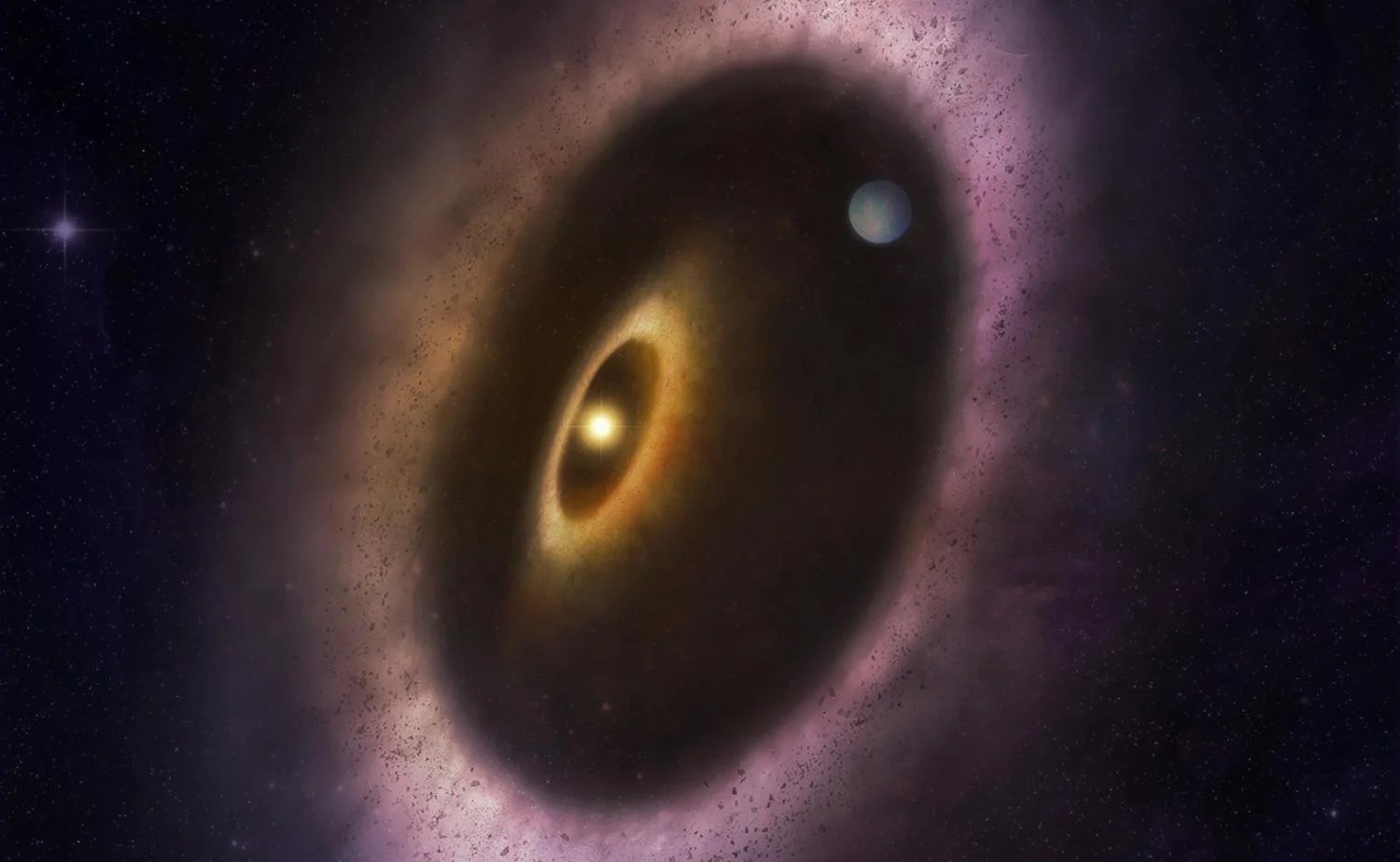
According to the most widely-accepted theory, planetary systems form from large clouds of dust and gas that form disks around young stars. Over time, these disks accrete to create planets of varying size, composition, and distance from their parent star. In the past few decades, observations in the mid- and far-infrared wavelengths have led to the discovery of debris disks around young stars (less than 100 million years old). This has allowed astronomers to study planetary systems in their early history, providing new insight into how systems form and evolve.
This includes the SpHere INfrared survey for Exoplanets (SHINE) consortium, an international team of astronomers dedicated to studying star systems in formation. Using the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), the SHINE collaboration recently directly imaged and characterized the debris disk of a nearby star (HD 114082) in visible and infrared wavelengths. Combined with data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Space Satellite (TESS), they were able to detect a gas giant many times the size of Jupiter (a “Super-Jupiter”) embedded within the disk.
Continue reading “Astronomers Directly Image Debris Disk and find a Jupiter-Sized Planet Orbiting a Sunlike Star”