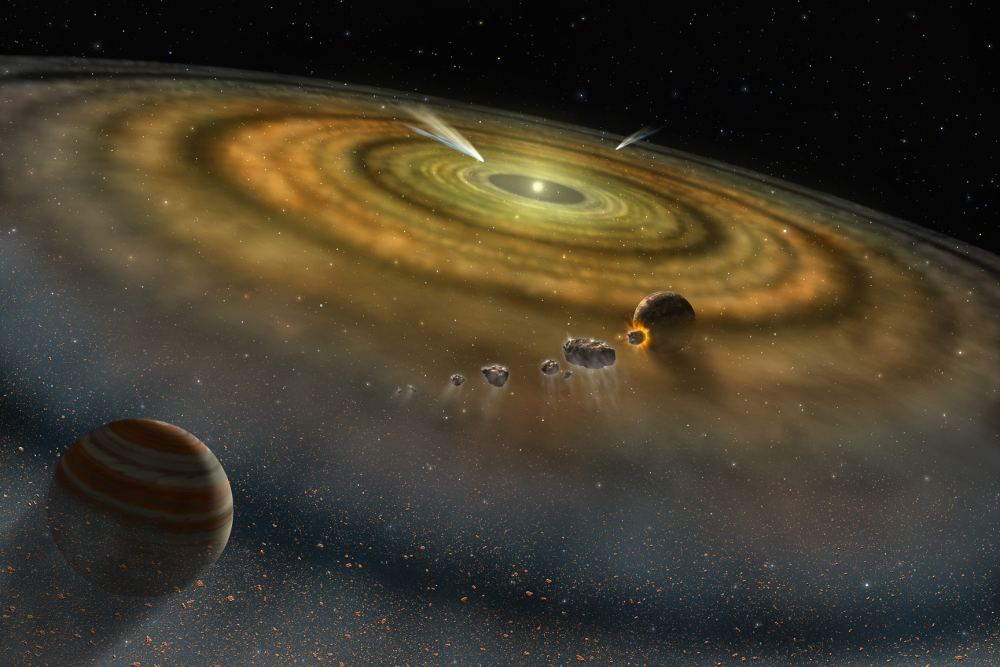
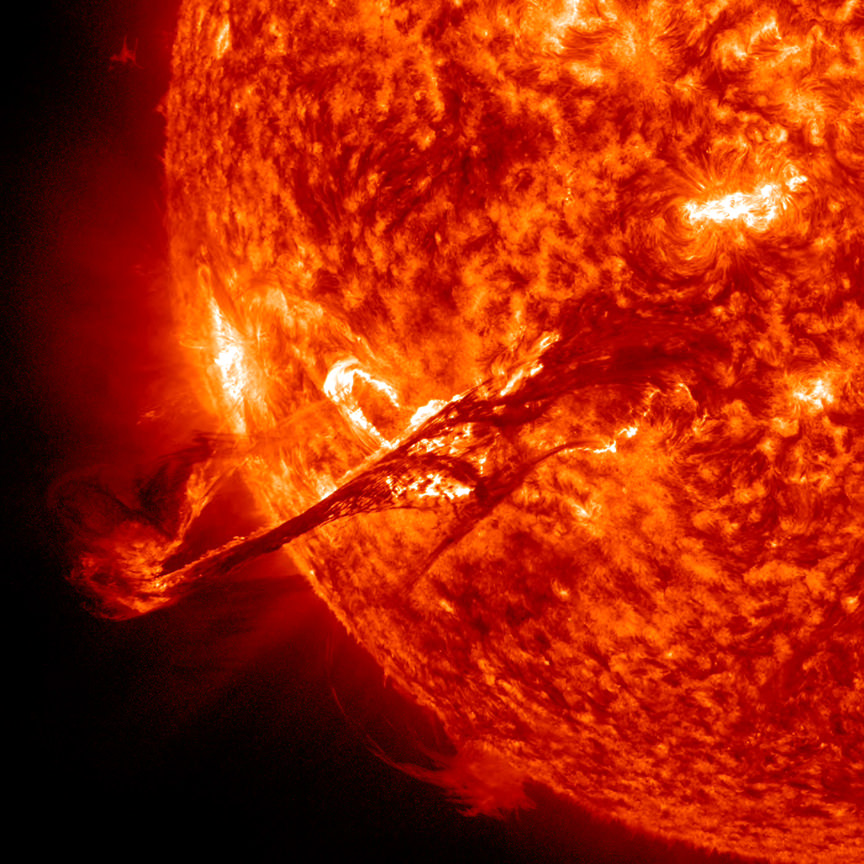
In the beginning, the big bang created three elements: hydrogen, helium, and lithium. But it only produced a trace of lithium. For every lithium atom created, the big bang produced about 10 billion hydrogen atoms, and 3 billion helium atoms. The ratio of primordial elements is one of the triumphs of the big bang model. It predicts the ratio of hydrogen (H) and helium (4He) perfectly, and even works for the ratios of other isotopes, such as deuterium (2H) and helium-3 (3He). But it doesn’t work for lithium, and we aren’t sure why.
Continue reading “Stars Like Our Sun Become Lithium Factories as They Die”Stars Like Our Sun Become Lithium Factories as They Die