had a Gap Where the Asteroid Belt is Today”The Biggest Comet Ever Seen Will get as Close as Saturn in 2031

A mega-comet – potentially the largest ever discovered – is heading from the Oort Cloud towards our direction. Estimated to be 100–200 kilometers across, the unusual celestial wanderer will make its closest approach to the Sun in 2031. However, the closest it will come to Earth is to the orbit of Saturn.
Continue reading “The Biggest Comet Ever Seen Will get as Close as Saturn in 2031”Images of 42 of the Biggest Asteroids in the Solar System

A huge team of astronomers have combined forces to use the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) to provide the sharpest view ever of 42 of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter.
Fittingly, the collection of images was released on the 42nd anniversary of the publication of “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy” by Douglas Adams. In the book, the number 42 is the answer to the “Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything.” These 42 images represent some of the sharpest views ever of these objects — which might contribute to answering these ultimate questions!
Plus, there’s a great poster of the asteroids, too:
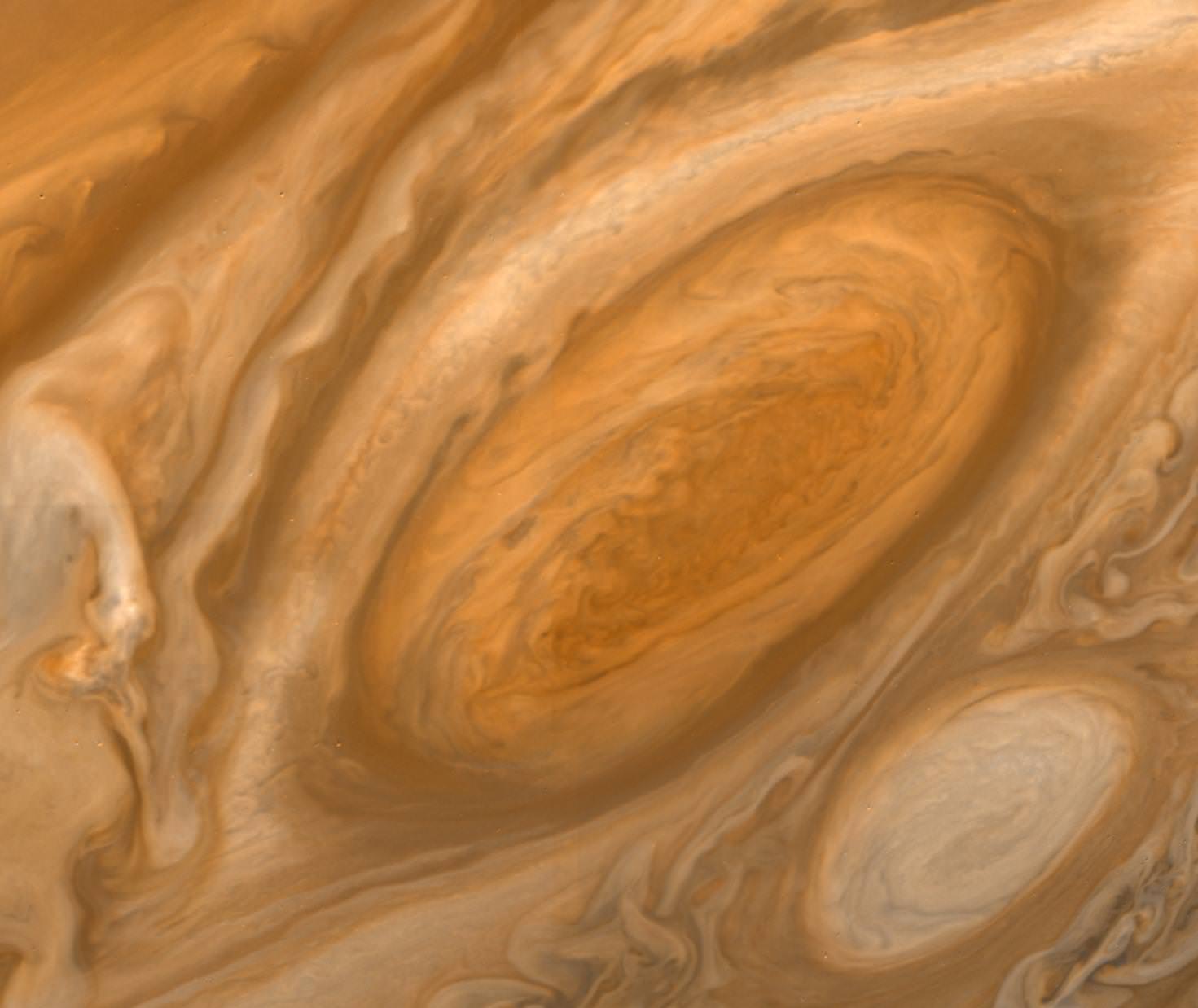
Continue reading “Images of 42 of the Biggest Asteroids in the Solar System”Wind Speeds in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot are Picking up
The Great Red Spot of Jupiter – the largest storm in the solar system – has been raging for centuries. Over the past 100 years however, the cyclone has been dwindling, but recent observations with Hubble show that the wind speeds may be picking up again. Is this just temporary, or will the storm return to its former glory?
Continue reading “Wind Speeds in Jupiter’s Great Red Spot are Picking up”The Early Solar System was Messier and More Violent Than Previously Believed
Our conventional models of planet formation may have to be updated, according to a pair of new papers.
Accretion is the keyword in current planet formation theory. The idea is that the planets formed out of the solar nebula, the material left over after the Sun formed. They did this through accretion, where small particles accumulate into more massive objects. These massive boulder-sized objects, called planetesimals, continued to merge together into larger entities, sometimes through collisions. Eventually, through repeated mergers and collisions, the inner Solar System was populated by four rocky planets.
But the new research suggests that the collisions played out much differently than thought and that objects collided with each other several times, in a series of hit and runs, before merging. This research fills some stubborn holes in our current understanding.
Continue reading “The Early Solar System was Messier and More Violent Than Previously Believed”


