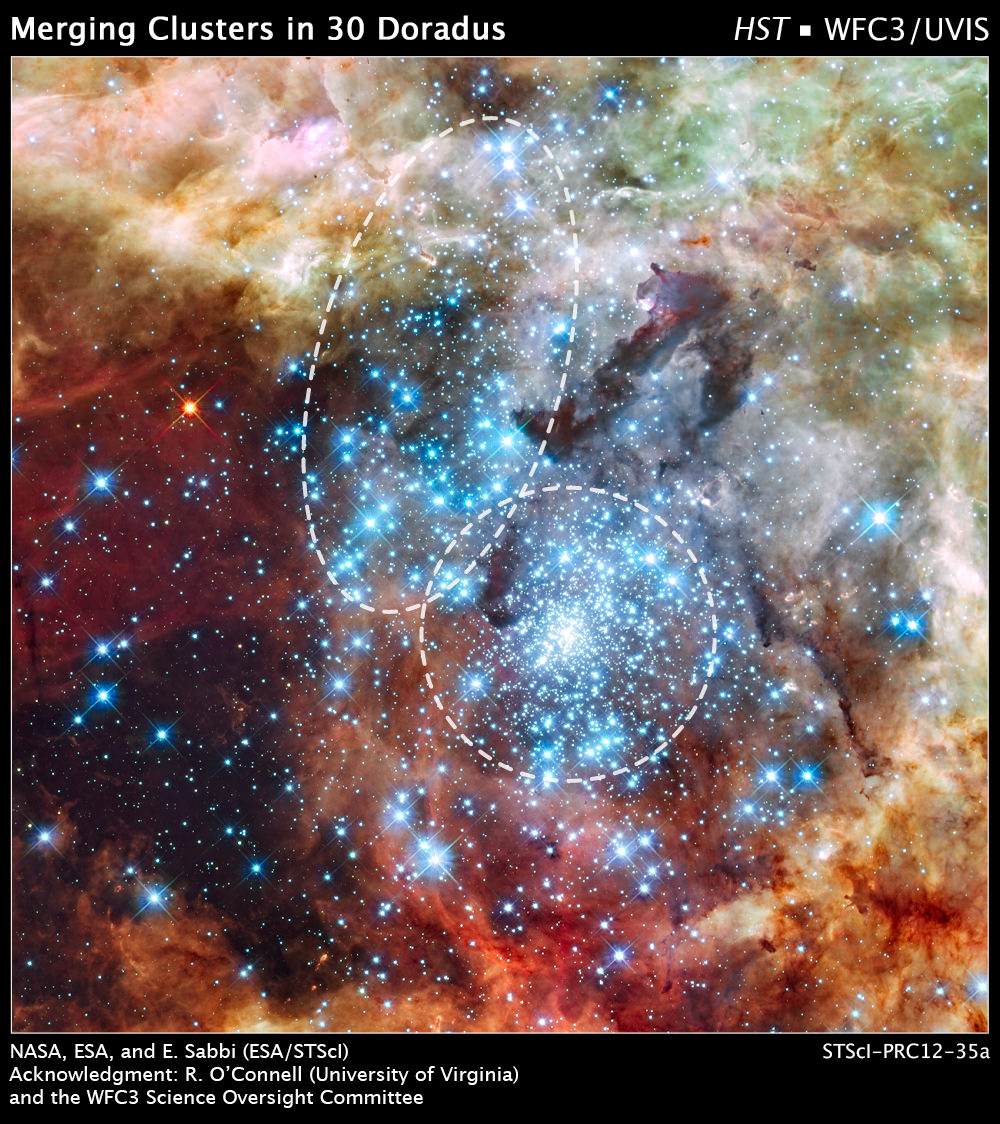
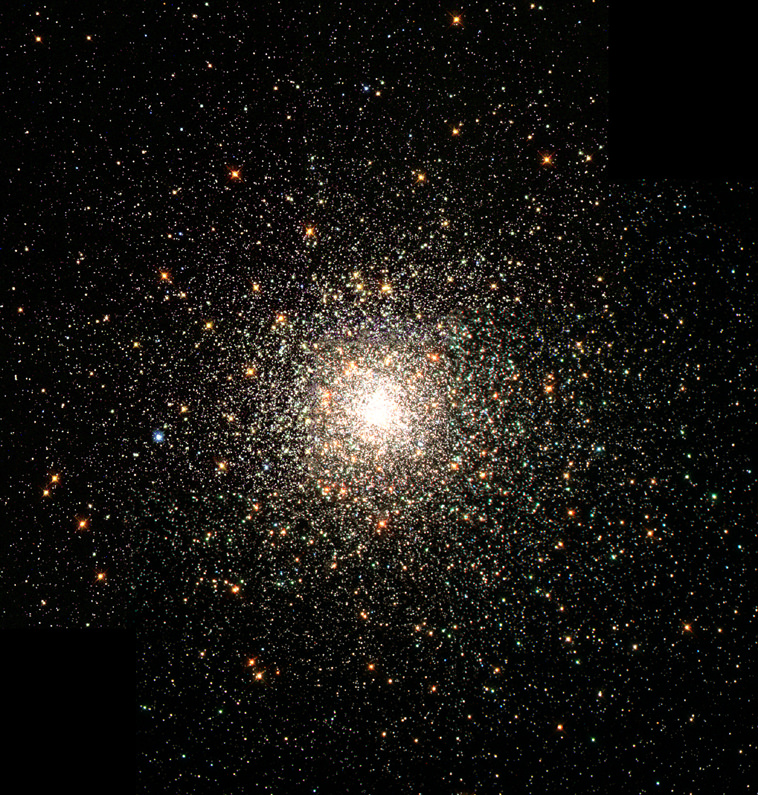
Astronomers originally thought that just one massive star cluster shone brightly in a huge star forming region of the Tarantula Nebula, also known as 30 Doradus. But closer analysis using data from the Hubble Space Telescope shows that it is actually two different clusters that are just starting to collide and merge. A team of astronomers led by Elena Sabbi of the Space Telescope Science Institute noticed that different stars in the same region were of different ages, by at least one million years. Besides the age differences, the scientists also noticed two distinct regions, with one having the elongated “look” of a merging cluster.
“Stars are supposed to form in clusters,” said Sabbi, “but there are many young stars outside 30 Doradus that could not have formed where they are; they may have been ejected at very high velocity from 30 Doradus itself.”
Sabbi and her team were initially looking for runaway stars — fast-moving stars that have been kicked out of their stellar nurseries where they first formed.
But they noticed something unusual about the cluster when looking at the distribution of the low-mass stars detected by Hubble. It is not spherical, as was expected, but has features somewhat similar to the shape of two merging galaxies where their shapes are elongated by the tidal pull of gravity.
Some models predict that giant gas clouds out of which star clusters form may fragment into smaller pieces. Once these small pieces precipitate stars, they might then interact and merge to become a bigger system. This interaction is what Sabbi and her team think they are observing in 30 Doradus.
There are also an unusually large number of runaway, high-velocity stars around 30 Doradus, and after looking more closely at the clusters, the astronomers believe that these runaway stars were expelled from the core of 30 Doradus as the result of the dynamical interactions between the two star clusters. These interactions are very common during a process called core collapse, in which more-massive stars sink to the center of a cluster by dynamical interactions with lower-mass stars. When many massive stars have reached the core, the core becomes unstable and these massive stars start ejecting each other from the cluster.
The big cluster R136 in the center of the 30 Doradus region is too young to have already experienced a core collapse. However, since in smaller systems the core collapse is much faster, the large number of runaway stars that has been found in the 30 Doradus region can be better explained if a small cluster has merged into R136.
The entire 30 Doradus complex has been an active star-forming region for 25 million years, and it is currently unknown how much longer this region can continue creating new stars. Smaller systems that merge into larger ones could help to explain the origin of some of the largest known star clusters, Sabbi and her team said.
Follow-up studies will look at the area in more detail and on a larger scale to see if any more clusters might be interacting with the ones observed. In particular the infrared sensitivity of NASA’s planned James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will allow astronomers to look deep into the regions of the Tarantula Nebula that are obscured in visible-light photographs. In these areas cooler and dimmer stars are hidden from view inside cocoons of dust. Webb will better reveal the underlying population of stars in the nebula.
The 30 Doradus Nebula is particularly interesting to astronomers because it is a good example of how star-forming regions in the young universe may have looked. This discovery could help scientists understand the details of cluster formation and how stars formed in the early Universe.
Science Paper by: E. Sabbi, et al. (ApJL, 2012) (PDF document)
Source: HubbleSite