Ever since they were first produced, carbon nanotubes have managed to set off a flurry excitement in the scientific community. With applications ranging from water treatment and electronics, to biomedicine and construction, this should come as no surprise. But a team of NASA engineers from the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, has pioneered the use of carbon nanotubes for yet another purpose – space-based telescopes.
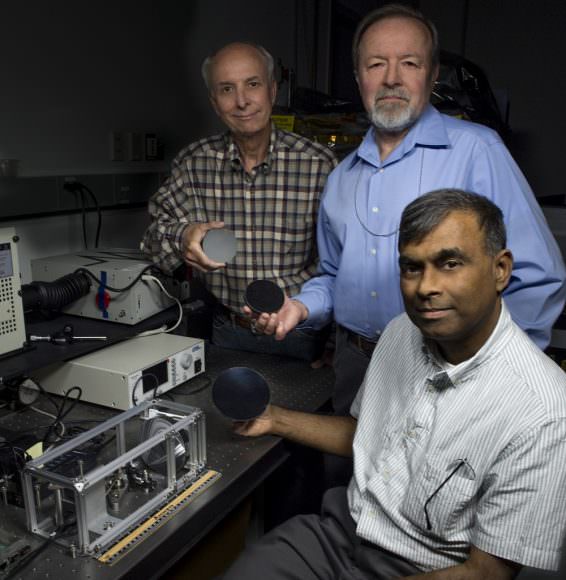
Using carbon nanotubes, the Goddard team – which is led by Dr. Theodor Kostiuk of NASA’s Planetary Systems Laboratory and Solar System Exploration Division – have created a revolutionary new type of telescope mirror. These mirrors will be deployed as part of a CubeSat, one which may represent a new breed of low-cost, highly effective space-based telescopes.
This latest innovation also takes advantage of another field that has seen a lot of development of late. CubeSats, like other small satellites, have been playing an increasingly important role in recent years. Unlike the larger, bulkier satellites of yesteryear, miniature satellites are a low-cost platform for conducting space missions and scientific research.
Beyond federal space agencies like NASA, they also offer private business and research institutions the opportunity to conduct communications, research and observation from space. On top of that, they are also a low-cost way to engage students in all phases of satellite construction, deployment, and space-based research.
Granted, missions that rely on miniature satellites are not likely to generate the same amount of interest or scientific research as large-scale operations like the Juno mission or the New Horizons space probe. But they can provide vital information as part of larger missions, or work in groups to gather greater amounts of data.
With the help of funding from Goddard’s Internal Research and Development program, the team created a laboratory optical bench made of regular off-the-shelf components to test the telescope’s overall design. This bench consists of a series of miniature spectrometers tuned to the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared wavelengths, which are connected to the focused beam of the nanotube mirrors via an optic cable.
Using this bench, the team is testing the optical mirrors, seeing how they stand up to different wavelengths of light. Peter Chen – the president of Lightweight Telescopes a Maryland-based company – is one of the contractors working with the Goddard team to create the CubeSat telescope. As he was quoted as saying by a recent NASA press release:
“No one has been able to make a mirror using a carbon-nanotube resin. This is a unique technology currently available only at Goddard. The technology is too new to fly in space, and first must go through the various levels of technological advancement. But this is what my Goddard colleagues (Kostiuk, Tilak Hewagama, and John Kolasinski) are trying to accomplish through the CubeSat program.
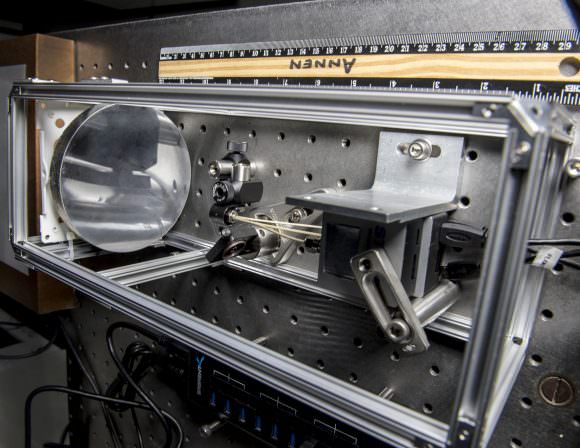

Unlike other mirrors, the one created by Dr. Kostiuk’s team was fabricated out of carbon nanotubes embedded in an epoxy resin. Naturally, carbon nanotubes offer a wide range of advantages, not the least of which are structural strength, unique electrical properties, and efficient conduction of heat. But the Goddard team also chose this material for their lenses because it offers a lightweight, highly stable and easily reproducible option for creating telescope mirrors.
What’s more, mirrors made of carbon-nanotubes do not require polishing, which is a time-consuming and expensive process when it comes to space-based telescopes. The team hopes that this new method will prove useful in creating a new class of low-cost, CubeSat space telescopes, as well as helping to reduce costs when it comes to larger ground-based and space-based telescopes.
Such mirrors would be especially useful in telescopes that use multiple mirror segments (like the Keck Observatory at Mauna Kea and the James Webb Space Telescope). Such mirrors would be a real cost-cutter since they can be easily produced and would eliminate the need for expensive polishing and grinding.
Other potential applications include deep-space communications, improved electronics, and structural materials for spacecraft. Currently, the production of carbon nanotubes is quite limited. But as it becomes more widespread, we can expect this miracle material to be making its way into all aspects of space exploration and research.
Further Reading: NASA








