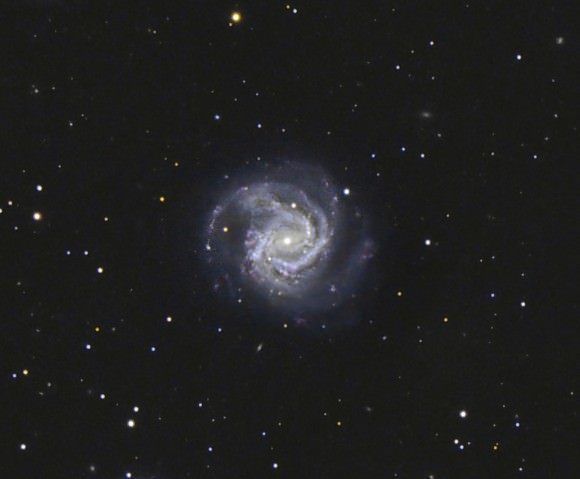
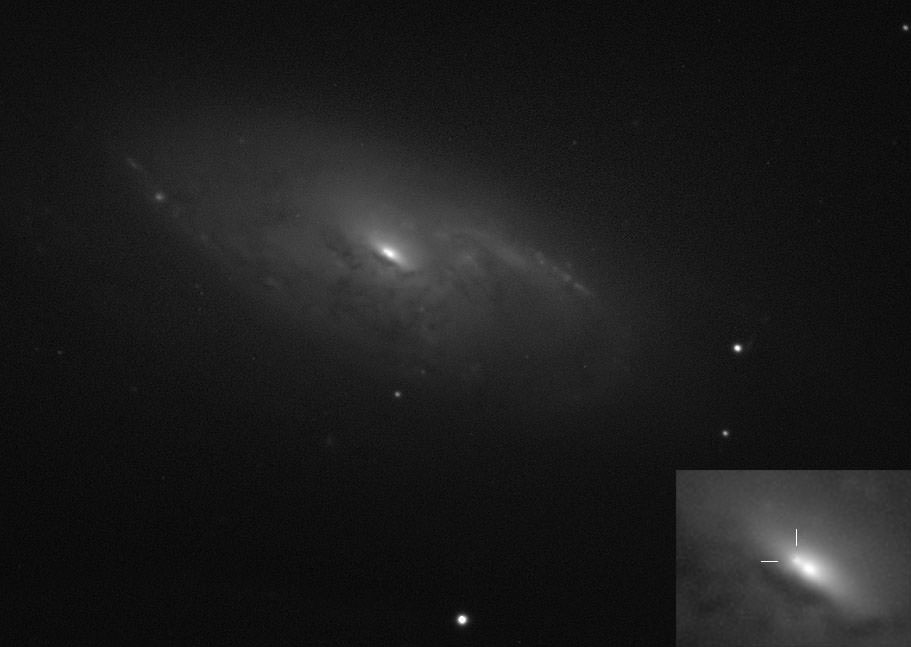
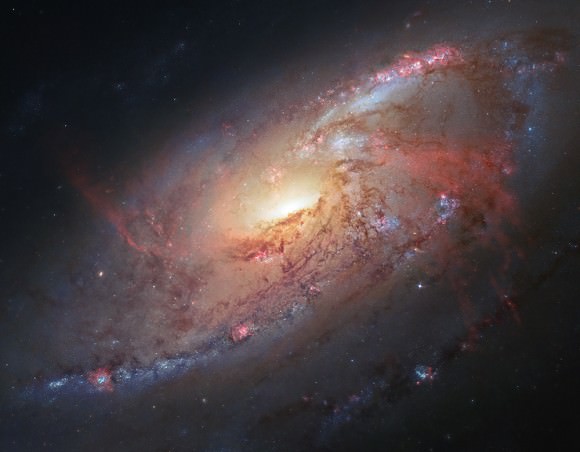
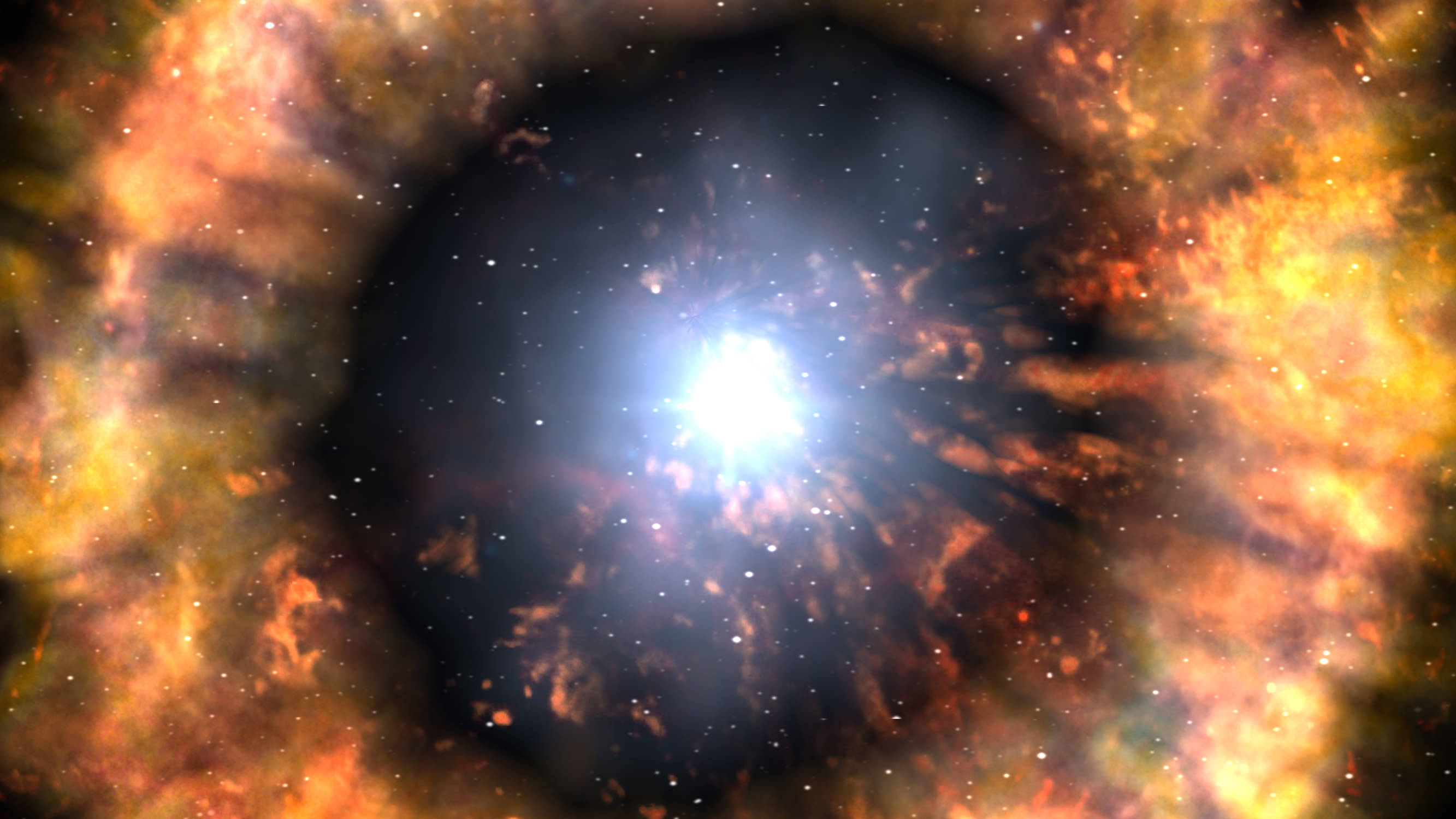
A star can burn its hydrogen for millions or even billions of years. But when the party’s over, black holes form in an instant. How long does it all take to happen.
Uh-oh! You’re right next to a black hole that’s starting to form.
In the J.J. Abrams Star Trek Universe, this ended up being a huge inconvenience for Spock as he tried to evade a ticked off lumpy forehead Romulan who’d made plenty of questionable life choices, drunk on Romulan ale and living above a tattoo parlor.
So, if you were piloting Spock’s ship towards the singularity, do you have any hope of escaping before it gets to full power? Think quickly now. This not only has implications for science, but most importantly, for the entire Star Trek reboot! Or you know, we can just create a brand new timeline. Everybody’s doing it. Retcon, ftw.
Most black holes come to be after a huge star explodes into a supernova. Usually, the force of gravity in a huge star is balanced by its radiation – the engine inside that sends out energy into space. But when the star runs out of fuel to burn, gravity quickly takes over and the star collapses. But how quickly? Ready your warp engines and hope for the best.
Here’s the bad news – there’s not much hope for Spock or his ship. A star’s collapse happens in an instant, and the star’s volume gets smaller and smaller. Your escape velocity – the energy you need to escape the star – will quickly exceed the speed of light.
You could argue there’s a moment in time where you could escape. This isn’t quite the spot to argue about Vulcan physiology, but I assume their reaction time is close to humans. It would happen faster than you could react, and you’d be boned.
But look at the bright side – maybe you’d get to discover a whole new universe. Unless of course Black holes just kill you, and aren’t sweet magical portals for you and your space dragon which you can name Spock, in honor of your Vulcan friend who couldn’t outrun a black hole.

Here we’ve been talking about what happens if a black hole suddenly appears beside you. The good news is, supernovae can be predicted. Not very precisely, but astronomers can say which stars are nearing the end of their lives.
Here’s an example. In the constellation Orion, Betelgeuse the bright star on the right shoulder, is expected to go supernova sometime in the next few hundred thousand years.
That’s plenty of time to get out of the way.
So: black holes are dangerous for your health, but at least there’s lots of time to move out of the way if one looks threatening. Just don’t go exploring too close!
If you were to fall through a black hole, what do you think would happen? Naw, just kidding, we all know you’d die. Why don’t you tell us what your favorite black hole sci fi story is in the comments below!
And if you like what you see, come check out our Patreon page and find out how you can get these videos early while helping us bring you more great content!