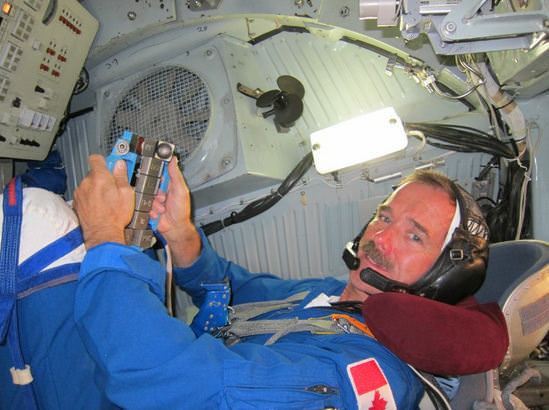
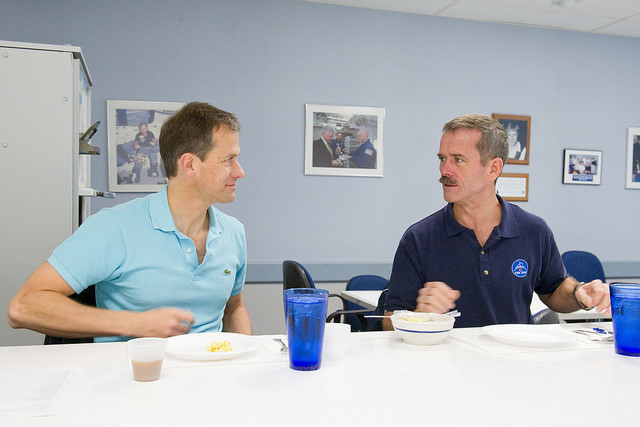
Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield (right)and NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn participate in a food tasting session in the Habitability and Environmental Factors Office at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
Food is important for everyone, for reasons beyond dietary and health issues, as sometimes just the right meal can make (or break) your day. That’s just one of the reasons why the space agencies involved with the International Space Station put a lot of work into creating a variety of foods for the astronauts and cosmonauts that are on long duration missions in space. And variety is key.
“On Earth, we take for granted that if nothing in your fridge appeals to you, you just go out,” Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield told Universe Today. “But on a long-duration mission in space, you can’t just order a pizza or go out for a burger or Baskin Robbins.”
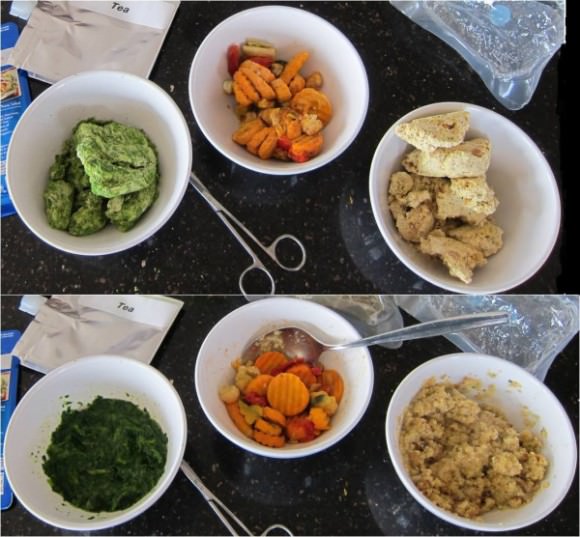

“Space Vegetables, before and after. Tastes better than it looks,” Hadfield Tweeted.
The primary food on the ISS is supplied by NASA and the Russian Space Agency. Each of the other space agencies provide supplemental food, or special items, too.
“Space food is fine, pretty tasty, and of good variety,” Hadfield said. “It’s limited to food that has a long shelf life, with no refrigeration and no microwave, so it’s a lot like camping food or Army rations. The majority of it is dehydrated, so we add cold or hot water to it, like Ramen noodles or instant soup or powdered drinks. But we have a mixture of Russian and American foods, plus specialty items from Canada, Europe and Japan, so we eat really well.”
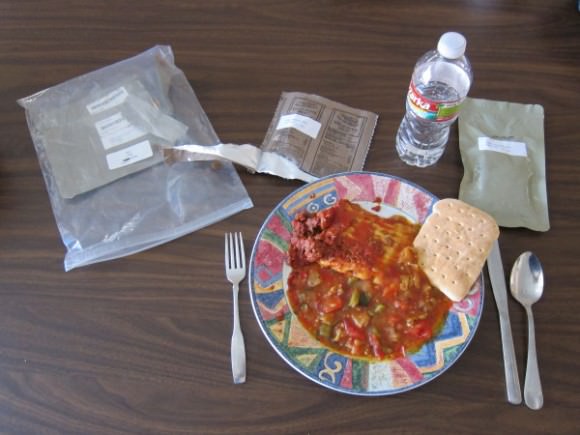

“Astronaut Diet – on 4-day prescribed meals of low sodium to test how my body reacts. This is lunch,” said Hadfield.
Crews eat three meals a day, with two snacks.
Hadfield explained the way it normally works is that NASA and Roscosmos each have a menu of hundreds of potential food items.
“So, some days when it is lunch time, our dieticians and food preparation kitchen have us over for a food tasting, and we try a mouthful of about thirty different things for lunch one day,” Hadfield said. “We rank them from 1 to 9, with 9 being ‘I could eat this for every meal for the rest of my life,’ and 0 being ‘this makes me gag.’ We do that in Houston for all the NASA food and in Russia for all the Russian food, and limited tastings for all the food that comes from the other partners.”
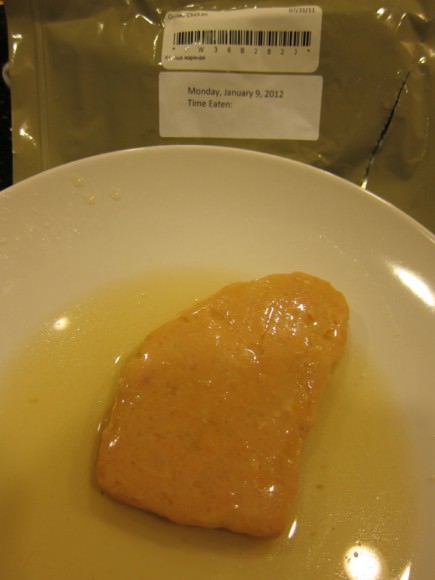

Space-grilled chicken. Via Chris Hadfield.
From there, the astronauts put together a list of the food they would like to have in orbit, in addition to the ‘generic’ or staple foods that are always on board. “The food that all the astronauts on average have rated the highest, they try to keep in stock on the ISS,” Hadfield said. “We also have bonus containers that are personal, where you have food that you ranked as ‘9,’ or you can bring in supplemental food from your country – in my case, Canada– so I can enjoy it and also share it with the other crew on special occasions or holidays that you’ll be on orbit for.”
Hadfield launches this week, on Dec. 19, and so will be on orbit for the Christmas and New Year’s holidays.
During Hadfield’s Expedition 34/35, the Canadian specialty food includes candied wild smoked salmon, smoked salmon pate, cranberry buffalo stix, cereal, dried apple chunks, fruit bars, green tea cookies with orange zest, maple syrup cookies, organic chocolate, honey drops, chocolate bars and maple syrup.
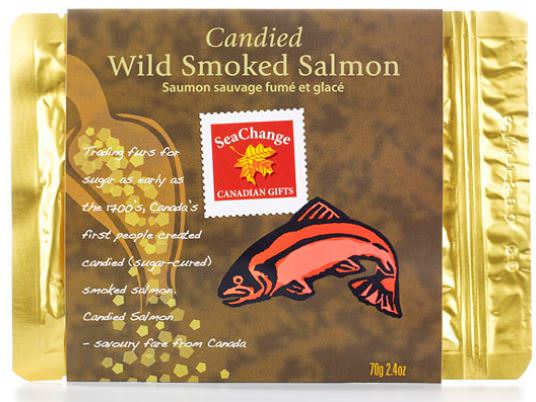

SeaChange Candied Wild Smoked Salmon that will heading to the ISS.
Some of this food was chosen as part of a contest held by the Canadian Space Agency, Canadian Snacks for Space.
The first shipment of the Canadian treats were delivered to the ISS on board the SpaceX Dragon capsule that brought supplies to the space station in October. The second shipment should be sent on an automated resupply spacecraft in February 2012.
Hadfield said the addition of Japanese and Italian modules on the ISS has also resulted in tasty international food being part of the regular ISS rations.

“Italian space food – scallopine, lasagne and freeze-dried pea and carrot blocks. Their tiramisu is delicious!” said Hadfield via Twitter.
Hadfield said the dieticians are interested in the balance of salt content, protein and carbohydrates as they want to keep the astronauts healthy, and to have them maintain their weight. But they also need to have food that is appealing. A well-known problem is that astronaut’s taste buds seems to go flat while in space, so spicy food is appreciated even though it might not be a favorite on the ground.
“The food is important, but sometimes things can happen,” said Hadfield, “like one of the resupply ships get delayed and your favorite food isn’t there, and you have to eat the leftovers of the previous crews, or eat a future crew’s food. So it never goes perfectly. So, part of being an astronaut is not being too picky!
Hadfield said they are provided a wide variety of lots of different food, and you can see Hadfield’s potential menu here.
But, like on Earth, mealtime is vital for other reasons, too.
“The food is important, but we also use dinner as a good time to get together and talk, relax, and be human,” Hadfield said.
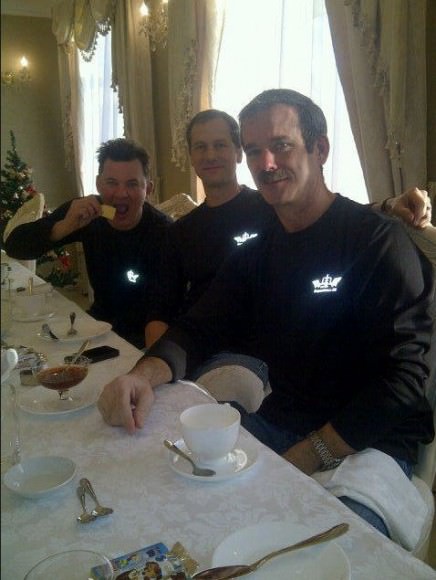

“Crew at Breakfast – with our new Expedition shirts shining. Roman (left) is going to be a hoot to fly with,” Hadfield Tweeted.
As for what Hadfield’s last Earthly meal will be before he launches on Wednesday morning, it won’t be anything big or fancy.
“Imagine what it is going to be like to be in a small, cramped spaceship for two days,” he said. “My last meal will be beef broth.”
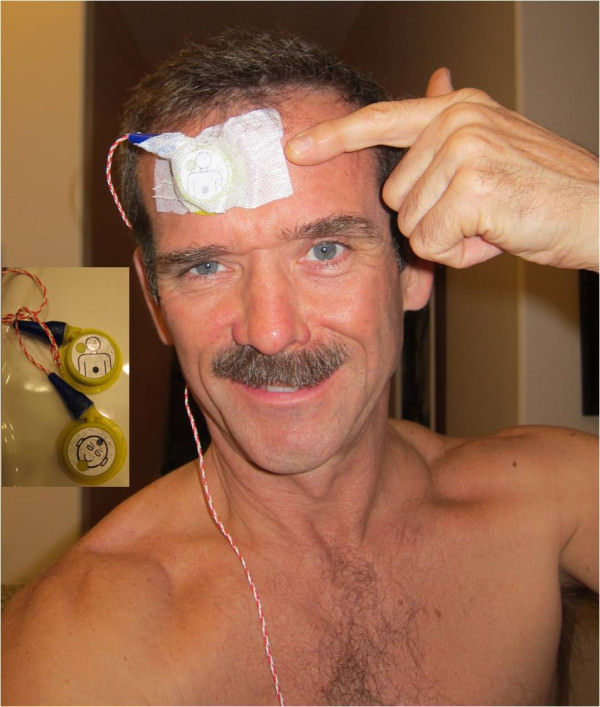
Note what Hadfield has in front of him in the image above, which he shared this morning via Twitter and Facebook.
Previous articles in this series:
How to Train for Long Duration Space Flight with Chris Hadfield
How to Train for a Mission to the ISS: Medical Mayhem