There’s a lot you can learn by just staring at an object, watching how it changes in brightness. This is the technique of photometry, and it has helped astronomers discover variable stars, extrasolar planets, minor planets, supernovae, and much more.
Continue reading “Astronomy Cast Ep. 337: Photometry”
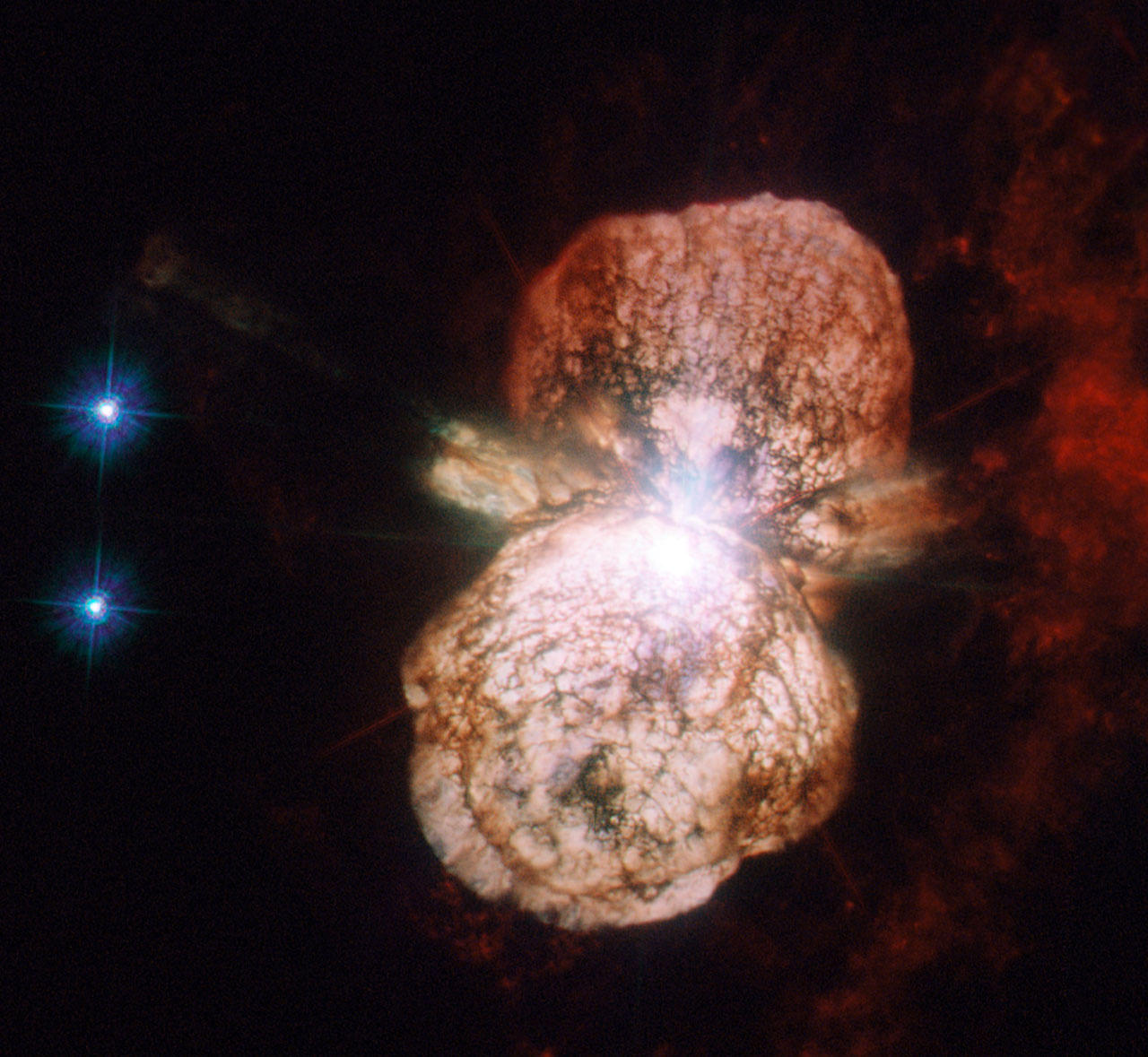
Is Eta Carinae Heading Toward Another Eruption?
Massive stars can devastate their surroundings, unleashing hot winds and blasting radiation. With a mass over 100 times heavier than the Sun and a luminosity a million times brighter than the Sun, Eta Carinae clocks in as one of the biggest and brightest stars in our galaxy.
The enigmatic object walks a thin line between stellar stability and tumultuous explosions. But now a team of international astronomers is growing concerned that it’s leaning toward instability and eruption.
In the 19th Century the star mysteriously threw off unusually bright light for two decades in an event that became known as the “Great Eruption,” the causes of which are still up for debate. John Herschel and others watched as Eta Carinae’s brightness oscillated around that of Vega — rivaling a supernova explosion.
We now know the star ejected material in the form of two big globes. “During the eruption the star threw off more than 10 solar masses, which can now be observed as the surrounding bipolar nebula,” said lead author Dr. Andrea Mehner from the European Southern Observatory. Miraculously the star survived, but the nebula has been expanding into space ever since.
Eta Carinae has been observed at the South African Astronomical Observatory — a 0.75m telescope outside of Cape Town — for more than 40 years, providing a wealth of data. From the start of observations in 1976 until 1998, astronomers saw an increase across the J, H, K and L bands — filters, which allow certain wavelength ranges of infrared light to pass through.
“This data set is unique for its consistency over a timespan of more than 40 years,” Mehner told Universe Today. “It provides us with the opportunity to analyze long-term changes in the system as Eta Carinae still recovers from its Great Eruption.”
In order to understand the longterm overall increase in light we have to look at a more recent discovery noted in 2005 when scientists discovered that Eta Carinae is actually two stars: a massive blue star and a smaller companion. The temperature increased for 15 years until the companion came very close to the massive star, reaching periastron.
This increase in brightness is likely due to an overall increase in temperature of some component of the Eta Carinae system (which includes the massive blue star, its smaller companion, and the shells of gas and dust that now enshroud the system).
After 1998, however, the linear trend changed significantly and the star’s brightness increased much more rapidly in the J and H bands. It’s getting bluer, which in astronomy, typically means it’s getting hotter.
However, it’s unlikely the star itself is getting hotter. Instead we are seeing the effect of dust around the star being destroyed rapidly. Dust absorbs blue light. So if the dust is getting destroyed, more blue light will be able to pass through the nebulous globes surrounding the system. If this is the case, then we’re really seeing the star as it truly is, without dust absorbing certain wavelengths of its light.
While the nebula is slowly expanding and the dust is therefore dissipating, the authors do not think it’s enough to account for the recent brightening. Instead Eta Carinae is likely rotating at a different speed or losing mass at a different rate. “The changes observed may imply that the star is becoming more unstable and may head towards another eruptive phase,” Mehner told Universe Today.
Perhaps Eta Carinae is heading toward another “Great Eruption.” Only time will tell. But in a field where most events occur on a timescale of millions of years, it’s a great opportunity to watch the system evolve on a human time scale. And when Eta Carinae reaches periastron in the middle of this year, tens of telescopes will be collecting its light, hoping to see a sudden turn of events that may help us explain this exotic system.
The paper has been accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics and is available for download here.
Will The Sun Explode?
All stars die, some more violently than others.
Once our own Sun has consumed all the hydrogen fuel in its core, it too will reach the end of its life. Astronomers estimate this to be a short 7 billion years from now. For a few million years, it will expand into a red giant, puffing away its outer layers. Then it’ll collapse down into a white dwarf and slowly cool down to the background temperature of the Universe.
I’m sure you know that some other stars explode when they die. They also run out of fuel in their core, but instead of becoming a red giant, they detonate in a fraction of a second as a supernova.
So, what’s the big difference between stars like our Sun and the stars that can explode as supernovae?
Mass. That’s it.
Supernova progenitors – these stars capable of becoming supernovae – are extremely massive, at least 8 to 12 times the mass of our Sun. When a star this big runs out of fuel, its core collapses. In a fraction of a second, material falls inward to creating an extremely dense neutron star or even a black hole. This process releases an enormous amount of energy, which we see as a supernova.
If a star has even more mass, beyond 140 times the mass of the Sun, it explodes completely and nothing remains at all. If these other stars can detonate like this, is it possible for our Sun to explode?
Could there be some chain reaction we could set off, some exotic element a rare comet could introduce on impact, or a science fiction doomsday ray we could fire up to make the Sun explode?
Nope, quite simply, it just doesn’t have enough mass. The only way this could ever happen is if it was much, much more massive, bringing it to that lower supernovae limit.
In other words, you would need to crash an equally massive star into our Sun. And then do it again, and again.. and again… another half dozen more times. Then, and only then would you have an object massive enough to detonate as a supernova.

Now, I’m sure you’re all resting easy knowing that solar detonation is near the bottom of the planetary annihilation list. I’ve got even better news. Not only will this never happen to the Sun, but there are no large stars close enough to cause us any damage if they did explode.
A supernova would need to go off within a distance of 100 light-years to irradiate our planet.
According to Dr. Phil Plait from Bad Astronomy, the closest star that could detonate as a supernova is the 10 solar mass Spica, at a distance of 260 light-years. No where near close enough to cause us any danger.
So don’t worry about our Sun exploding or another nearby star going supernova and wiping us out. You can put your feet up and relax, as it’s just not going to happen.
Can Stars Collide?
Imagine a really bad day. Perhaps you’re imagining a day where the Sun crashes into another star, destroying most of the Solar System.
No? Well then, even in your imagination things aren’t so bad… It’s all just matter of perspective.
Fortunately for us, we live in out the boring suburbs of the Milky Way. Out here, distances between stars are so vast that collisions are incredibly rare. There are places in the Milky Way where stars are crowded more densely, like globular clusters, and we get to see the aftermath of these collisions. These clusters are ancient spherical structures that can contain hundreds of thousands of stars, all of which formed together, shortly after the Big Bang.
Within one of these clusters, stars average about a light year apart, and at their core, they can get as close to one another as the radius of our Solar System. With all these stars buzzing around for billions of years, you can imagine they’ve gotten up to some serious mischief.
Within globular clusters there are these mysterious blue straggler stars. They’re large hot stars, and if they had formed with the rest of the cluster, they would have detonated as supernovae billions of years ago. So scientists figure that they must have formed recently.
How? Astronomers think they’re the result of a stellar collision. Perhaps a binary pair of stars merged, or maybe two stars smashed into one another.
Professor Mark Morris of the University of California at Los Angeles in the Department of Physics and Astronomy helps to explain this idea.
“When you see two stars colliding with each other, it depends on how fast they’re moving. If they’re moving at speeds like we see at the center of our galaxy, then the collision is extremely violent. If it’s a head-on collision, the stars get completely splashed to the far corners of the galaxy. If they’re merging at slower velocities than we see at our neck of the woods in our galaxy, then stars are more happy to merge with us and coalesce into one single, more massive object.”
There’s another place in the Milky Way where you’ve got a dense collection of stars, racing around at breakneck speeds… near the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
This monster black hole contains the mass of 4 million times the Sun, and dominates the region around the center of the Milky Way.

“The core of the Milky Way is one of those places where you find the extremes of nature. The density of stars there is higher than anywhere else in the galaxy,”Professor Morris continues. “Overall, in the center of our galaxy on scales of hundreds of light years, there is much more gas present than anywhere else in the galaxy. The magnetic field is stronger there than anywhere else in the galaxy, and it has it’s own geometry there. So it’s an unusual place, an energetic place, a violent place, because everything else is moving so much faster there than you see elsewhere.”
“We study the stars in the immediate vicinity of the black hole, and we find that there’s not as many stars as one might have expected, and one of the explanations for that is that stars collide with each other and either eliminate one another or merge, and two stars become one, and both of those processes are probably occurring.”
Stars whip around it, like comets dart around our Sun, and interactions are commonplace.
There’s another scenario that can crash stars together.
The Milky Way mostly has multiple star systems. Several stars can be orbiting a common center of gravity. Many are great distances, but some can have orbits tighter than the planets around our Sun.
When one star reaches the end of its life, expanding into a red giant, It can consume its binary partner. The consumed star then strips away 90% of the mass of the red giant, leaving behind a rapidly pulsating remnant.
What about when galaxies collide? That sounds like a recipe for mayhem.
Surprisingly, not so much.
“That’s actually a very interesting question, because if you imagine two galaxies colliding, you’d imagine that to be an exceptionally violent event,’ Professor Morris explains. “But in fact, the stars in those two galaxies are relatively unaffected. The number of stars that will collide when two galaxies collide is possibly counted on the fingers of one or two hands. Stars are so few and far between that they just aren’t going to meet each other with any significance in a field like that.”

“What you see when you see two galaxies collide, however, on the large scale, is that the tidal forces of the two galaxies will rip each of the galaxies apart in terms of what it will look like. Streams of stars will be strewn out in various directions depending on the precise history of the interaction between the two galaxies. And so, eventually over time, the galaxies will merge, the whole configuration of stars will settle down into something that looks unlike either of the two initially colliding galaxies. Perhaps something more spheroidal or spherical, and it might look more like an elliptical galaxy than the spiral galaxy that these two galaxies now are.”
Currently, we’re on a collision course with the Andromeda Galaxy, and it’s expected we’ll smash into it in about 4 billion years. The gas and dust will collide and pile up, igniting an era of furious star formation. But the stars themselves? They’ll barely notice. The stars in the two galaxies will just streak past each other, like a swarm of angry bees.
Phew.
So, good news! When you’re imagining a worse day, you won’t have to worry about our Sun colliding with another star. We’re going to be safe and sound for billions of years. But if you live in a globular cluster or near the center of the galaxy, you might want to check out some property here in the burbs.
Thanks to Professor Mark Morris at UCLA – visit their Physics and Astronomy program homepage here.
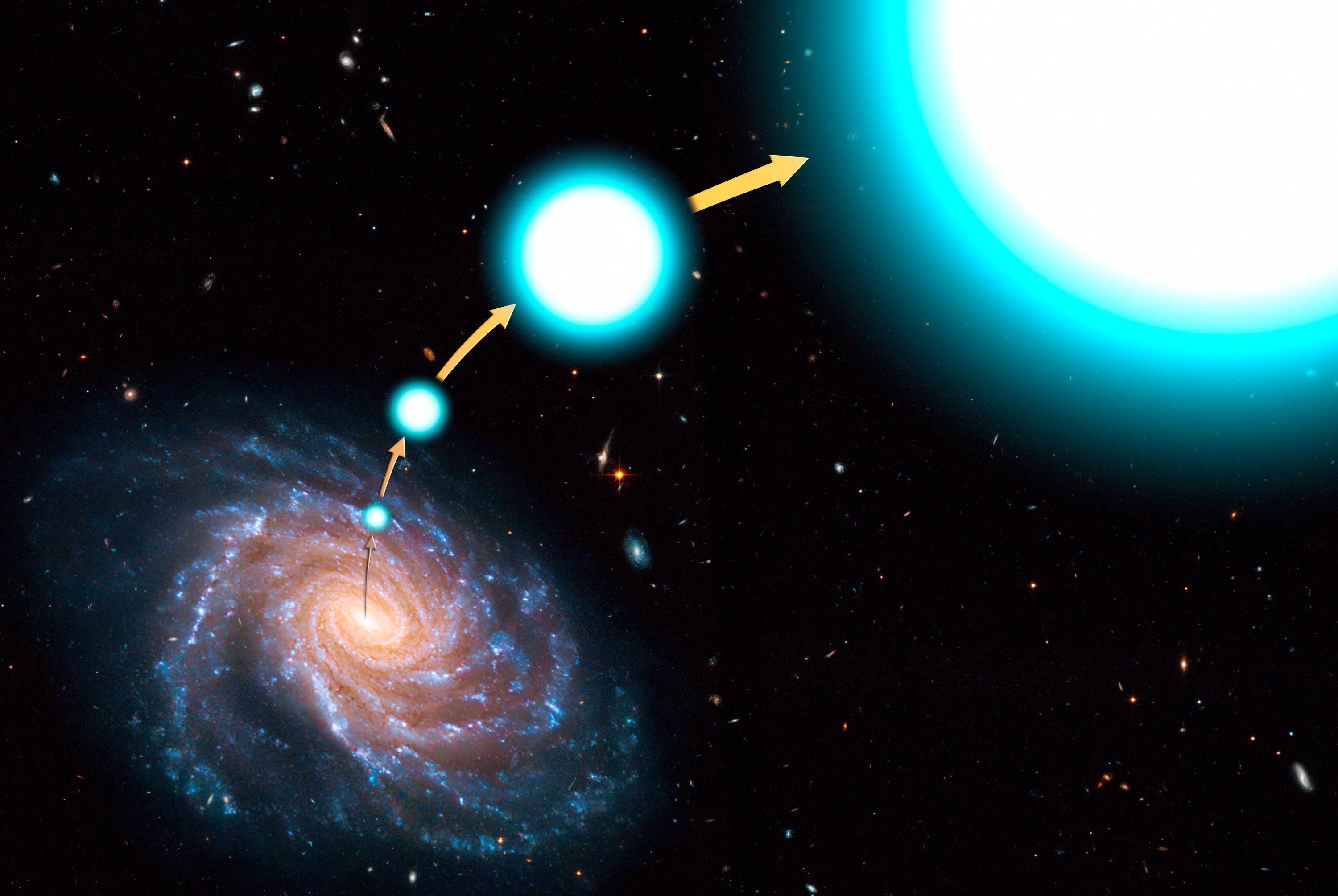
How do Hypervelocity Stars End up Breaking The Speed Limit?
The Sun is racing through the Galaxy at a speed that is 30 times greater than a space shuttle in orbit (clocking in at 220 km/s with respect to the galactic center). Most stars within the Milky Way travel at a relatively similar speed. But certain stars are definitely breaking the stellar speed limit. About one in a billion stars travel at a speed roughly 3 times greater than our Sun – so fast that they can easily escape the galaxy entirely!
We have discovered dozens of these so-called hypervelocity stars. But how exactly do these stars reach such high speeds? Astronomers from the University of Leicester may have found the answer.
The first clue comes in observing hypervelocity stars, where we can note their speed and direction. From these two measurements, we can trace these stars backward in order to find their origin. Results show that most hypervelocity stars begin moving quickly in the Galactic Center.
We now have a rough idea of where these stars gain their speed, but not how they reach such high velocities. Astronomers think two processes are likely to kick stars to such great speeds. The first process involves an interaction with the supermassive black hole (Sgr A*) at the center of our Galaxy. When a binary star system wanders too close to Sgr A*, one star is likely to be captured, while the other star is likely to be flung away from the black hole at an alarming rate.
The second process involves a supernova explosion in a binary system. Dr. Kastytis Zubovas, lead author on the paper summarized here, told Universe Today, “Supernova explosions in binary systems disrupt those systems and allow the remaining star to fly away, sometimes with enough velocity to escape the Galaxy.”
There is, however, one caveat. Binary stars in the center of our Galaxy will both be orbiting each other and orbiting Sgr A*. They will have two velocities associated with them. “If the velocity of the star around the binary’s center of mass happens to line up closely with the velocity of the center of mass around the supermassive black hole, the combined velocity may be large enough to escape the Galaxy altogether,” explained Zubovas.
In this case, we can’t sit around and wait to observe a supernova explosion breaking up a binary system. We would have to be very lucky to catch that! Instead, astronomers rely on computer modeling to recreate the physics of such an event. They set up multiple calculations in order to determine the statistical probability that the event will occur, and check if the results match observations.
Astronomers from the University of Leicester did just this. Their model includes multiple input parameters, such as the number of binaries, their initial locations, and their orbital parameters. It then calculates when a star might undergo a supernova explosion, and depending on the position of the two stars at that time, the final velocity of the remaining star.
The probability that a supernova disrupts a binary system is greater than 93%. But does the secondary star then escape from the galactic center? Yes, 4 – 25% of the time. Zubovas described, “Even though this is a very rare occurrence, we may expect several tens of such stars to be created over 100 million years.” The final results suggest that this model ejects stars with rates high enough to match the observed number of hypervelocity stars.
Not only do the number of hypervelocity stars match observations but also their distribution throughout space. “Hypervelocity stars produced by our supernova disruption method are not evenly distributed on the sky,” said Dr. Graham Wynn, a co-author on the paper. “They follow a pattern which retains an imprint of the stellar disk they formed in. Observed hypervelocity stars are seen to follow a pattern much like this.”
In the end, the model was very successful at describing the observed properties of hypervelocity stars. Future research will include a more detailed model that will allow astronomers to understand the ultimate fate of hypervelocity stars, the effect that supernova explosions have on their surroundings, and the galactic center itself.
It’s likely that both scenarios – binary systems interacting with the supermassive black hole and one undergoing a supernova explosion – form hypervelocity stars. Studying both will continue to answer questions about how these speedy stars form.
The results will be published in the Astrophysical Journal (preprint available here)
Hubble Telescope Breaks Record in Finding Most Distant Type Ia Supernova
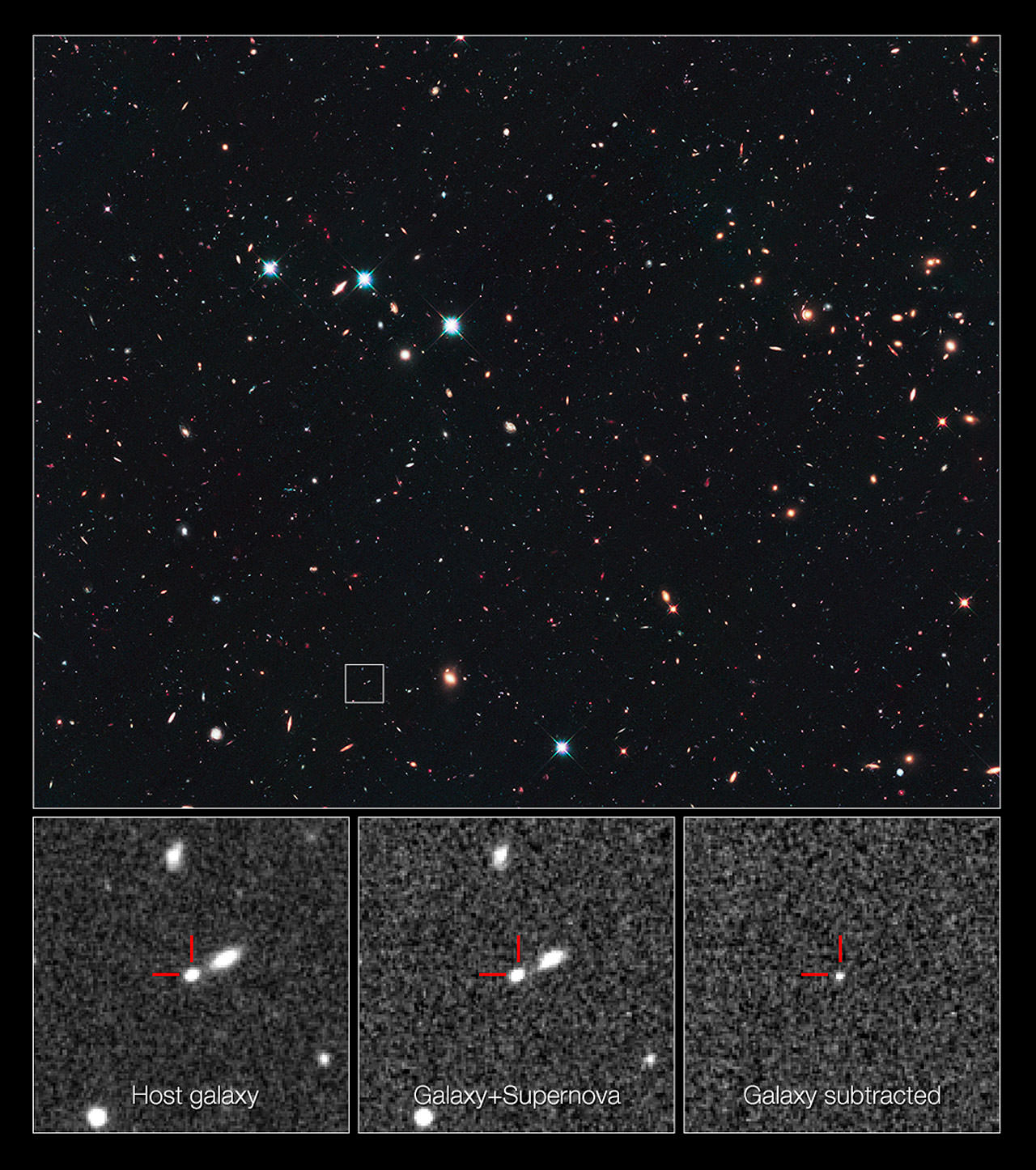

Astronomers just keep honing their skills and refining their techniques to get the most out of their telescopes. Scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope have now broken the record for the most distant Type Ia supernova ever imaged. This supernova is over 10 billion light-years away, with a redshift of 1.914. When this star exploded 10 billion years ago, the Universe was in its early formative years and stars were being born at a rapid rate.
“This new distance record holder opens a window into the early Universe, offering important new insights into how these supernovae form,” said astronomer David O. Jones of The Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Md., lead author on the science paper detailing the discovery. “At that epoch, we can test theories about how reliable these detonations are for understanding the evolution of the Universe and its expansion.”

Designated as SN UDS10Wil (and nicknamed SN Wilson after American President Woodrow Wilson (president from 1913-1921), the distant supernova was part of a three-year Hubble program to survey faraway Type Ia supernovae and determine whether they have changed during the 13.8 billion years since the explosive birth of the universe. Since 2010, the CANDELS+CLASH Supernova Project has uncovered more than 100 supernovae of all types that exploded from 2.4 to over 10 billion years ago.
The previous record holder for Type Ia was announced earlier this year, a supernova that exploded around 9 billion years ago and has a redshift of 1.7. Although SN Wilson is only 4 percent more distant than the previous record holder, it pushes roughly 350 million years farther back in time.
The most distant supernovae ever are a pair of super-luminous supernovae, at redshifts of 2.05 and 3.90, announced in November 2012. Read about that discovery here.
Astronomers took advantage of the sharpness and versatility of Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to search for supernovae in near-infrared light and verify their distance with spectroscopy. These bright beacons are prized by astronomers because they can be used as a yardstick for measuring cosmic distances, thereby yielding clues to the nature of dark energy, the mysterious force accelerating the rate of expansion of the Universe.
Additionally, finding remote supernovae provides a powerful method to measure the universe’s accelerating expansion.
“The Type Ia supernovae give us the most precise yardstick ever built, but we’re not quite sure if it always measures exactly a yard,” said team member Steve Rodney of Johns Hopkins University. “The more we understand these supernovae, the more precise our cosmic yardstick will become.”
Read the team’s paper: The Discovery of the Most Distant Known Type Ia Supernova at Redshift 1.914
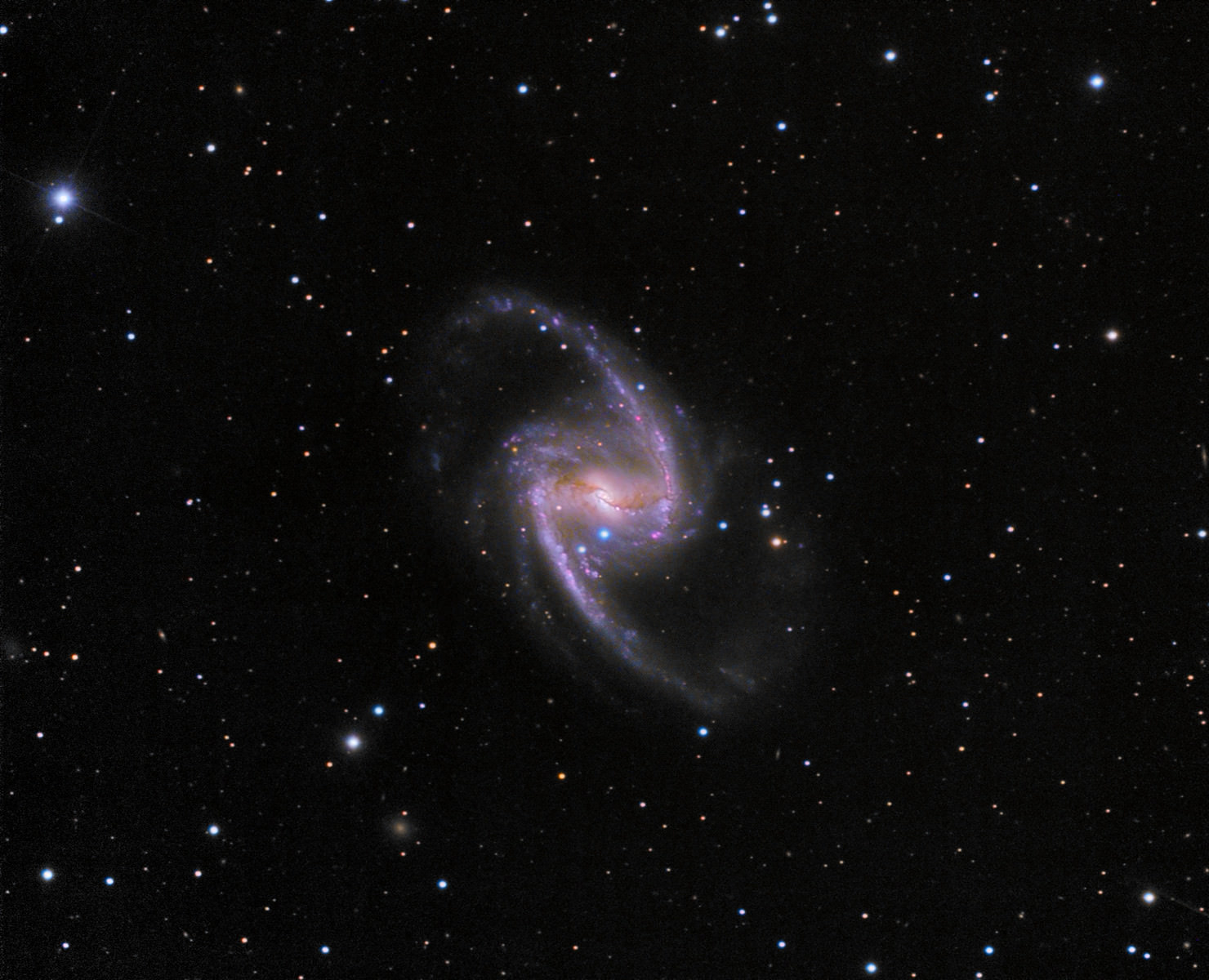
New Bright and Blue Supernova in NGC 1365
Supernova 2012fr in NGC 1365. It is the bright blue “star” directly below the galaxy core. Credit: Rolf Wahl Olsen. Click the image for larger version.
A very bright supernova has shown up in NGC 1365, the galaxy also known as the Great Barred Spiral Galaxy, visible now for southern hemisphere observers. This already elegant galaxy lies about 56 million light-years away in the constellation Fornax. The supernova, a type Ia, was discovered by Alain Klotz with the TAROT telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile on October 27, 2012. “The supernova is a very nice addition to the already highly photogenic galaxy,” said Rolf Wahl Olsen, who took the gorgeous image above. “I’m amazed by how blue it is; it’s really intense.”
Supernova 2012fr is the bright and intensely blue star directly below the galaxy core. Olsen said that as of November 10, 2012 the supernova appeared to be nearing its peak, with an R magnitude of 11.90.
“To get an idea of how bright this event is we can calculate the absolute magnitude M of the supernova using the following formula where m is the apparent magnitude and D the distance in parsecs: M = m – 5(log10(D) – 1),” Olsen wrote. “This gives an absolute magnitude of -19.27 for SN2012fr. This means that if the supernova had occurred at a distance to us similar to Betelgeuse (643 light years), then its apparent magnitude would be -12.80, same as the full Moon!”
Details about Olsen’s image:
Date: 7th and 9th November 2012
Exposure: LRGB: 205:57:56:51m, total 6hrs 9mins @ -30C
Telescope: 10″ Serrurier Truss Newtonian f/5
Camera: QSI 683wsg with Lodestar guider
Filters: Astrodon LRGB E-Series Gen 2
Taken from his observatory in Auckland, New Zealand
See more of Olsen’s astrophotography at his Flickr page.
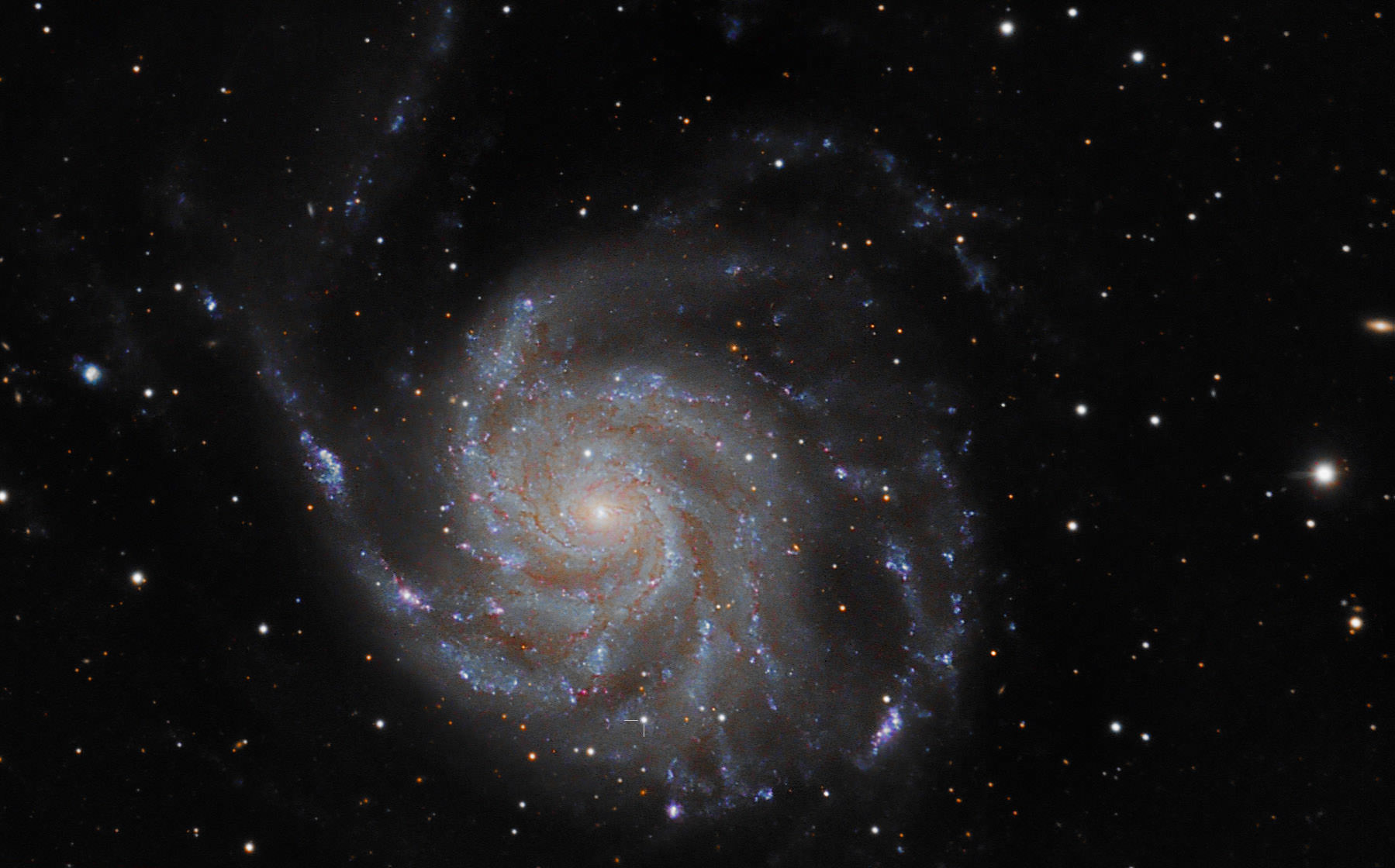
Astrophoto: Supernova PTF11kly During and After
It was literally an event of stellar proportions! In August 2011, a new Type Ia supernova was seen in spiral galaxy M101 a.k.a the Pinwheel Galaxy, located 25 million light-years away. Called PTF11kly, the bright supernova was a target for many astrophotographers. But what does it look like now? Here is a side-by-side comparison by Bill Schlosser from Ohio. It shows his image of the supernova on Sept. 26th, 2011 and then more recently, on June 9th, 2012. “The first was taken through my Astro Tech 10″ RC (I have since sold it) and the second through my TEC 140mm APO,” Bill wrote, and it clearly shows the supernova at its height (brightest object in the left picture, in the lower left side of the galaxy) to what it is today — a small blue blob in the right-hand image. Bill is wondering if it is possibly a becoming nebula now?
Great comparison shots! Check out Bill’s Flickr page for more great photos.
Want to get your astrophoto featured on Universe Today? Join our Flickr group or send us your images by email (this means you’re giving us permission to post them). Please explain what’s in the picture, when you took it, the equipment you used, etc.
The Contributor to SN 2011fe
[/caption]
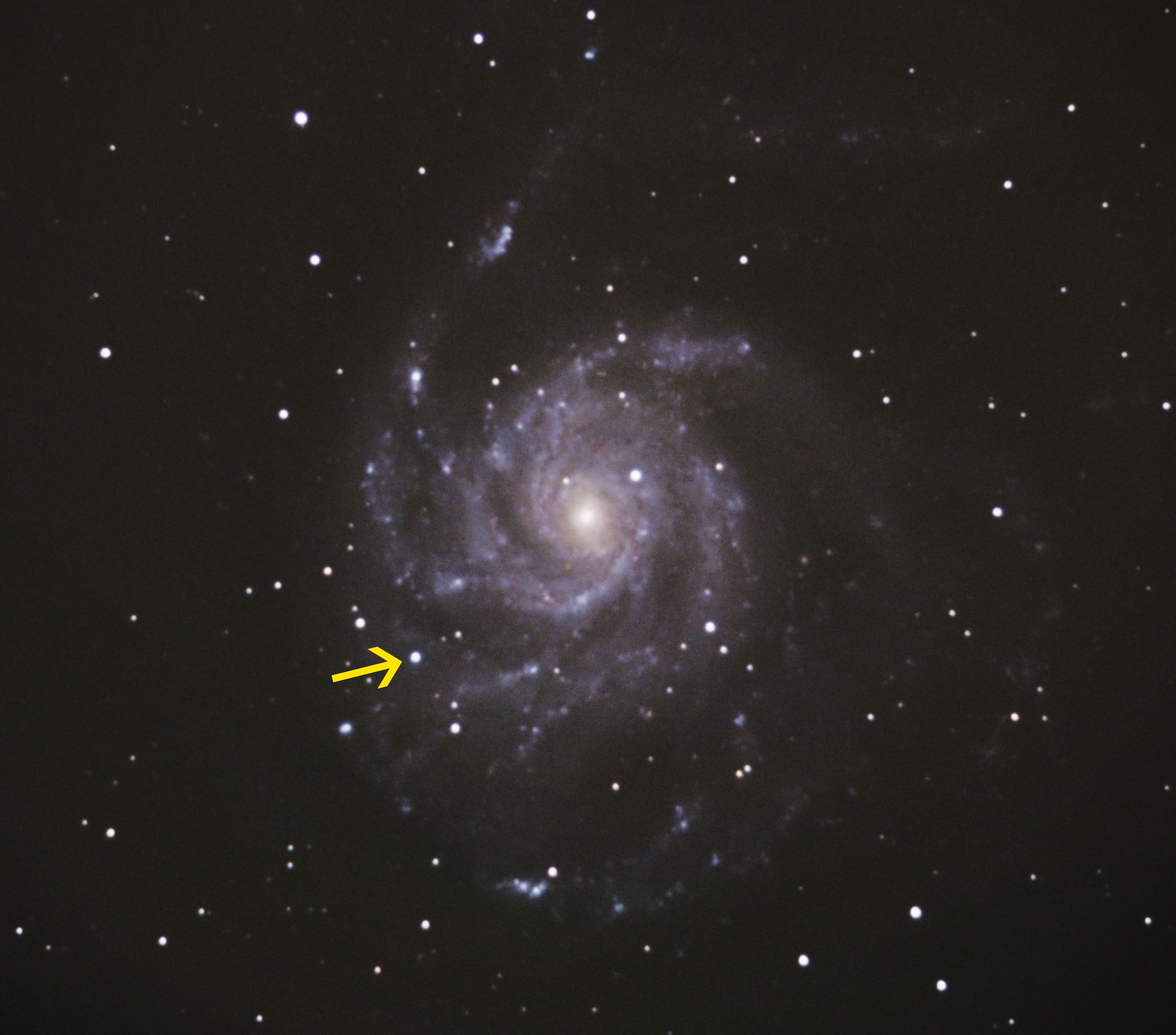
When discovered on August 24, 2011, supernova 2011fe was the closest supernova since the famous SN 1987A. Located in the relatively nearby Pinwheel galaxy (M101), it was a prime target for scientists to study since the host galaxy has been well studied and many high resolution images exist from before the explosion, allowing astronomers to search them for information on the star that led to the eruption. But when astronomers, led by Weidong Li, at the University of California, Berkeley searched, what they found defied the typically accepted explanations for supernovae of the same type as 2011fe.
SN 2011fe was a type 1a supernova. This class of supernova is expected to be caused by a white dwarf which accumulates mass contributed by a companion star. The general expectation is that the companion star is a star evolving off the main sequence. As it does, it swells up, and matter spills onto the white dwarf. If this pushes the dwarf’s mass over the limit of 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the star can no longer support the weight and it undergoes a runaway collapse and rebound, resulting in a supernova.
Fortunately, the swollen up stars, known as red giants, become exceptionally bright due to their large surface area. The eighth brightest star in our own sky, Betelgeuse, is one of these red giants. This high brightness means that these objects are visible from large distances, potentially even in galaxies as distant as the Pinwheel. If so, the astronomers from Berkeley would be able to search archival images and detect the brighter red giant to study the system prior to the explosion.
But when the team searched the images from the Hubble Space Telescope which had snapped pictures through eight different filters, no star was visible at the location of the supernova. This finding follows a quick report from September which announced the same results, but with a much lower threshold for detection. The team followed up by searching images from the Spitzer infrared telescope which also failed to find any source at the proper location.
While this doesn’t rule out the presence of the contributing star, it does place constraints on its properties. The limit on brightness means that the contributor star could not have been a luminous red giant. Instead, the result favors another model of mass donation known as a double-degenerate model
In this scenario, two white dwarfs (both supported by degenerate electrons) orbit one another in a tight orbit. Due to relativistic effects, the system will slowly lose energy and eventually the two stars will become close enough that one will become disrupted enough to spill mass onto the other. If this mass transfer pushes the primary over the 1.4 solar mass limit, it would trigger the same sort of explosion.
This double degenerate model does not exclusively rule out the possibility of red giants contributing to type Ia supernovae, but recently other evidence has revealed missing red giants in other cases.
Supernova Alphabet Soup
[/caption]
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is the sole body responsible for the official naming of astronomical objects. So if you have a problem with the way things in the Universe are named, you now know where to send your email and letters of protest.
Before we get into this, a quick grammar note. When we discuss more than one supernova, they are called supernovae (super- no- vee), not supernovas. The same holds true for more than one nova. They are novae (no- vee). Please don’t write and ask me about Novas. Those are old Chevrolets, not stars.
Fortunately, the naming convention used for supernovae is pretty simple and straightforward.
The name is formed by combining the prefix SN, for supernova, the year of discovery and a one- or two-letter designation. The first 26 supernovae of the year get an upper case letter from A to Z (SN 1987A). After that, we start over with pairs of lower-case letters are used, starting with aa, ab, and so on (SN 2005ap).
Of course there are exceptions, there are always exceptions. That’s one of the things about astronomical nomenclature that is maddening, but I digress…
Four important historical supernovae are known simply by the year they occurred- SN 1006, SN 1054, SN 1572 (more commonly referred to as Tycho’s Nova), and SN 1604 (also known as Kepler’s Star).
One reason I’m bringing this subject up now is that we are ending the year, so we are approaching the time where we reset the naming schema for 2012 and the first supernova of the new year will get named SN 2012A. With the annual number of discoveries rising each year to well over 500, it is always a bit surprising how long it takes for that first one of the year to get named. So each year we hold an unofficial contest to see who will discover the first SN of the new year.
One of the reasons it usually doesn’t occur on the first day of the year is that supernova discoveries have to be officially confirmed spectroscopically before they get an official IAU designation. When someone discovers a possible supernova it gets reported to the IAU and then listed on the CBAT Transient Objects Confirmation Page. If it is a possible SN it gets a temporary designation of PSN (possible supernova) followed by its coordinates (PSN J01560719+1738468).
Only after someone has taken a spectrum confirming it is a supernova does it get a name with the year and letter combination. This can take several days, so it is unlikely a SN discovered on January 1 will be named until later in the week or the second week of the month. If it were discovered on December 23rd and confirmed on the 1st of January it would still get a name from the previous year.
This time lag will not be acceptable in the near future, with surveys like LSST coming on line. Astronomers will want immediate notification of discoveries of all types of transient objects including supernovae, so what has happened is new groups searching for SNe have begun to make up their own names.
The Catalina Real Time Survey is one such group. They are discovering dozens of possible supernovae that don’t always get official IAU designations. Their discoveries are all named CSS (Catalina Sky Survey) followed by the date in yymmdd format and then the rough coordinates, like this CSS111227:104742+021815. Crazy, huh?
ROTSE, the Robotic Optical Transient Search Experiment, also discoveries SNe and gives them their own designation in the form of ROTSE3 (the third iteration of this experiment) followed by coordinates, such as ROTSE3 J133033.0-313427.
And there is the Palomar Transient Factory which names its discoveries with the prefix PTF of course, such as PTF11kly, the nearest supernovae in decades, visible with small telescopes in M101. This SN eventually received an IAU designation, SN 2011fe, but that just created more confusion, since now it is known variously by both names in the literature.
Somehow managing to keep it all together amidst the confusion, David Bishop maintains the Latest Supernova Website where you can see discovery images and keep track of your favorite supernovae and related news. There is an excellent article about David and how his website evolved from simple beginnings.
So if you’re asking WTF? about the latest SNe the on the WWW the URL that will lead you through the ABC’s is definitely http://www.rochesterastronomy.org/supernova.html.
Got that? Good, there will be a quiz later…