In a recent study submitted to High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena, a team of researchers from Japan discuss strategies to observe, and possibly predict precursor signatures for an explosion from Local Type II and Galactic supernovae (SNe). This study has the potential to help us better understand both how and when supernovae could occur throughout the universe, with supernovae being the plural form of supernova (SN). But just how important is it to detect supernovae before they actually happen?
Continue reading “Can Astronomers Predict Which Stars Are About to Explode as Supernovae?”Recent Supernovae Produced Giant Cavities in the Orion Nebula
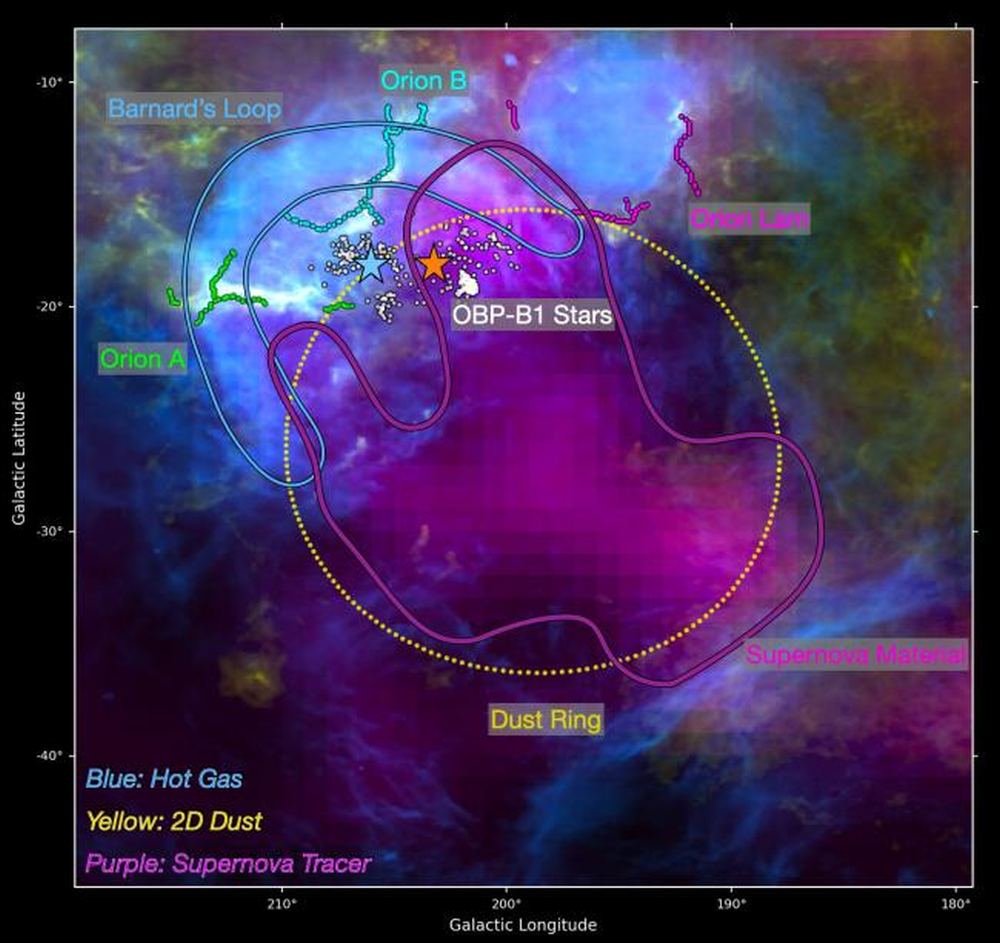
The Orion Nebula is a well-known feature in the night sky and is visible in small backyard telescopes. Orion is a busy place. The region is known for active star formation and other phenomena. It’s one of the most scrutinized features in the sky, and astronomers have observed all kinds of activity there: planets forming in protoplanetary disks, stars beginning their lives of fusion inside collapsing molecular clouds, and the photoevaporative power of massive hot stars as they carve out openings in clouds of interstellar gas.
But supernova explosions are leaving their mark on the Orion Nebula too. New research says supernovae explosions in recent astronomical history are responsible for a mysterious feature first formally identified in the night sky at the end of the 19th century. It’s called Barnard’s Loop, and it’s a gigantic loop of hot gas as large as 300 light-years across.
Continue reading “Recent Supernovae Produced Giant Cavities in the Orion Nebula”Astronomers Find a Star That Contains 65 Different Elements

Have you ever held a chunk of gold in your hand? Not a little piece of jewelry, but an ounce or more? If you have, you can almost immediately understand what drives humans to want to possess it and know where it comes from.
We know that gold comes from stars. All stars are comprised primarily of hydrogen and helium. But they contain other elements, which astrophysicists refer to as a star’s metallicity. Our Sun has a high metallicity and contains 67 different elements, including about 2.5 trillion tons of gold.
Now astronomers have found a distant star that contains 65 elements, the most ever detected in another star. Gold is among them.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find a Star That Contains 65 Different Elements”A Recently Discovered Double Binary System is Unstable. Stars Could Collide, Leading to a Supernova
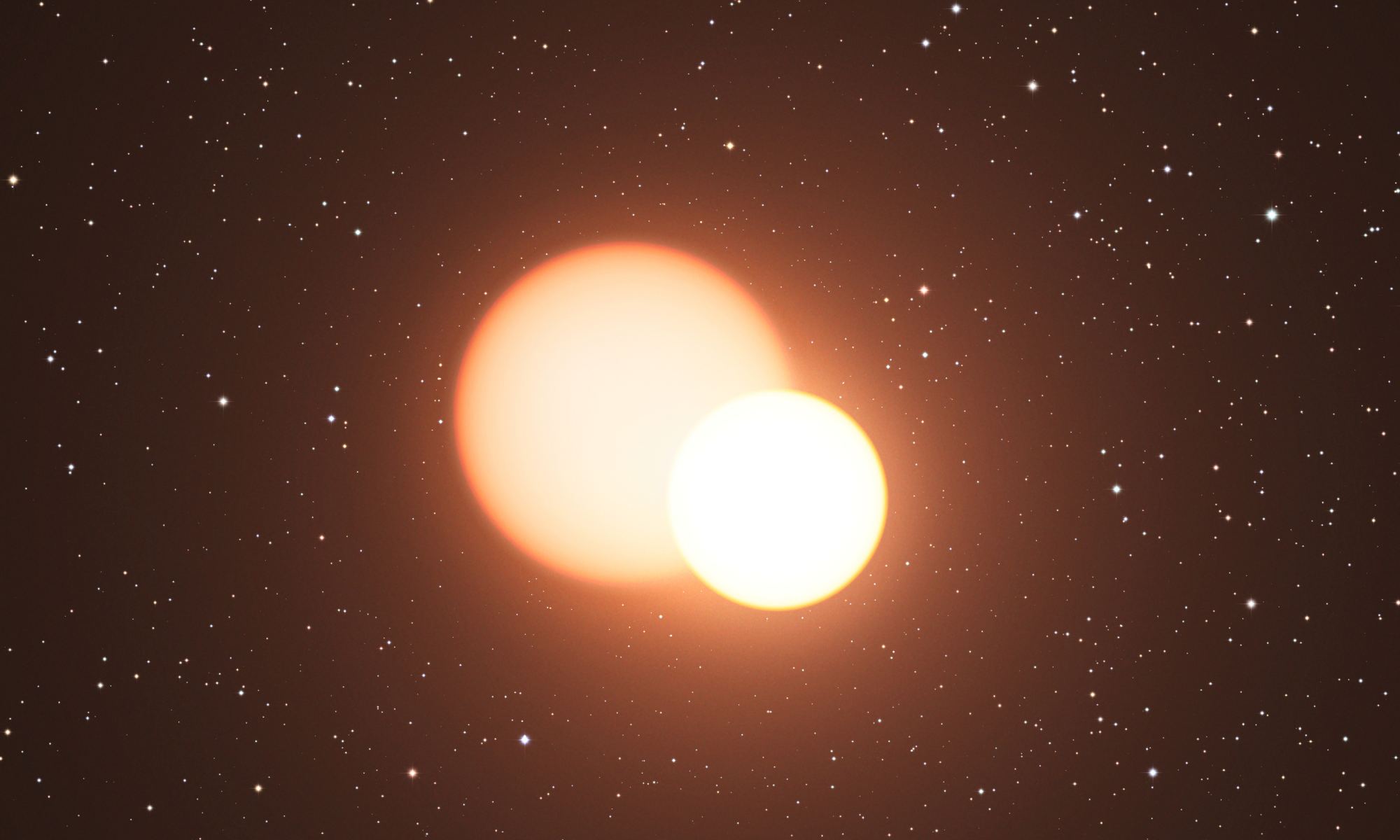
Multiple star systems are very common in the Milky Way. While most of these systems are binary systems consisting of two stars, others contain three, four, or even six stars. These systems tend to be pretty stable since unstable systems tend to break apart or merge fairly quickly, but sometimes you can get a kind of meta-stable system. One that lasts long enough for stars to evolve while still being stable in the end. And that end could be a supernova.
Continue reading “A Recently Discovered Double Binary System is Unstable. Stars Could Collide, Leading to a Supernova”We can Probably Find Supernovae Enhanced by Gravitational Lensing, We Just Need to Look
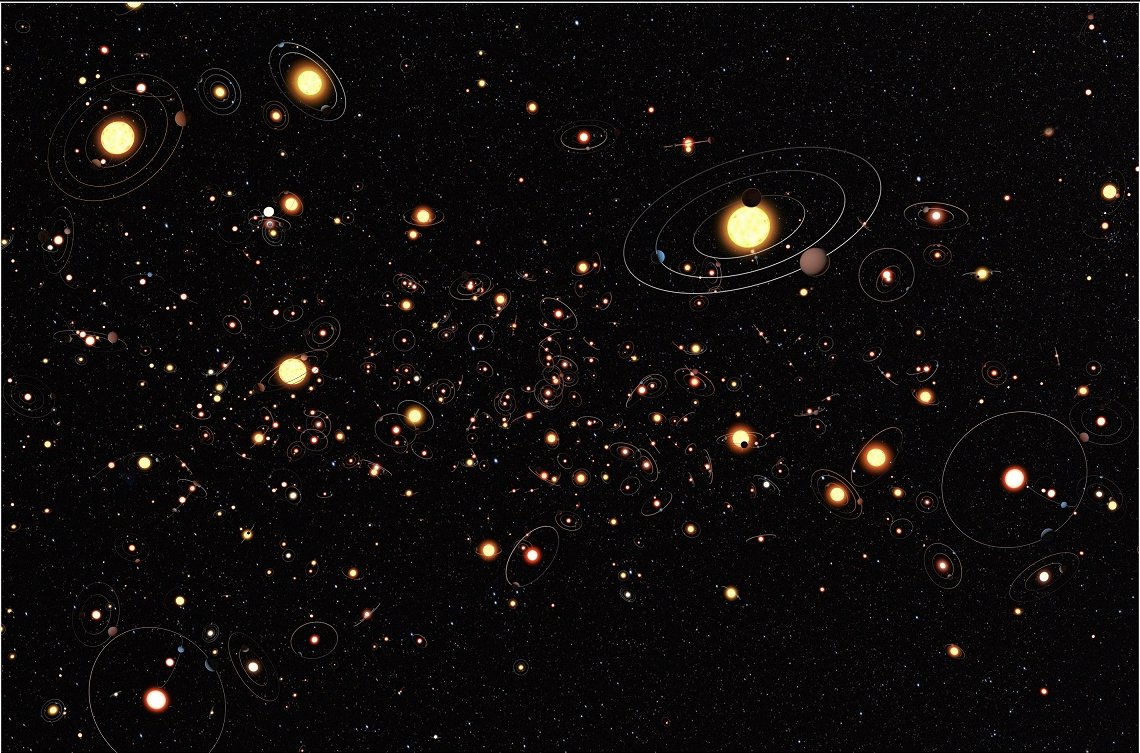

Gravitational lensing provides an opportunity to see supernovae and other transients much farther than we normally can. A new research proposal outlines a plan to use a comprehensive catalog of strong gravitational lenses to capture these rare events at extreme distances.
Continue reading “We can Probably Find Supernovae Enhanced by Gravitational Lensing, We Just Need to Look”Nearby Supernovae Exploded Just a few Million Years Ago, Leading to a Wave of Star Formation Around the Sun
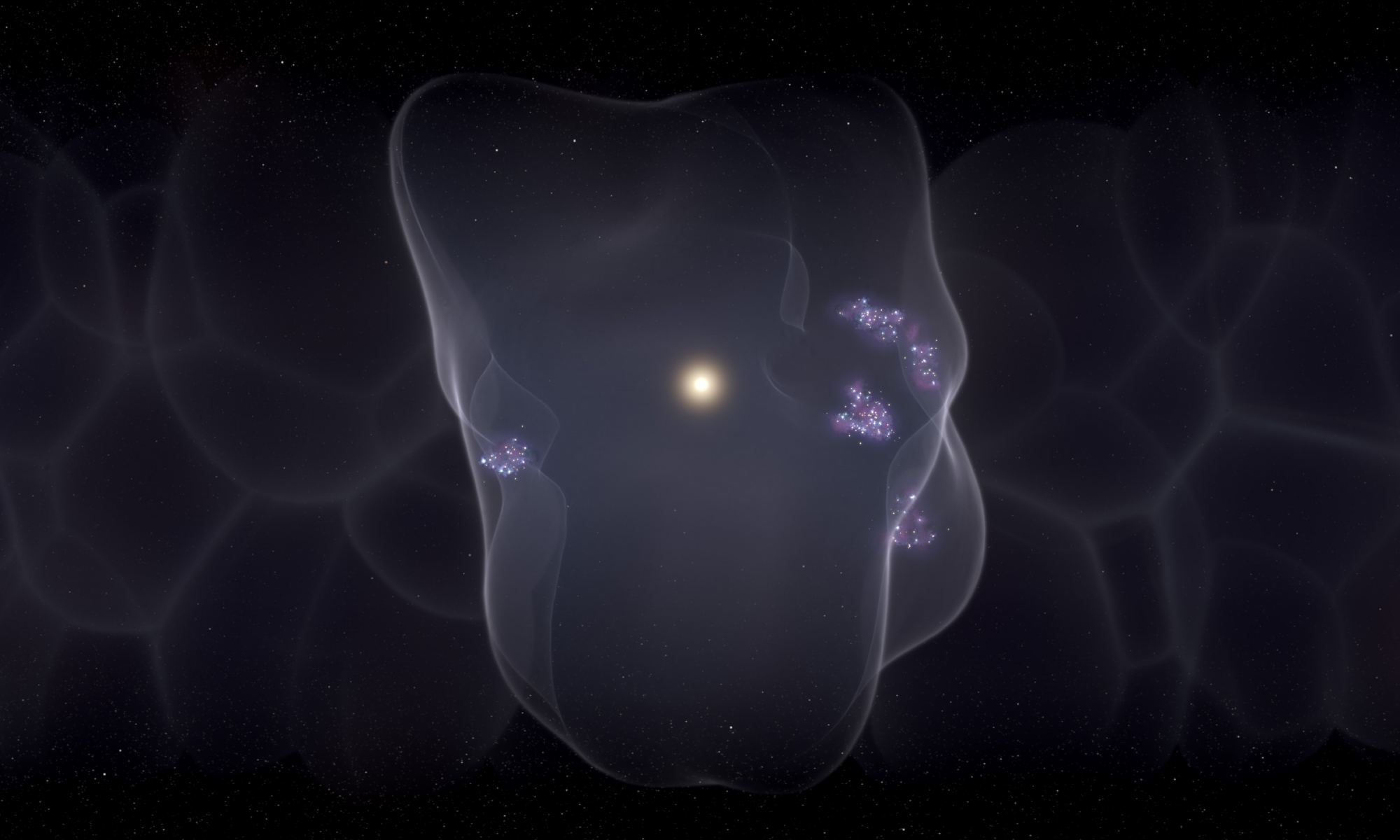

The Sun isn’t the only star in this galactic neighbourhood. Other stars also call this neighbourhood home. But what’s the neighbourhood’s history? What triggered the birth of all those stars?
A team of astronomers say they’ve pieced the history together and identified the trigger: a series of supernovae explosions that began about 14 million years ago.
Continue reading “Nearby Supernovae Exploded Just a few Million Years Ago, Leading to a Wave of Star Formation Around the Sun”Nearby Supernovae Were Essential to Life on Earth
It’s almost impossible to comprehend a supernova explosion’s violent, destructive power. An exploding supernova can outshine its host galaxy for a few weeks or even months. That seems almost impossible when considering that a galaxy can contain hundreds of billions of stars. Any planet too close to a supernova would be completely sterilized by all the energy released, its atmosphere would be stripped away, and it may even be shredded into pieces.
But like many things in nature, it all comes down to dose.
A certain amount of supernova activity might be necessary for life to exist.
Continue reading “Nearby Supernovae Were Essential to Life on Earth”Quick Action Let Hubble Watch the Earliest Stages of an Unfolding Supernova Detonation
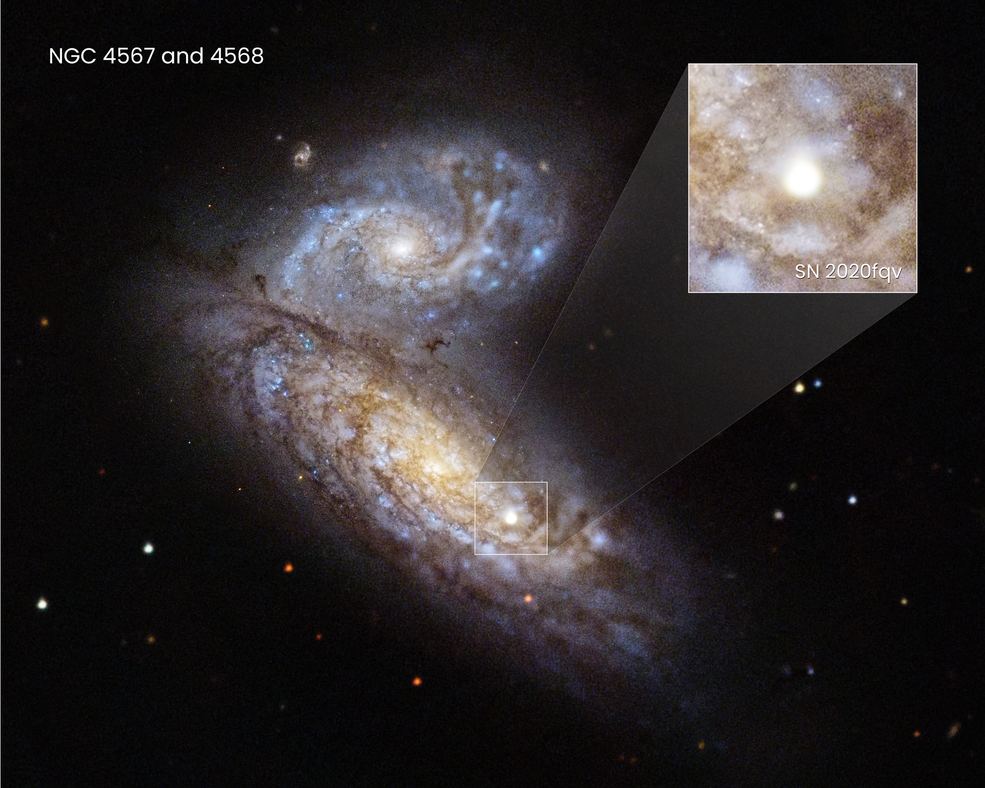

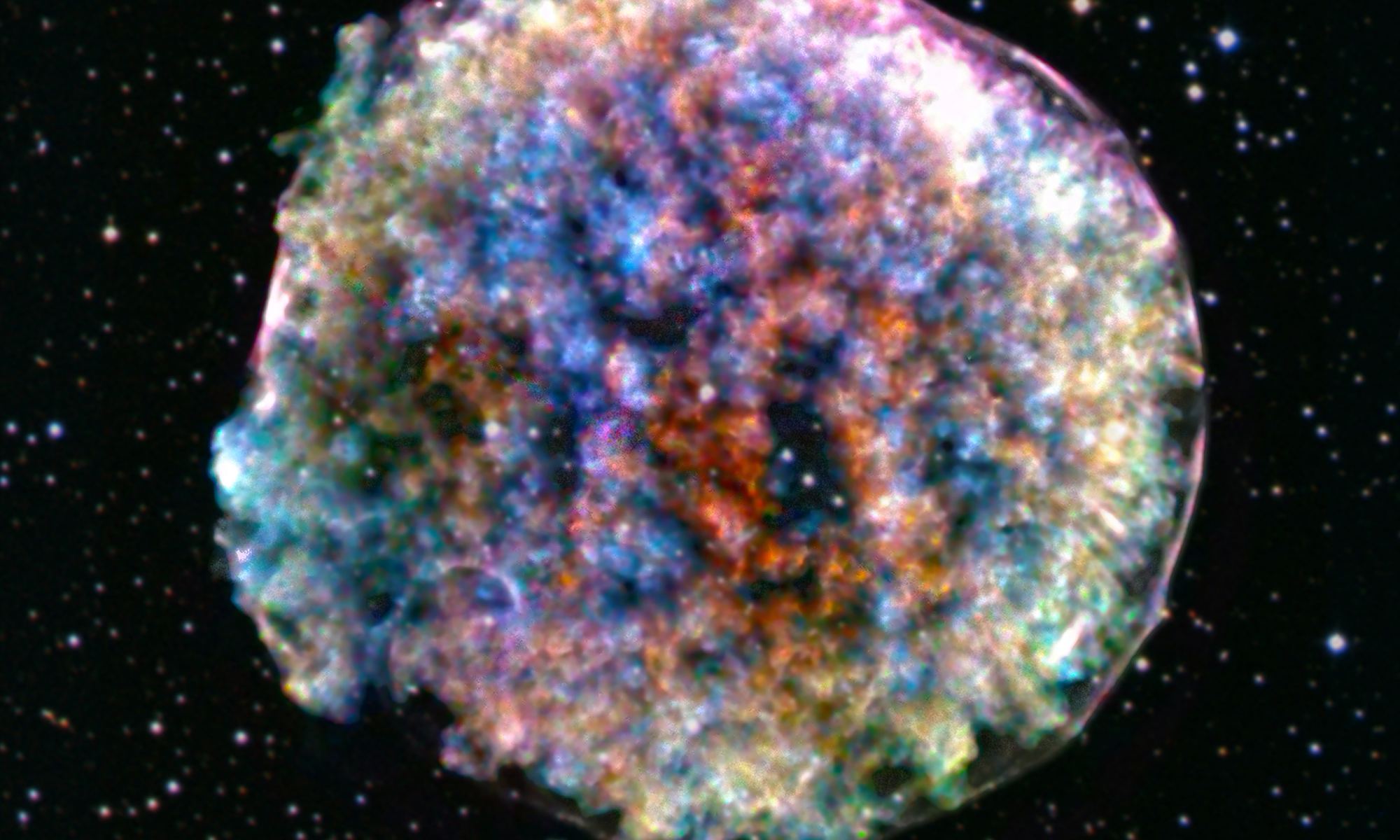
If it weren’t for supernova remnants we wouldn’t have much knowledge of supernovae themselves. If a supernova explosion is the end of a star’s life, then we can also thank forensic astrophysics for much of our knowledge. The massive exploding stars leave behind brilliant and mesmerizing evidence of their catastrophic ends, and much of what we know about supernovae comes from studying the remnants rather than the explosions themselves. Supernova remnants like the Crab Nebula and SN 1604 (Kepler’s Supernova) are some of our most-studied objects.
Observing an active supernova in the grip of its own destruction can be difficult. But it looks like the Hubble Space Telescope is up to the task.
Continue reading “Quick Action Let Hubble Watch the Earliest Stages of an Unfolding Supernova Detonation”Astronomers Find a Giant Cavity in Space, Hollowed out by an Ancient Supernova
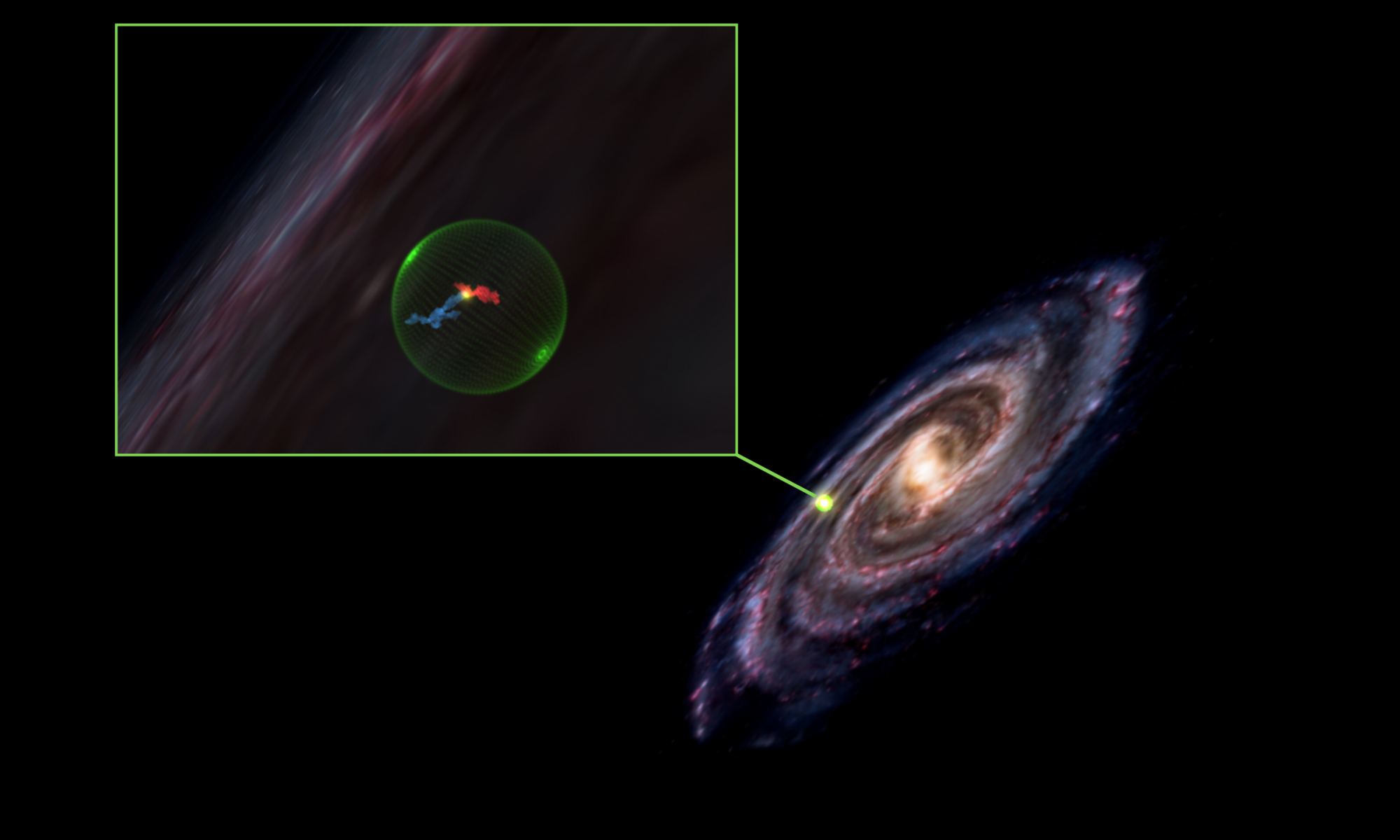

Star formation is a topic astronomers are still trying to fully understand. We know, for example, that stars don’t form individually, but rather are born within vast interstellar molecular clouds. These stellar nurseries contain gas dense enough for gravity to trigger the formation of stars. In spiral galaxies, these molecular clouds are most commonly found within spiral arms, which is why stars are most often born in spiral arms.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find a Giant Cavity in Space, Hollowed out by an Ancient Supernova”Hubble Reveals the Final Stages of a Dying Star
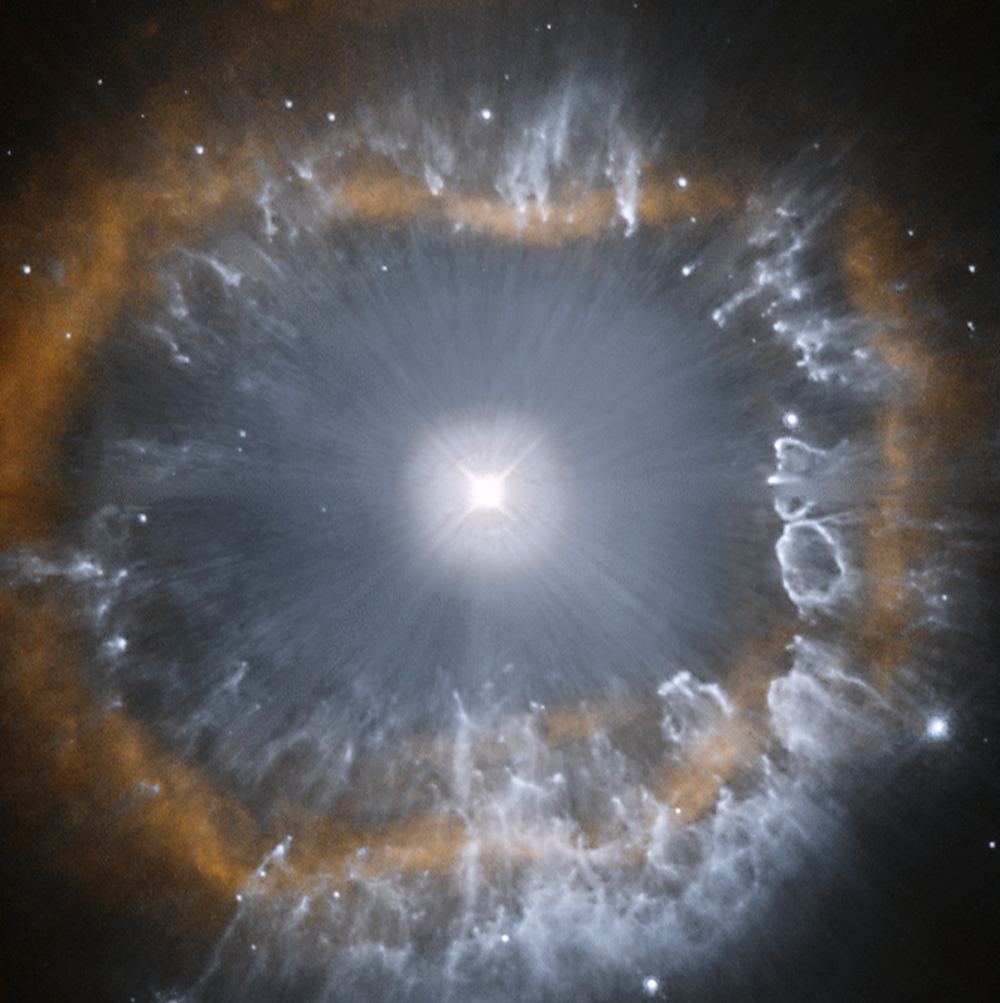
In April 2021 Hubble released its 31st-anniversary image. It’s a portrait of AG Carinae, one of the most luminous stars in the entire Milky Way. AG Carinae is in a reckless struggle with itself, periodically ejecting matter until it reaches stability sometime in the future.
Thanks to the Hubble, we get to watch the brilliant struggle.
Continue reading “Hubble Reveals the Final Stages of a Dying Star”

