(Note: we’ll be posting this article as a running blog with updates over the next few mornings, as the Orionids are already moderately active for this week. Watch this space for info as it is added after our first meteor vigil tomorrow morning and Wednesday, weather and clear skies willing…)
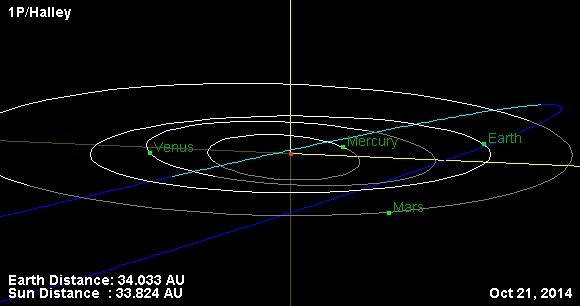
The month of October is about midway through meteor shower season for the northern hemisphere, and one of the annual sure-fire best bets is the Orionid meteor shower. One of two meteor showers emanating from debris shed by that most famous of all periodic comets –1/P Halley—the Orionids generate a typical zenithal hourly rate of around 20 per hour, though surges heading towards a ZHR of in the range 70 are not unknown on some years.
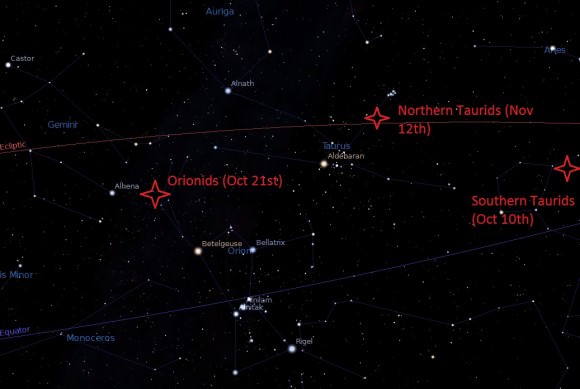
2015 sees the shower peaking right around the morning of Wednesday, October 21st. This will place the Moon at a 59% illuminated waxing gibbous phase and setting around local midnight, setting the stage for dark AM skies, perfect for meteor hunting.
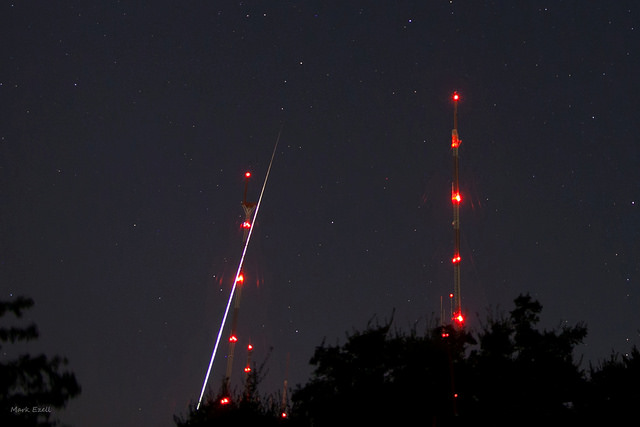
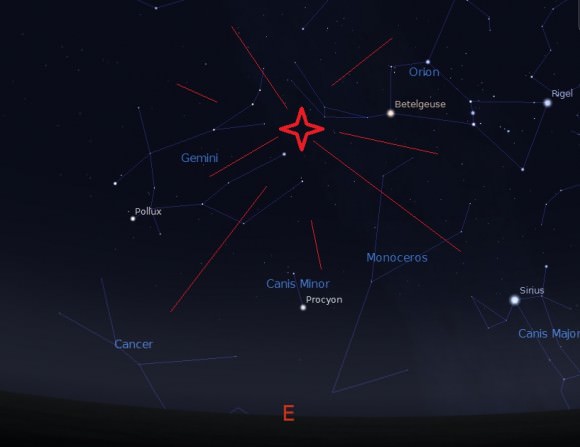
Like the springtime Eta Aquarids also generated by Halley’s Comet, the Orionids are swift movers, striking the atmosphere at about 66 kilometers per second. The shower’s radiant drifts across the club of Orion the Hunter toward the astronomical constellation Gemini near its peak, and the radiant rides highest around 4 AM local time. This is also typically the best time to carry out a meteor vigil, as early morning hours places an Earth-bound observer facing forward into the oncoming meteor stream.
The twin Spring and Fall showers hailing from Halley’s are a product of the geometry of its elliptical orbit: Halley’s Comet spends most of its 75.3 year orbit south of the ecliptic, and only briefly ‘pops up’ northward above the Earth’s orbit for northern hemisphere viewers for a few months around perihelion, which next occurs on July 28th, 2061.
Let’s see, I’ll be 90-something next time Halley’s Comet comes ‘round next…
Like many meteor showers, researchers (with the tongue-twisting title of meteoriticists) are still working to precisely model the debris streams of showers such as the Orionids. There’s evidence to suggest an 11 year periodicity for the Orionid meteor stream undergoing modification by the gravitational influence of the giant planet Jupiter, a period which we’re approximately passing the mid-point low for in 2015.
Rates for the Orionids from previous years seem to support this trend: over the last few years, observers saw the Orionids top out at a ZHR of 21(2014), 45(2012), 33(2011) and 38(2010) as per the International Meteor Organization (IMO).
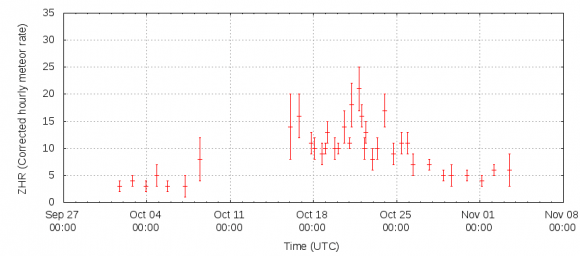
The next few mornings are key for a successful Orionid vigil. The Orionids also display a broad swath of activity, typically running from early October, to the first week of November before falling back down to levels below the background sporadic rate.
And while 2015 may be an off year for the Orionids, another shower may prompt a once a decade fireball swarm to rival the Full Moon this Halloween right into early November…
Will the Northern Taurids of 2015 perform? Stay tuned!
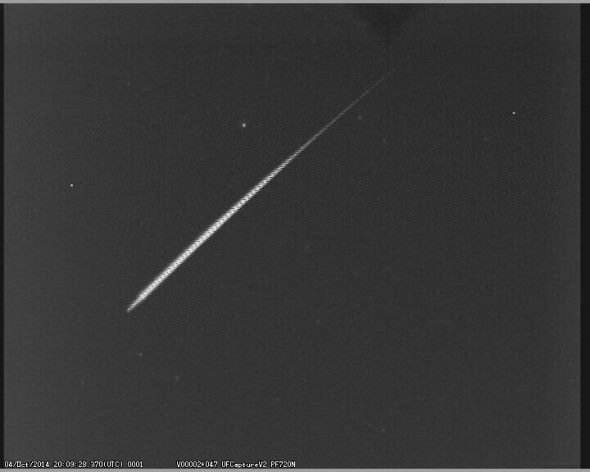
Update: Well, skies were indeed clear over the Central Florida peninsula this AM, allowing for a brief one hour vigil before dawn ensued. We counted three swift Orionids for about 40 minutes of total effective observing time, suggesting the the current rate is already well above the background sporadic rate, not bad. A late season Draconid meteor, and a curious unidentified tumbling satellite on a retrograde (read ‘Earth observing’ or spy satellite) orbit also joined the fray, along with the current cavalcade of dawn planets. A nice pass of the Hubble Space Telescope capped off the session as dawn broke, not bad.

The Orionids are noticeably speedy, flitting briefly in and out of view. Another great plus with this shower: The radiant is almost directly at the zenith for Florida residents at around 5 AM or so. This means that the Orionids can be enjoyed fairly far southward as well… has anyone ever studied just why a majority of major meteor shower radiants reside in the northern hemisphere?
The IMO hasn’t yet put up their live tracker yet, but hey, you can still report those Orionid rates worldwide…. We’ll see what Wednesday and Thursday morning brings as the Orionid meteor peak arrives. Unlike many showers, the Orionids have a very broad peak, and should be active all week into late October.
And don’t forget the tweet those sightings to #Meteorwatch!