In a recent study submitted to the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society for the 8th Interstellar Symposium special issue, which is due for publication sometime in 2024, Dr. Jacob Haqq-Misra, who is a senior research investigator and the Chief Operating Officer and co-founder at the Blue Marble Space Institute of Science, examines how future space exploration governing laws could evolve, either crewed or uncrewed and in the solar system or beyond. He views this study as an expansion of interplanetary governance models he previously discussed in his book, Sovereign Mars, to explore potential limits on space governance at interstellar distances.
Continue reading “The Outer Space Treaty was Signed in 1967. Can it Handle the Future of Space Exploration?”The Space Court Foundation Presents: “Women of Color in Space”
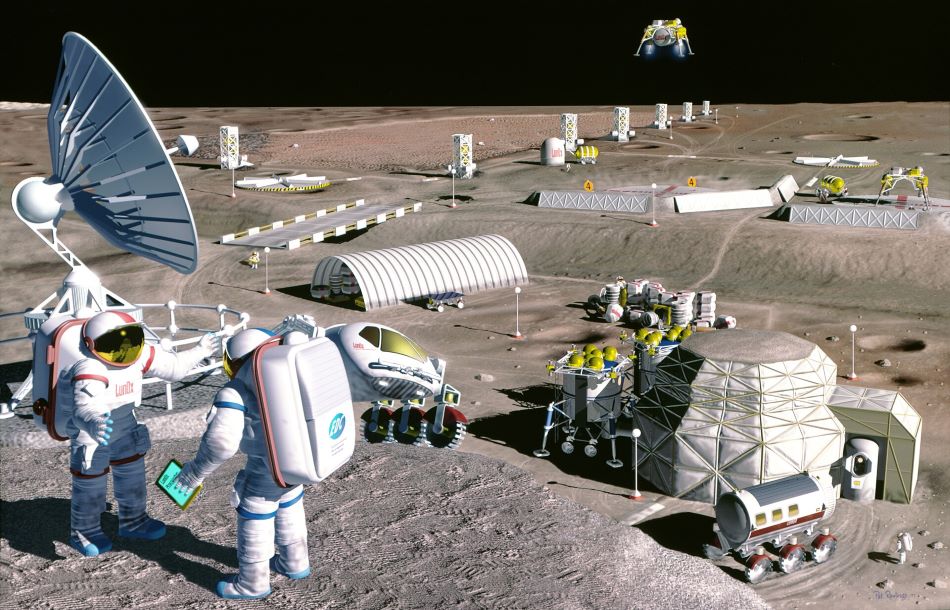
In the coming generations, humanity’s presence in space is expected to grow considerably. With everything from space tourism, the commercialization of Low Earth Orbit (LEO), asteroid mining, and maybe even settlements on the Moon and Mars in mind, there appears to be no limit to what we hope to accomplish. Another interesting thing about the modern space age is the way it is becoming more open and accessible, with more people and nations able to take part.
Unlike the Space Race, where two nations dominated the playing field and astronauts corps were almost exclusively made up of white men, space exploration today is more representative. However, there are still many challenges and barriers for women and people of color in space exploration and the related STEAM fields, not all of which are visible. Addressing these requires that we become better at listening to those who deal with them.
To this end, the Space Court Foundation (SCF) is launching a new series titled “Women of Color in Space.” As part of their mission to foster a conversation about space law and the future of space exploration today, this series interviews women of color who have made it their mission to advance space exploration and fulfill the promise of making space “the province of all of humanity.”
Continue reading “The Space Court Foundation Presents: “Women of Color in Space””The Space Court Foundation is Now in Session!
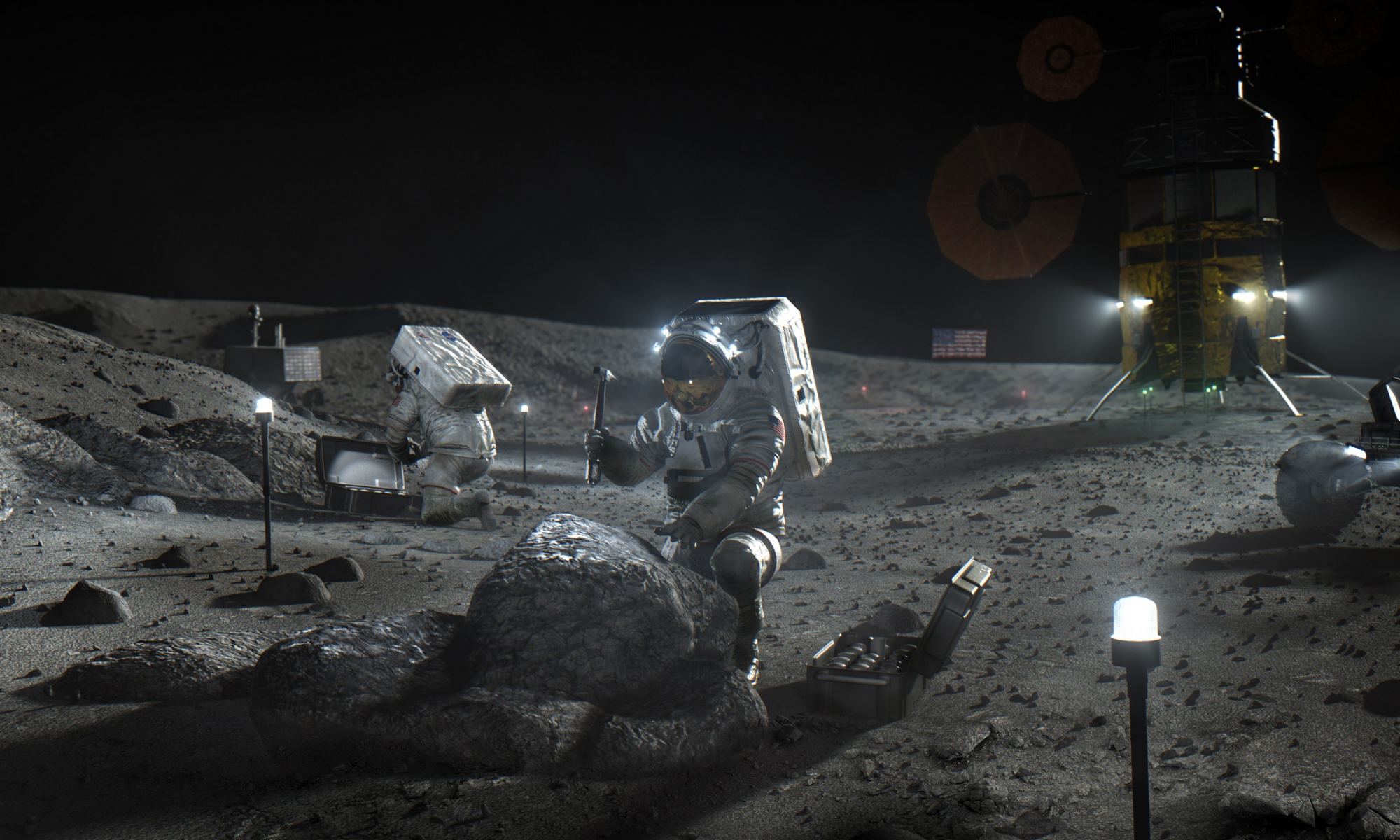
With the closing of the Apollo Era, the priorities of the world’s space agencies began to shift. Having spent the past two decades racing to send astronauts to orbit and to the Moon, the focus now changed towards developing the technologies needed to stay there. A new era of international cooperation, space stations, and partnerships between space agencies and the commercial industry is what followed.
In the near future, things are expected to become even more interesting, with plans for the commercialization of Low Earth Orbit (LEO), the mining of Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs), and the establishment of a permanent human presence on the Moon. Beyond the logistical and technical challenges this poses, there’s been no shortage of concern about the legal issues and implications this will raise as well.
To this end, a group of legal scholars and space experts recently came together to form the Space Court Foundation (SCF), a non-profit educational organization created to foster a conversation about these and other related space issues. By beginning the conversation now, they hope, the public will be able to play an active role in the burgeoning and evolving domain known as “space law.”
Continue reading “The Space Court Foundation is Now in Session!”SpaceX Calls In The Lawyers For 2018 Mars Shot
A manned mission to Mars is a hot topic in space, and has been for a long time. Most of the talk around it has centred on the required technology, astronaut durability, and the overall feasibility of the mission. But now, some of the talk is focussing on the legal framework behind such a mission.
In April 2016, SpaceX announced their plans for a 2018 mission to Mars. Though astronauts will not be part of the mission, several key technologies will be demonstrated. SpaceX’s Dragon capsule will make the trip to Mars, and will conduct a powered, soft landing on the surface of the red planet. The capsule itself will be launched by another new piece of technology, SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket.
It’s a fascinating development in space exploration; a private space company, in cooperation with NASA, making the trip to Mars with all of its own in-house technology. But above and beyond all of the technological challenges, there is the challenge of making the whole endeavour legal.
Though it’s not widely known or talked about, there are legal implications to launching things into space. In the US, each and every launch by a private company has to have clearance from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
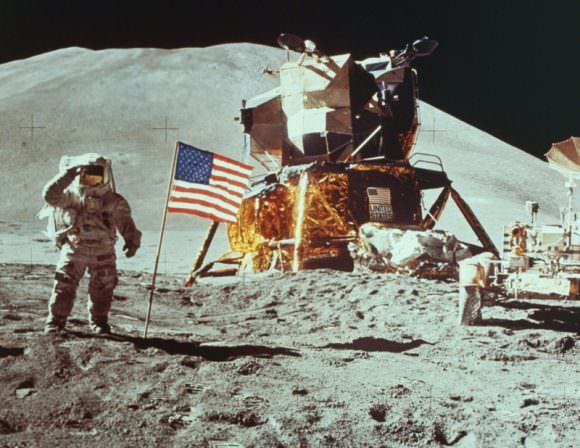
That’s because the US signed the Outer Space Treaty in 1969, a treaty that sets out the obligations and limitations to activities in space. The FAA has routinely given their ascent to commercial launches, but things may be starting to get a little tricky in space.
The most recent Humans To Mars Summit, a conference focussed on Mars missions and explorations, just wrapped up on May 19th. At that conference, George Nield, associate administrator for commercial space transportation at the FAA, addressed the issue. “That’ll be an FAA licensed launch as well,” said Nield of the SpaceX mission to Mars. “We’re already working with SpaceX on that mission,” he added. “There are some interesting policy questions that have to do with the Outer Space Treaty,” said Nield.
The Outer Space Treaty was signed in 1967, and has some sway over space exploration and colonization. Though it gives wide latitude to governments that are exploring space, how it will affect commercial activity like resource exploitation, and installations like settlements in other planets, is not so clear.

According to Nield, the FAA is interested in Article VI of the treaty and how it might impact SpaceX’s planned mission to Mars. Article VI states that all signees to the treaty “shall bear international responsibility for national activities in outer space, including the Moon and other celestial bodies, whether such activities are carried on by governmental agencies or by non-governmental entities.”
Article VI also says, “the activities of non-governmental entities in outer space, including the Moon and other celestial bodies, shall require authorization and continuing supervision by the appropriate State Party to the Treaty.”
What this language means is that the US government itself will bear responsibility for the SpaceX Mars mission. Obviously, this kind of treaty obligation is important. There isn’t exactly a huge list of private companies exploring space, but that will change as the years pass. It seems likely that the bulk of commercial space exploration and resource utilization will be centred in the US, so how the US deals with their treaty obligations will be of immense interest now and in the future.
The treaty itself is mostly focused on avoiding military activity in space. It prohibits things like weapons of mass destruction in space, and weapons testing or military bases on the Moon or other celestial bodies. The treaty also states that the Moon and other planets and bodies cannot be claimed by any nation, and that these and other bodies “are the common heritage of mankind.” Good to know.
Taken as a whole, it’s easy to see why the Treaty is important. Space can’t become a free-for-all like Earth has been in the past. There has to be some kind of framework. “A government needs to oversee these non-governmental activities,” according to Nield.
There’s another aspect to all of this. Governments routinely sign treaties, and then try to figure out ways around them, while hoping their rivals won’t do the same. It’s a sneaky, tactical business, because governments can’t grossly ignore treaties, else the other co-signatories abandon said treaty completely. A case in point is last year’s law, signed by the US Congress, which makes it legal for companies to mine asteroids. This law could be interpreted as violating the Treaty.

Governments can claim, for instance, that their activities are scientific rather than military. Geo-political influence depends greatly on projecting power. If one nation can project power into space, while claiming their activities are scientific rather than military, they will gain an edge over their rivals. Countries also seek to bend the rules of a treaty to satisfy their own interests, while preventing other countries from doing the same. Just look at history.
We’re not in that type of territory yet. So far, no nation has had an opportunity to really violate the treaty, though the asteroid mining law passed by the US Congress comes close.
The SpaceX mission to Mars is a very important one, in terms of how the Outer Space Treaty will be tested and adhered to. More and more countries, and private companies, are becoming space-farers. The legality of increasingly complex missions in space, and the eventual human presence on the Moon and Mars, is a fascinating one not usually addressed by the space science community.
We in the space science community are primarily interested in technological advances, and in the frontiers of human knowledge. It might be time for us to start paying attention to the legal side of things. Space exploration could turn out to have an element of courtroom drama to it.