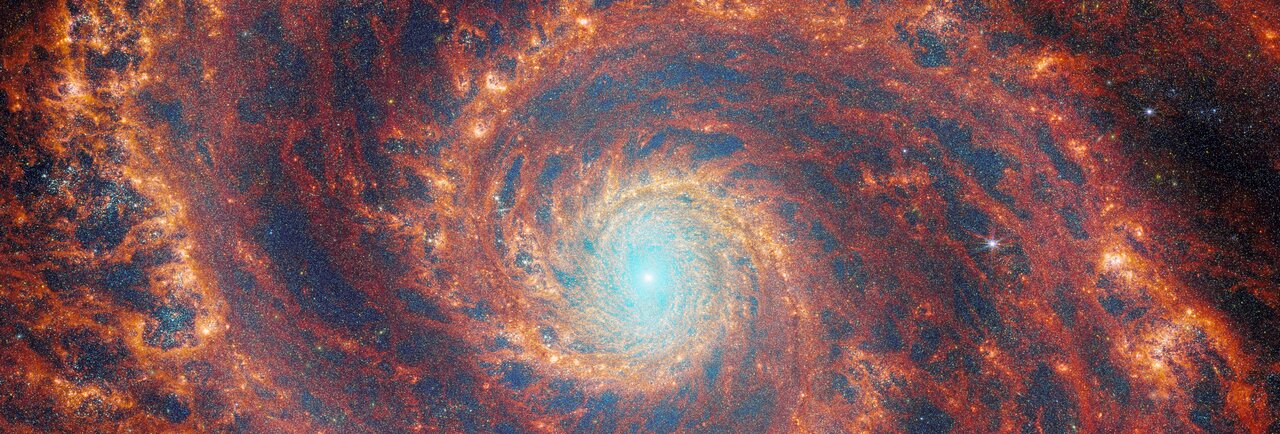
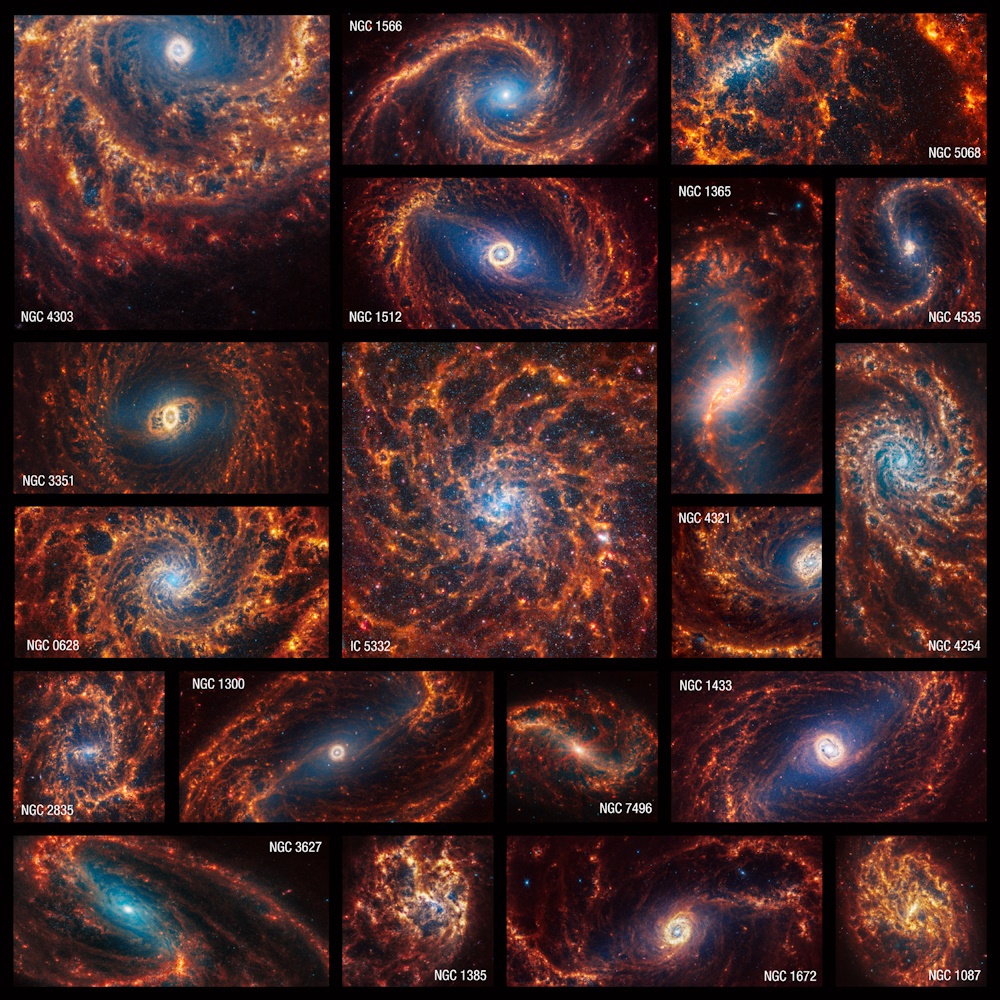
As a species, we’ve come to the awareness that we’re a minuscule part of a vast Universe defined by galaxy superclusters and the large-scale structure of the Universe. Driven by a healthy intellectual curiosity, we’re examining our surroundings and facing the question posed by Nature: how did everything get this way?
We only have incremental answers to that huge, almost infinitely-faceted question. And the incremental answers are unearthed by our better instruments, including space telescopes, which get better and more capable as time passes.
Enter the James Webb Space Telescope.
Continue reading “Webb Sees a Supercluster of Galaxies Coming Together”