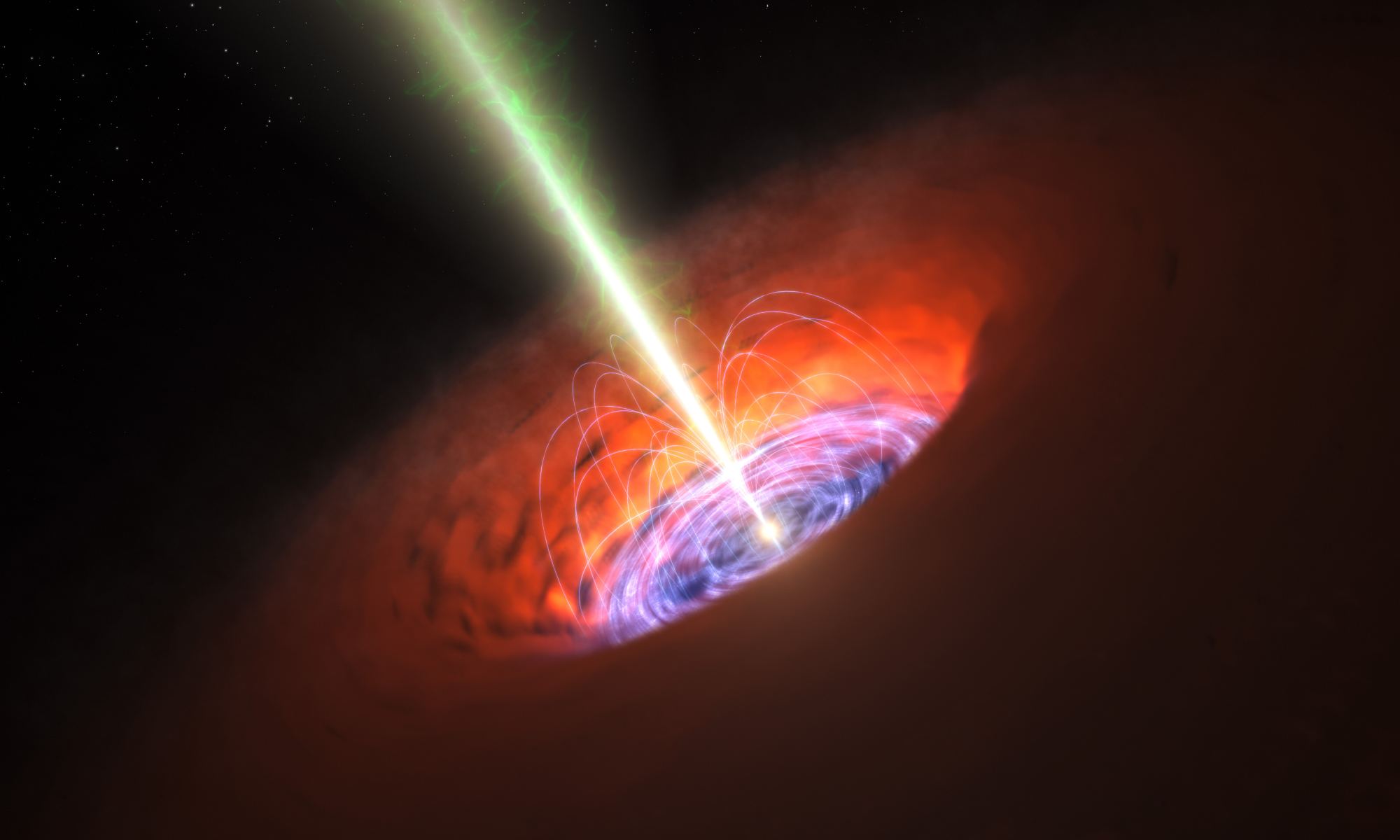
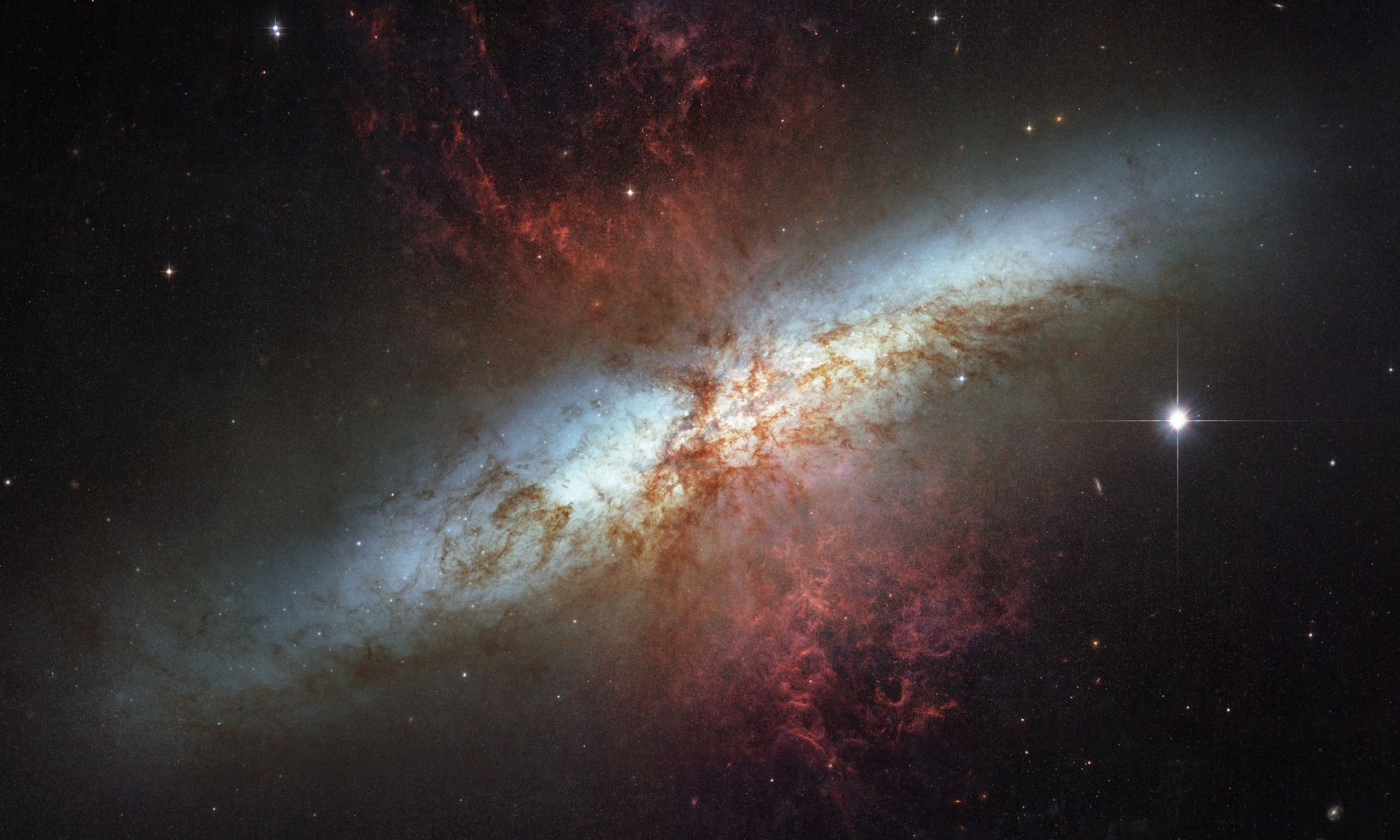
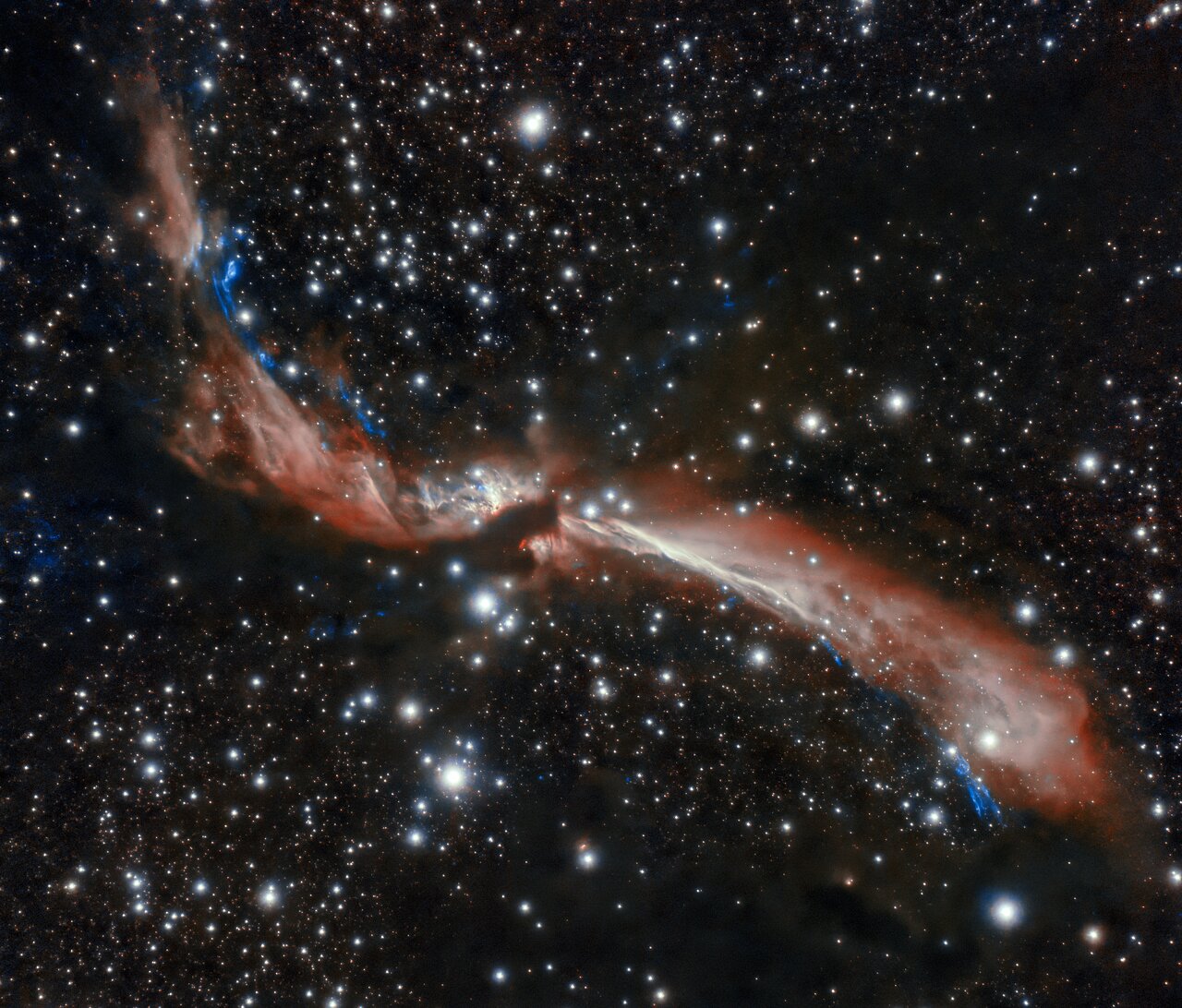
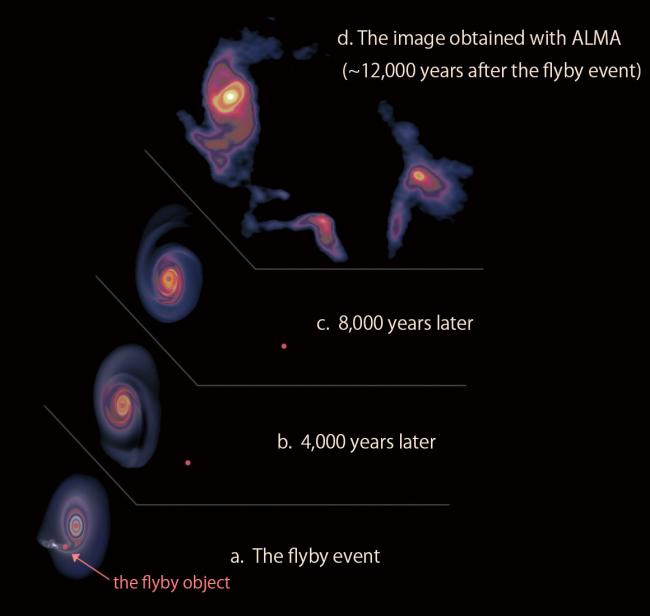
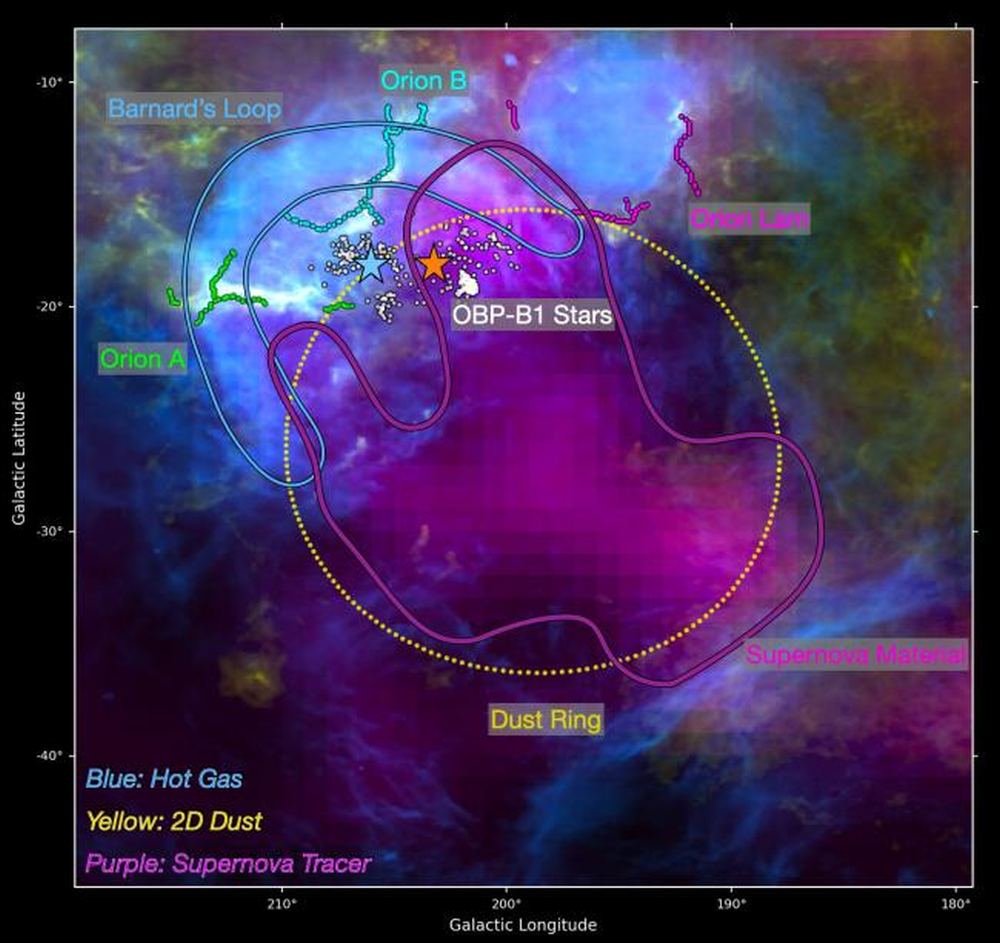
Black holes are gluttonous behemoths that lurk in the center of galaxies. Almost everybody knows that nothing can escape them, not even light. So when anything made of simple matter gets too close, whether a planet, a star or a gas cloud, it’s doomed.
But the black hole doesn’t eat it at once. It plays with its food like a fussy kid. Sometimes, it spews out light.
When the black hole is not only at the center of a galaxy but the center of a cluster of galaxies, these burps and jets carve massive cavities out of the hot gas at the center of the cluster called radio bubbles.
Continue reading “A Black Hole has been Burping for 100 Million Years”