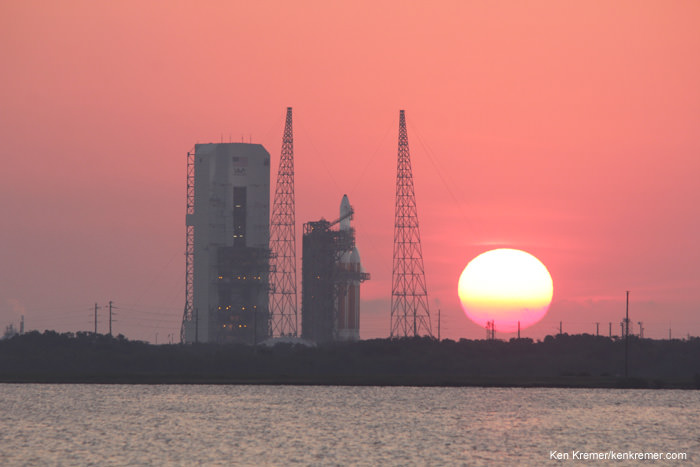
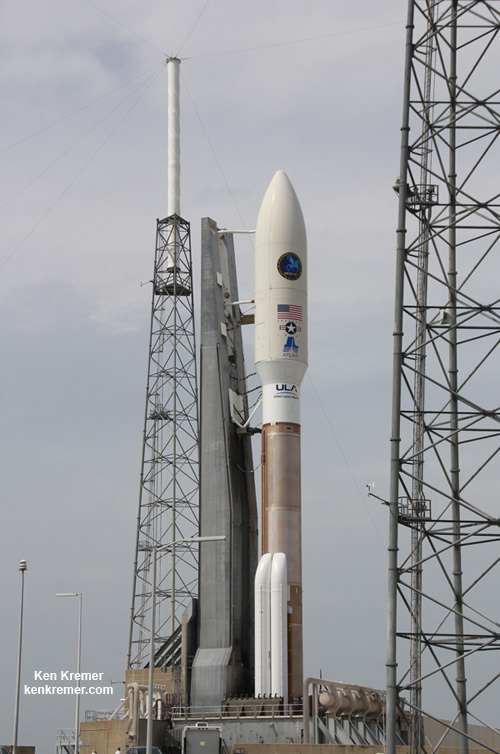
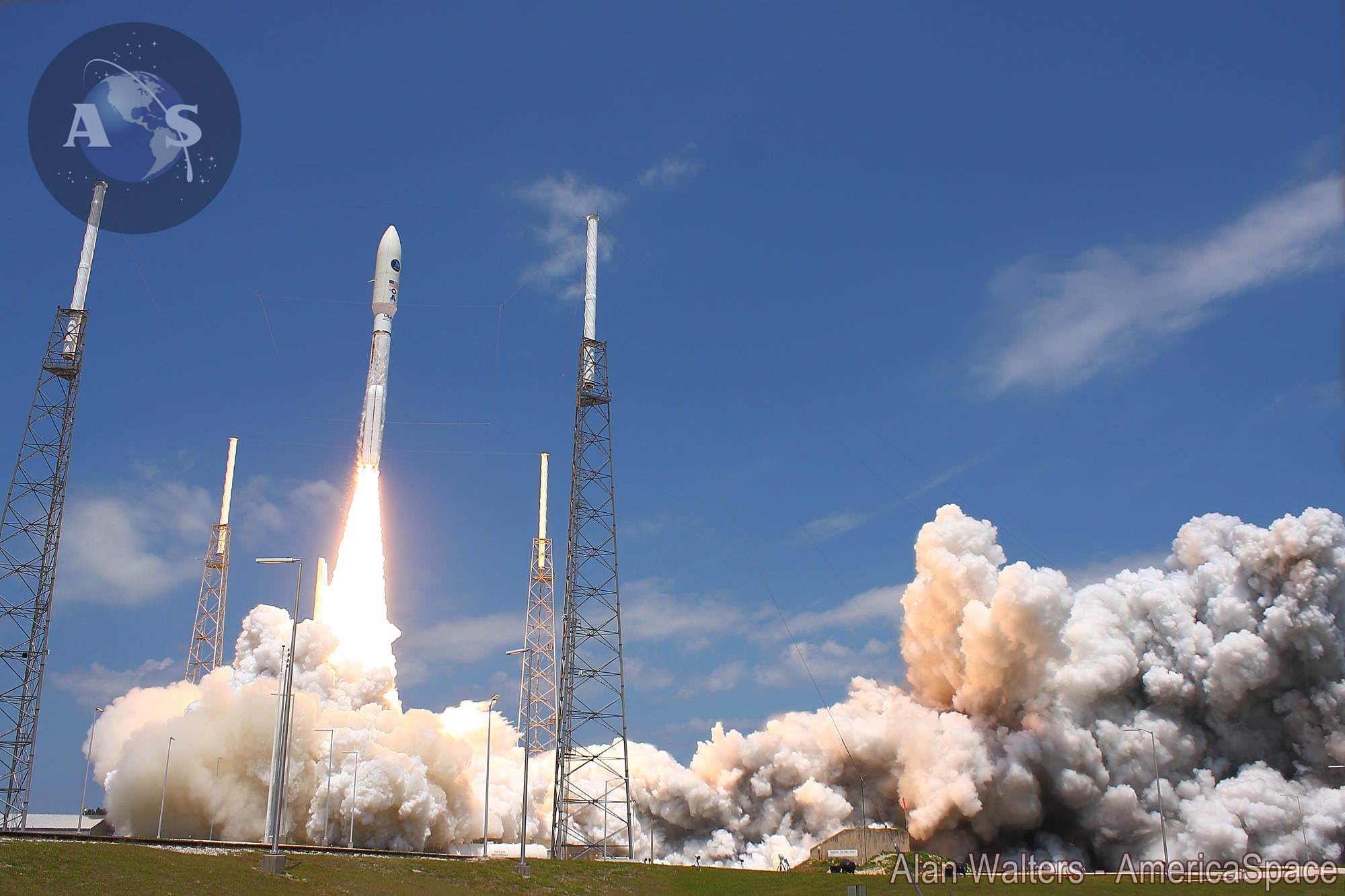
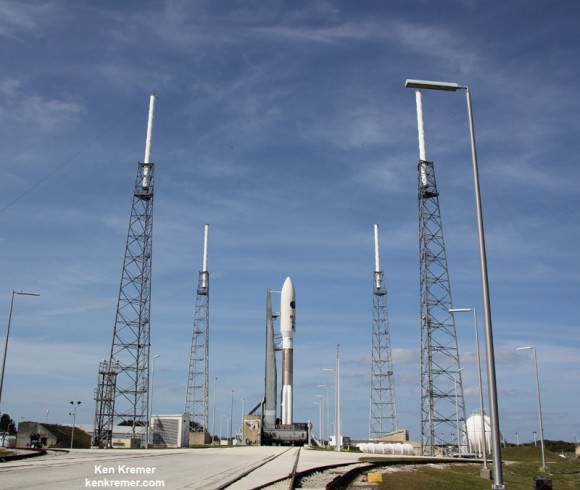
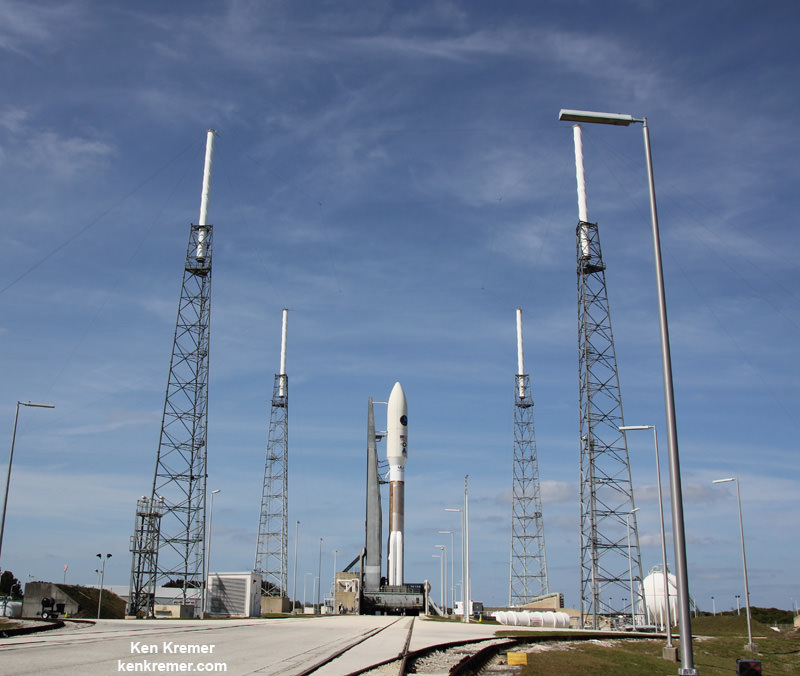
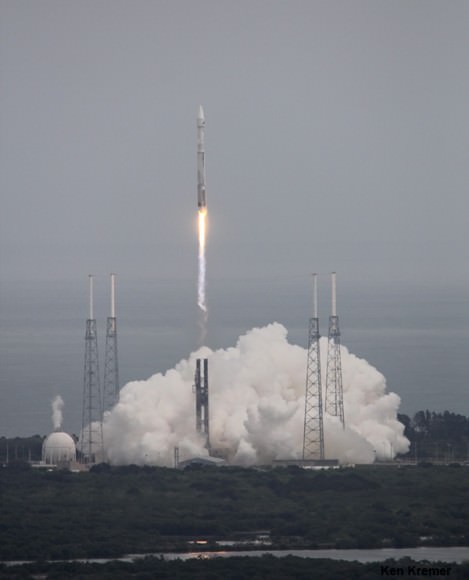
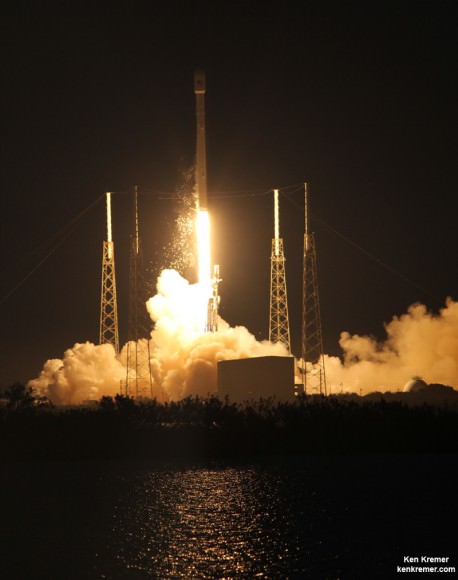
CAPE CANAVERAL, FL — A classified surveillance satellite set to fortify the reconnaissance capabilities of America’s spy masters is now scheduled to launch this Thursday afternoon, June 9, atop America’s most powerful rocket – the Delta 4 Heavy.
Lift off of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta 4 Heavy carrying the classified NROL-37 spy satellite for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) on Thursday, June 9 is slated for 1:59 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 37 (SLC-37) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
This follows a four day delay from June 5 to deal with a last minute and unspecified payload issue.
“Spacecraft, rocket and support systems are ready!” tweeted the NRO.
Although almost everything about the clandestine payload, its mission, purpose and goals are classified top secret, it is certainly vital to America’s national security.
We do know that NROL-37 will be launched for the NRO on an intelligence gathering mission in support of US national defense.
The possible roles for the reconnaissance payload include signals intelligence, eavesdropping, imaging and spectroscopic observations, early missile warnings and much more.
The NRO runs a vast fleet of powerful orbital assets hosting a multitude of the most advanced, wide ranging and top secret capabilities.
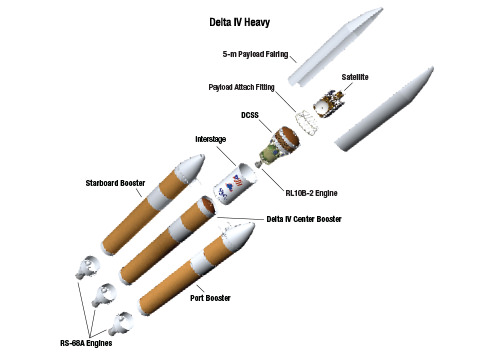
The payload is named NROL-37 and will be carried to an undisclosed orbit, possibly geostationary, by the triple barreled ULA Delta 4 Heavy rocket – currently the largest and most powerful rocket in the world.
It is manufactured and launched by ULA as part of the Delta rocket family. This includes the Delta 4 Medium which can launch with strap on solid rocket boosters. ULA also builds and launches the Atlas V rocket family.
To date nine NRO payloads have flown on Delta 4 rockets. NROL-37 will be the 32nd Delta IV mission since the vehicle’s inaugural launch.
The NRO was formed in response to the Soviet launch of Sputnik and secretly created on September 6, 1961.
“The purpose is overseeing all satellite and overflight reconnaissance projects whether overt or covert. The existence of the organization is no longer classified today, but we’re still pressing to perform the functions necessary to keep American citizens safe,” according to the official NRO website.
Precisely because this is a launch of the mighty triple barreled Delta 4 Heavy, the view all around is sure to be spectacular and is highly recommended – in case you are in the Florida Space Coast area or surrounding regions.
One thing for sure is the top secret payload is huge and weighty since it requires the heaviest of the heavies to blast off.
Watch this ULA video showing the mating of the classified reconnaissance payload to the rocket.
Video Caption: The NROL-37 payload is mated to a Delta IV Heavy rocket inside the Mobile Service Tower or MST at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex-37. Credit: ULA
Another unclassified aspect we know about this flight is that the weather forecast is rather iffy.
The official Air Forces prognosis calls for only a 40% chance of favorable weather conditions.
The primary concerns are for Anvil Clouds, Cumulus Clouds and Lightning.
In case of a scrub for any reason related to technical or weather issues, the next launch opportunity is 48 hours later on Saturday. June 11.
The weather odds rise significantly to an 80% chance of favorable weather conditions on June 11.
Somewhat surprisingly ULA has just announced the launch time – which is planned for 1:59 p.m. EDT (1759 GMT).
And you can even watch a ULA broadcast which starts 20 minutes prior to the given launch time at 1:39 p.m. EDT.
Webcast link: http://bit.ly/div_nrol37

Since this is a national security launch, the exact launch time is actually classified and could easily occur later than 1:59 p.m.
The launch period extends until 6:30 p.m. EDT (2230 GMT). The actual launch window is also classified and somewhere within the launch period.
Seeing a Delta 4 Heavy soar to space is a rare treat since they launch infrequently.
The last of these to launch from the Cape was for NASA’s inaugural test flight of the Orion crew capsule on the EFT-1 launch in Dec. 5, 2014. No other rocket was powerful enough.
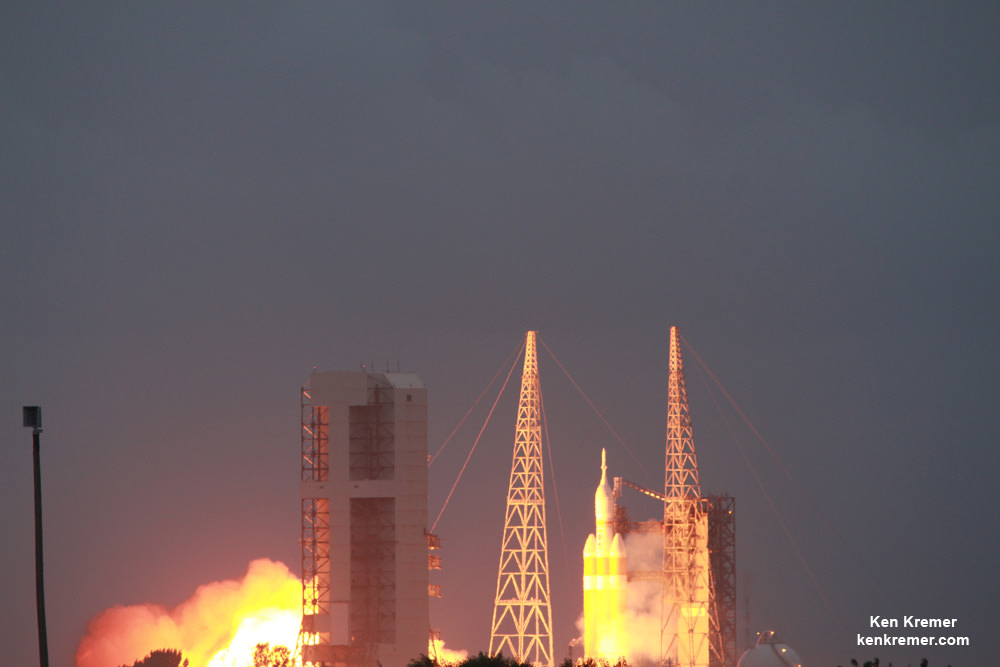

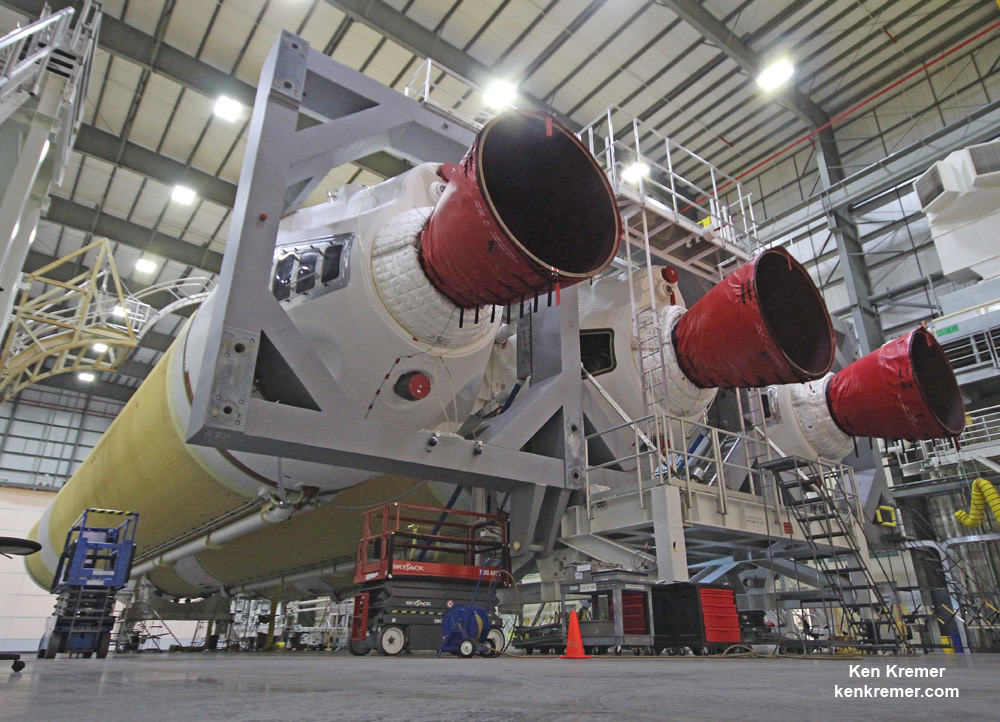
The Delta IV Heavy employs three Common Core Boosters (CBCs). Two serve as strap-on liquid rocket boosters (LRBs) to augment the first-stage CBC and 5-m-diameter payload fairing housing the payload.

Watch for Ken’s continuing on site reports direct from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and the SpaceX launch pad.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about ULA Atlas and Delta rockets, SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Orbital ATK Cygnus, ISS, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
June 8/9: “SpaceX, ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings