[/caption]
Make or break time for NASA’s big bet on commercial space transportation is at last in view. NASA has announced Feb. 7, 2012 as the launch target date for the first attempt by SpaceX to dock the firms Dragon cargo resupply spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS), pending final safety reviews.
The Feb. 7 flight will be the second of the so-called Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) demonstration flights to be conducted by Space Exploration Technologies, or SpaceX, under a contact with NASA.
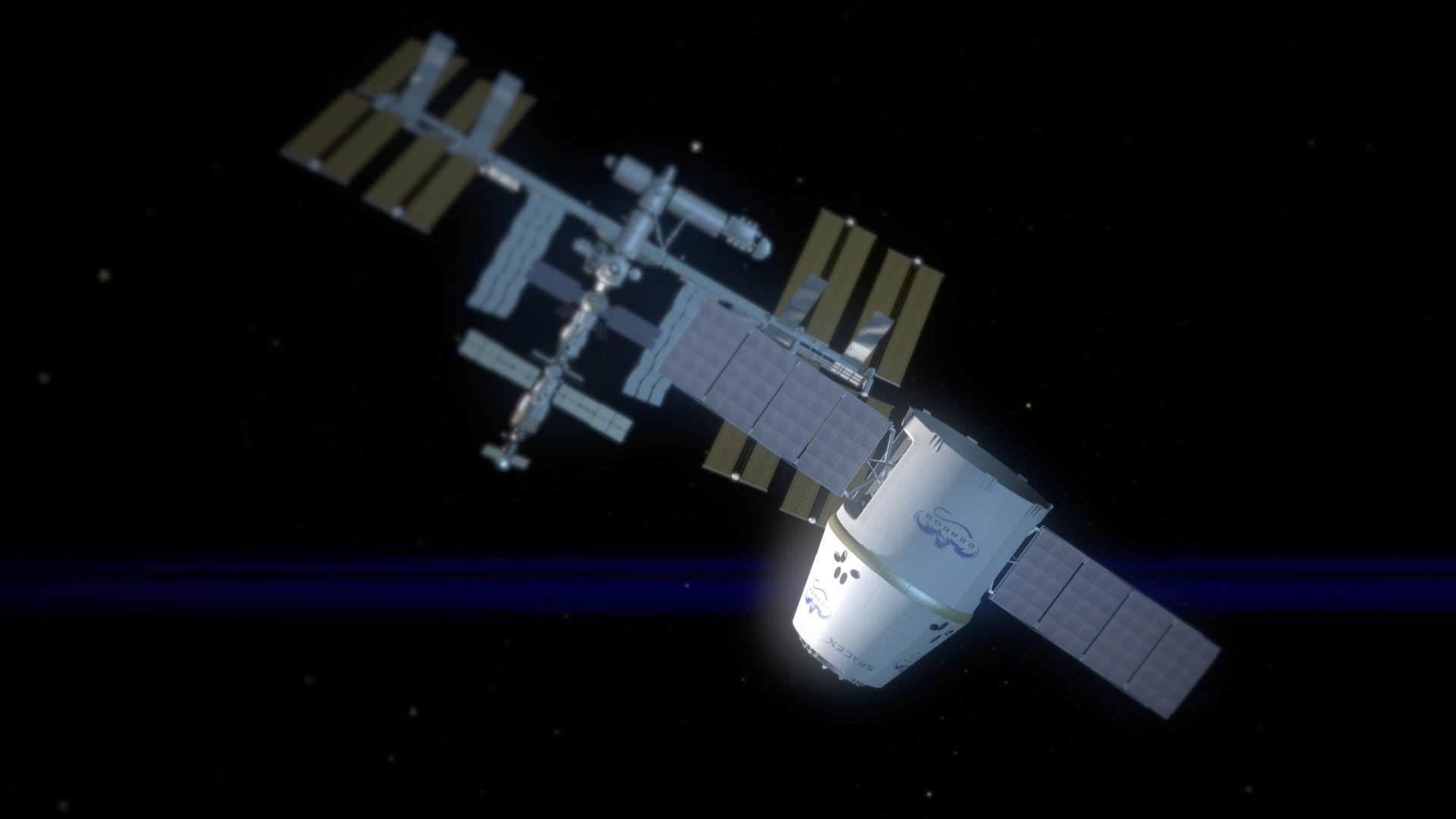
Several months ago SpaceX had requested that the objectives of the next two COTS flights, known as COTS 2 and COTS 3, be merged into one very ambitious flight and allow the Dragon vehicle to actually dock at the ISS instead of only accomplishing a rendezvous test on the next flight and waiting until the third COTS flight to carry out the final docking attempt.
The Dragon will remain attached to the ISS for about one week and astronauts will unload the cargo. Then the spacecraft will depart, re-enter the Earth atmosphere splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California.
“The cargo is hundreds of pounds of astronaut provisions,” SpaceX spokeswoman Kirstin Grantham told Universe Today.

Astronauts can reach it with the robotic arm and berth it at the Earth facing port of the Harmony node. Illustration: NASA /SpaceX
“SpaceX has made incredible progress over the last several months preparing Dragon for its mission to the space station,” said William Gerstenmaier, NASA’s associate administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. “We look forward to a successful mission, which will open up a new era in commercial cargo delivery for this international orbiting laboratory.”
Since the forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle following the final fight with orbiter Atlantis in July 2011 on the STS-135 mission, the US has had absolutely zero capability to launch either supplies or human crews to the massive orbiting complex, which is composed primarily of US components.
In a NASA statement, Gerstenmaier added, “There is still a significant amount of critical work to be completed before launch, but the teams have a sound plan to complete it and are prepared for unexpected challenges. As with all launches, we will adjust the launch date as needed to gain sufficient understanding of test and analysis results to ensure safety and mission success.”
SpaceX lofted the COTS 1 flight a year ago on Dec. 8, 2010 and became the first private company to successfully launch and return a spacecraft from Earth orbit. SpaceX assembled both the Falcon 9 booster rocket and the Dragon cargo vessel from US built components.

The new demonstration flight is now dubbed COTS 2/3. The objectives include Dragon safely demonstrating all COTS 2 operations in the vicinity of the ISS by conducting check out procedures and a series of rendezvous operations at a distance of approximately two miles and the ability to abort if necessary.
The European ATV and Japanese HTV cargo vessels carried out a similar series of tests during their respective first flights.
After accomplishing all the rendezvous tasks, Dragon will then receive approval to begin the COTS 3 activities, gradually approaching the ISS from below to within a few meters.
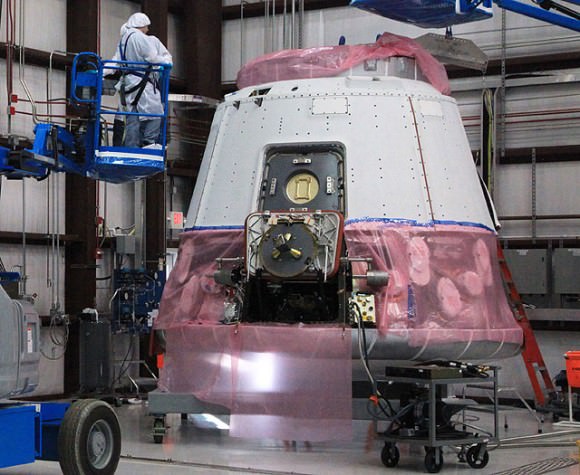
Specially trained astronauts working in the Cupola will then reach out and grapple Dragon with the Station’s robotic arm and then maneuver it carefully into place onto the Earth-facing side of the Harmony node. The operations are expected to take several hours.

If successful, the Feb. 7 SpaceX demonstration flight will become the first commercial mission to visit the ISS and vindicate the advocates of commercial space transportation who contend that allowing private companies to compete for contracts to provide cargo delivery services to the ISS will result in dramatically reduced costs and risks and increased efficiencies.
The new commercial paradigm would also thereby allow NASA to focus more of its scarce funds on research activities to come up with the next breakthroughs enabling bolder missions to deep space.
If the flight fails, then the future of the ISS could be in serious jeopardy in the medium to long term because there would not be sufficient alternative launch cargo capacity to maintain the research and living requirements for a full crew complement of six residents aboard the orbiting laboratory.
Feb. 7 represents nothing less than ‘High Stakes on the High Frontier’.
NASA is all about bold objectives in space exploration in both the manned and robotic arenas – and that’s perfectly represented by the agencies huge gamble with the commercial cargo and commercial crew initiatives.