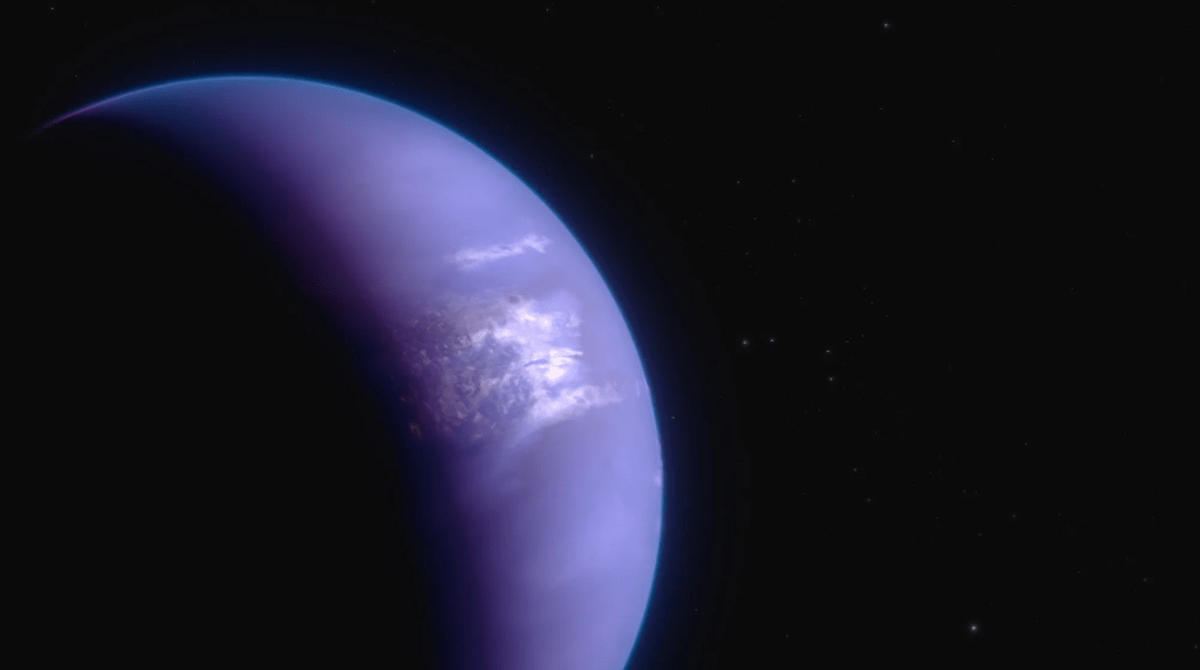
I’ve often stated that planets come in a wide range of sizes but rarely do I find myself stating they come in a wide range of shapes too! The discovery of WASP-107b is a case in point since this planet is the size of Jupiter but only a tenth of its mass. But there’s more… Using the James Webb Space Telescope a team of astronomers have accurately identified that the planet has an east-west asymmetry in its atmosphere, in other words, it’s lopsided. It is tidally locked to the star and on one side, the atmosphere seems to be inflated compared to the other.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find a Strange Lopsided Planet”Astronomers Find a Strange Lopsided Planet