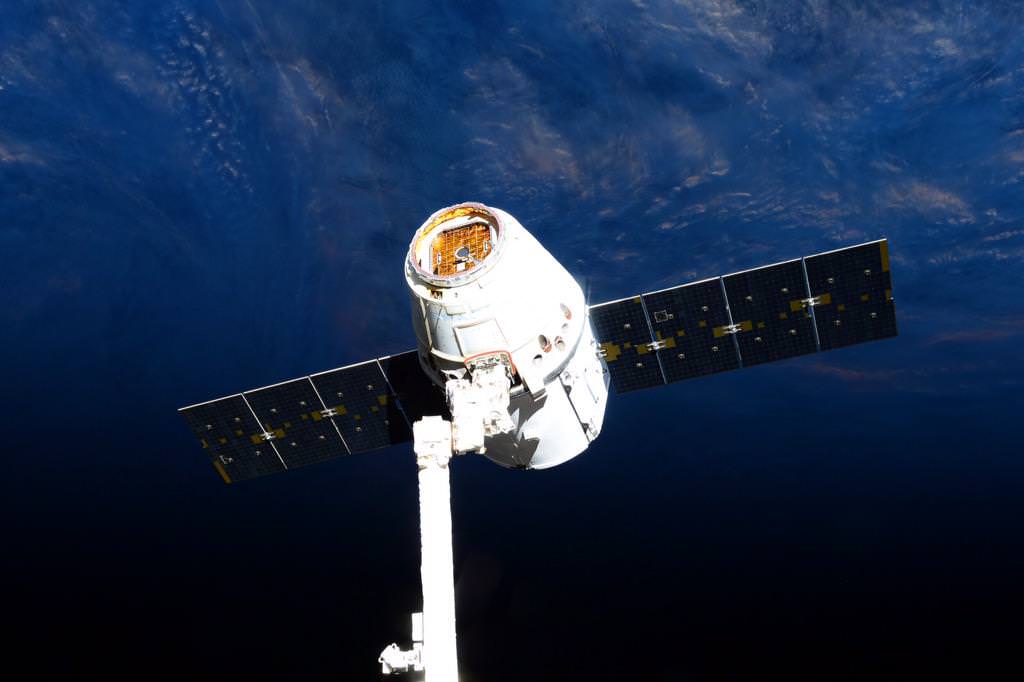
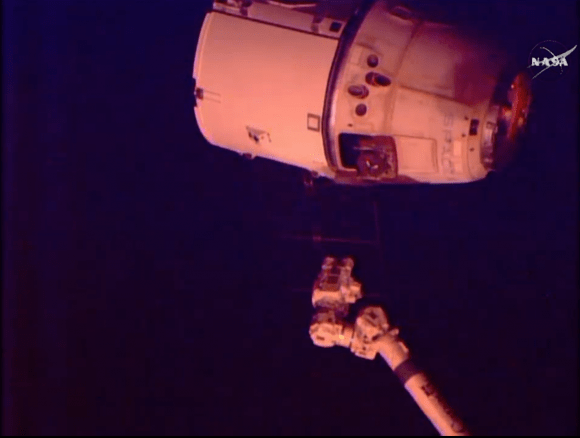
Release of SpaceX-6 Dragon on May 21, 2015 from the International Space Station for Pacific Ocean splashdown later in the day. Credit: NASA/Terry Virts
Story updated with further details and photos[/caption]
SpaceX Dragons seem to be flying nearly everywhere these days, coming and going at a record pace to the delight and relief of NASA, researchers and the space faring crews serving aboard the International Space Station (ISS). As one Dragon returned to Earth from space today, May 21, another Dragon prepares to soar soon to space.
The commercial SpaceX-6 cargo Dragon successfully splashed down in the Pacific Ocean at 12:42 p.m. EDT (1642 GMT) today, Thursday, about 155 miles southwest of Long Beach, California, some five hours after it was released from the grip of the stations robotic arm this morning at 7:04 a.m. EDT by the Expedition 43 crew as the craft were flying some 250 miles (400 km) above Australia.
The ocean splashdown marked the conclusion to the company’s sixth cargo resupply mission to the ISS under a commercial contract with NASA. Overall this was the seventh trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the station since the inaugural flight in 2012.
Following the launch failure and uncontrolled destructive plummet back to Earth of the Russian Progress 59 cargo freighter earlier this month, the station and its six person international crews are more dependent than ever on the SpaceX commercial supply train to orbit to keep it running and humming with productive science.
Working from a robotics work station in the domed cupola, NASA astronaut Scott Kelly released the Dragon CRS-6 spacecraft from the grappling snares of the 57.7-foot-long (17-meter-long) Canadian-built robotic arm with help from fellow NASA astronaut Terry Virts. Kelly is a member of the first 1 Year ISS mission crew, along with Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko.
The capsule then performed an intricate series of three departure burns and maneuvers to move beyond the imaginary 656-foot (200-meter) “keep out sphere” around the station and begin its five and a half hour long trip back to Earth.
The station crew had packed Dragon with almost 3,100 pounds of NASA cargo from the International Space Station. The including research samples pertaining to a host of experiments on how spaceflight and microgravity affect the aging process and bone health as well as no longer need items and trash to reduce station clutter.
“Spaceflight-induced health changes, such as decreases in muscle and bone mass, are a major challenge facing our astronauts,” said Julie Robinson, NASA’s chief scientist for the International Space Station Program Office at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, in a statement.
“We investigate solutions on the station not only to keep astronauts healthy as the agency considers longer space exploration missions but also to help those on Earth who have limited activity as a result of aging or illness.”
The Dragon was retrieved from the ocean by recovery boats following the parachute assisted splashdown. It will be transported to Long Beach, California for removal and return of the NASA cargo. The capsule itself will be shipped to SpaceX’s test facility in McGregor, Texas, for processing to remove cargo and inspection of its performance.

“The returning Space Aging study, for example, examines the effects of spaceflight on the aging of roundworms, widely used as a model for larger organisms,” noted NASA in a statement.
“By growing millimeter-long roundworms on the space station, researchers can observe physiological changes that may affect the rate at which organisms age. This can be applied to changes observed in astronauts, as well, particularly in developing countermeasures before long-duration missions.”
Dragon departed after having spent a record setting stay of 33 days berthed to the station at an Earth facing port on the Harmony node.
Dragon is also the only current US means for sending cargo to the station after the loss of the Orbital Sciences Cygnus craft in the Antares rocket explosion last October.
The SpaceX CRS-6 Dragon successfully blasted off atop a Falcon 9 booster from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on April 14, 2015 at 4:10 p.m. EDT (2010:41 GMT) on the CRS-6 (Commercial Resupply Services-6) mission.
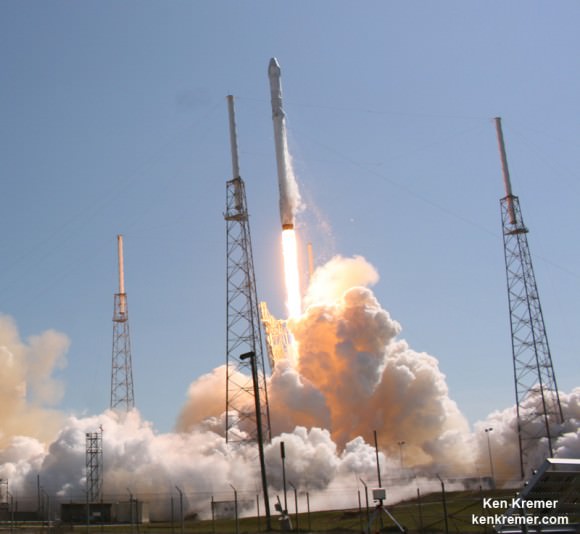

The resupply vessel had arrived three days later on April 17 and was successfully snared by the Expedition 43 Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency, the first female Italian astronaut.
Dragon launched on April 14 with more than 4,300 pounds of supplies, science experiments, and technology demonstrations, including critical materials to support about 40 of more than 250 science and research investigations during the station’s Expeditions 43 and 44.
An Espresso machine was also aboard and delivered to enhance station morale during the daily grind some 250 miles above Earth.
Among the research investigations were a fresh batch of 20 rodents for the Rodent Research Habitat, and experiments on osteoporosis to counteract bone deterioration in microgravity, astronaut vision loss, protein crystal growth, and synthetic muscle for prosthetics and robotics.
CRS-6 marks the company’s sixth operational resupply mission to the ISS under a $1.6 Billion contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg (44,000 pounds) of cargo to the station during a dozen Dragon cargo spacecraft flights through 2016 under NASA’s original Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.
Following the complete success of the SpaceX Dragon CRS-6 mission, NASA just announced that the next SpaceX Dragon is currently slated to launch on June 26 at 11:09 a.m. EDT.
The Dragon will carry critical US equipment enabling docking by the SpaceX Crew Dragon and Boeing CST-100 astronaut transporters.
Read Ken’s earlier onsite coverage of the CRS-6 launch from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
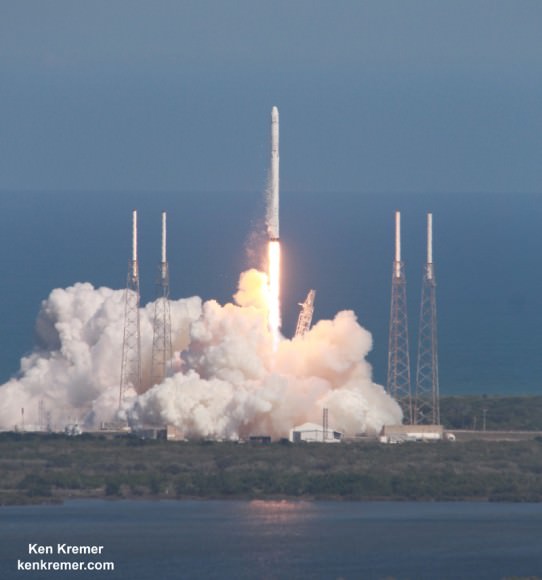

Video caption: SpaceX CRS-6 Falcon 9 Launch to the International Space Station on April 14, 2015. Credit: Alex Polimeni

