[/caption]
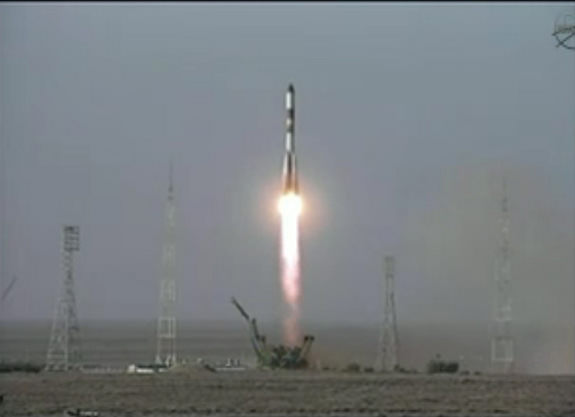
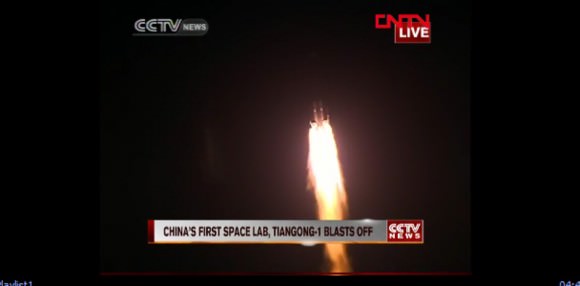
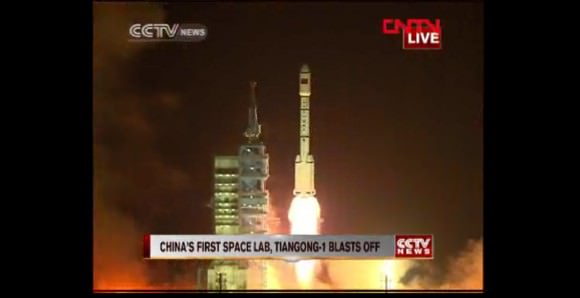
China launched their first space station module into orbit today (Sept. 29), marking a major milestone in the rapidly expanding Chinese space program. The historic liftoff of the man rated Tiangong 1 (Heavenly Palace 1) space lab on a Long March 2F rocket took place at 9:16 p.m. local time (9:16 a.m. EDT) from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center located in Gansu province in northwest China and is an impressive advance for China.
The beautiful nighttime liftoff occurred exactly on time and was carried live on China’s state run television – CCTV – and on the internet for all to see. Chinese President Hu Jintao and many of China’s other top government leaders witnessed the launch from the Beijing Aerospace Control Center as a gesture of confidence and support. Their presence was a clear sign of just how important China’s top leadership considers investments in research as a major driver of technological innovation that is bolstering China’s vigorously growing economy and employing tens of thousands of people.
The US – in sharp contrast – is cutting space spending and handing out pink slips to many thousands of shuttle workers, CCTV noted.
As a CCTV commentator said after the successful Tiangong 1 launch, “30 Years ago it was ‘science fiction’ to imagine a Chinese astronaut in space. Today it’s a reality!”
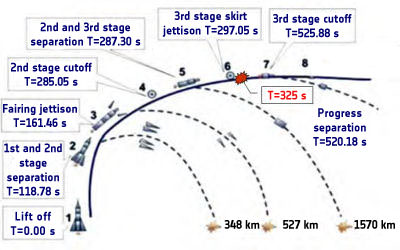
Long range cameras tracked rocket for several minutes and clearly showed the jettisoning of the first stage boosters and the payload fairing.
“The launch of Tiangong 1 has been successfully completed,” announced Gen. Chang Wanquan, chief commander of China’s manned space engineering project on CCTV

Tiangiong 1 will serve a crucial role as a docking target to carry out China’s first rendezvous and docking in space- initially with an unmanned vehicle and thereafter with astronauts crews. The US and the Soviet Union mastered these technologies back in the 1960’s, and China is rapidly catching up now.
Rendezvous and docking are key accomplishments that China must achieve in order to move forward and accomplish even more ambitious space goals – construction of a 60 ton space station by the year 2020.
The two stage Long March 2F rocket was upgraded with more than 170 improvements including a larger payload fairing to house bigger Tiangong 1 module, four longer liquid fueled strap on boosters with more powerful thrust capability and more precise guidance systems.
The 8.5 ton Tiangong 1 was designed to stay in space for at least 2 years and support crews of up to three astronauts for short duration stays. It will be the target of at least three upcoming space missions – Shenzhou 8, 9 and 10.
Shenzhou is China’s human spaceflight capsule, derived from the Russian Soyuz and also significantly upgraded with China’s own nationally developed technology.
The unmanned Shenzhou 8 will launch in about 1 month according to officials from the China Manned Space Engineering Office and reach the vicinity of Tiangong 1 after 2 days. Shenzhou 8 will conduct at least two practice test dockings to extensively check out all systems and experience.
Shenzhou 9 and 10 will dock during 2012 and are likely to include the first female Chinese astronaut.
Tiangong 1 is a prototype miniture space station module, not fully outfitted for long duration stays of astronauts. The space lab consists of two segments – a forward habitable, pressurized section for the astronauts (measuring some 530 cubic feet in volume) and an unpressurized resource compartment in the rear with two solar arrays consisting of four segments to provide ample power.
Read Ken’s related feature about Tiangong 1
China set to ‘Leap Forward in Space’ as Tiangong 1 Rolls to Launch Pad