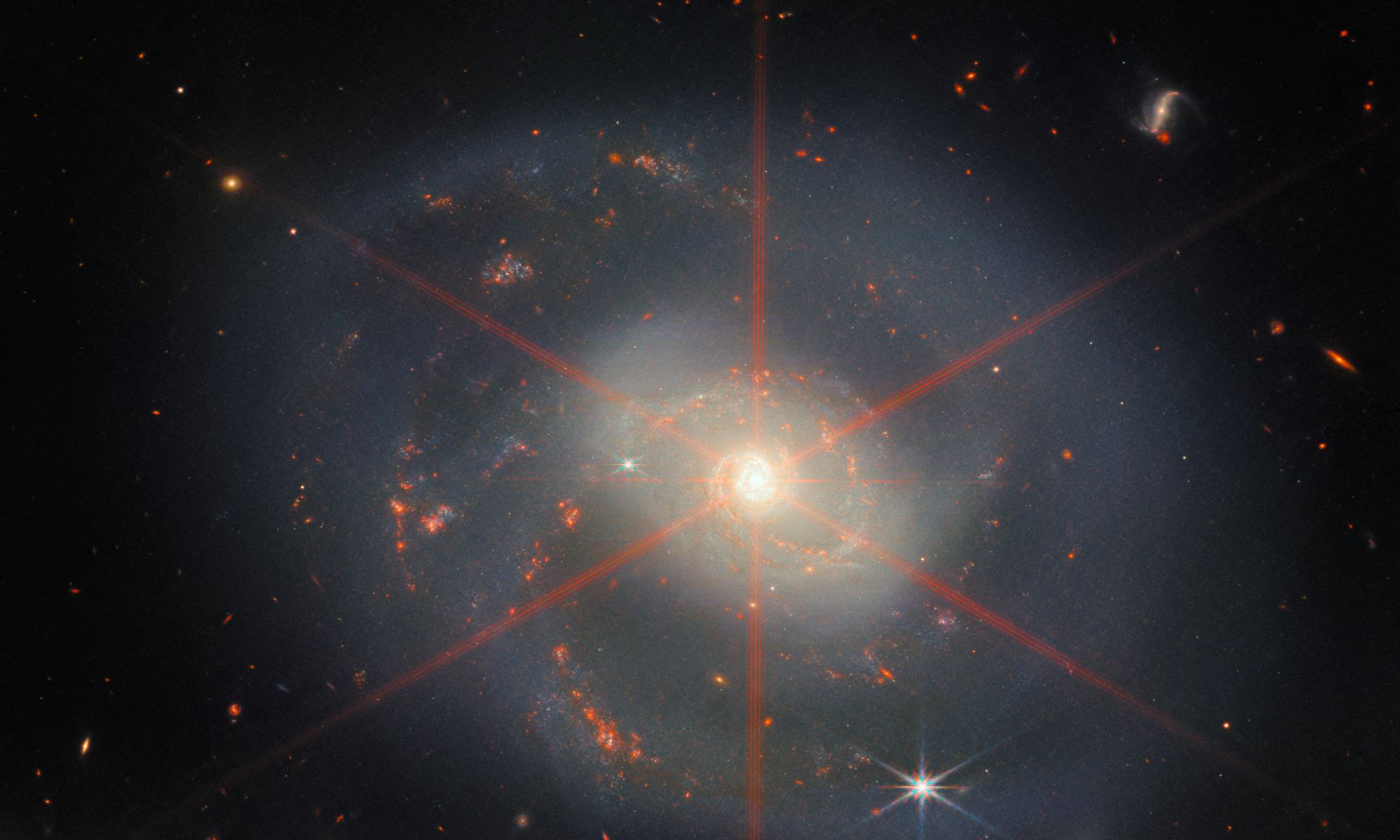
You’re looking at NGC 346, a star cluster 210 light years away that is energetically pumping out brand new stars from a dense cloud of gas and dust. Between 10 and 11 billion years ago, nearly all galaxies in the Universe underwent an era of intense star formation similar to what we see in NGC 346. This flurry of stellar birth is poetically nicknamed cosmic noon. Since then, star formation in the Universe has gradually dwindled, though it still blazes away in small pockets. By studying NGC 346 and other clusters like it, we can learn more about the era of cosmic noon and the evolution of galaxies.
To that end, researchers pointed the James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam infrared camera at NGC 346 last year, and they announced their preliminary findings at the American Astronomical Society’s annual meeting on January 11, 2023.
Continue reading “Cosmic Noon was Billions of Years ago, When Many Galaxies Were Filled With Star-Forming Nebulae Like This”