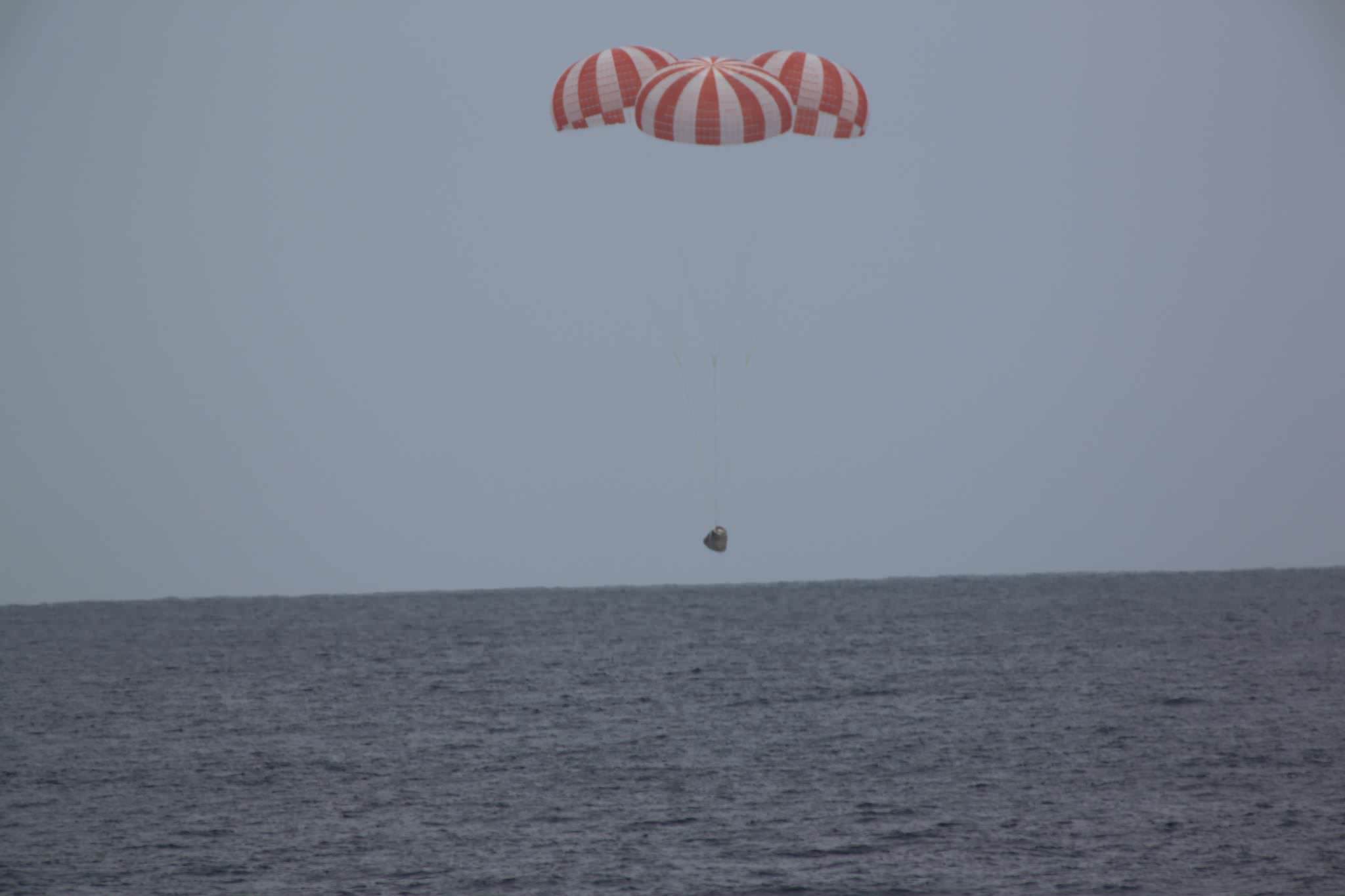
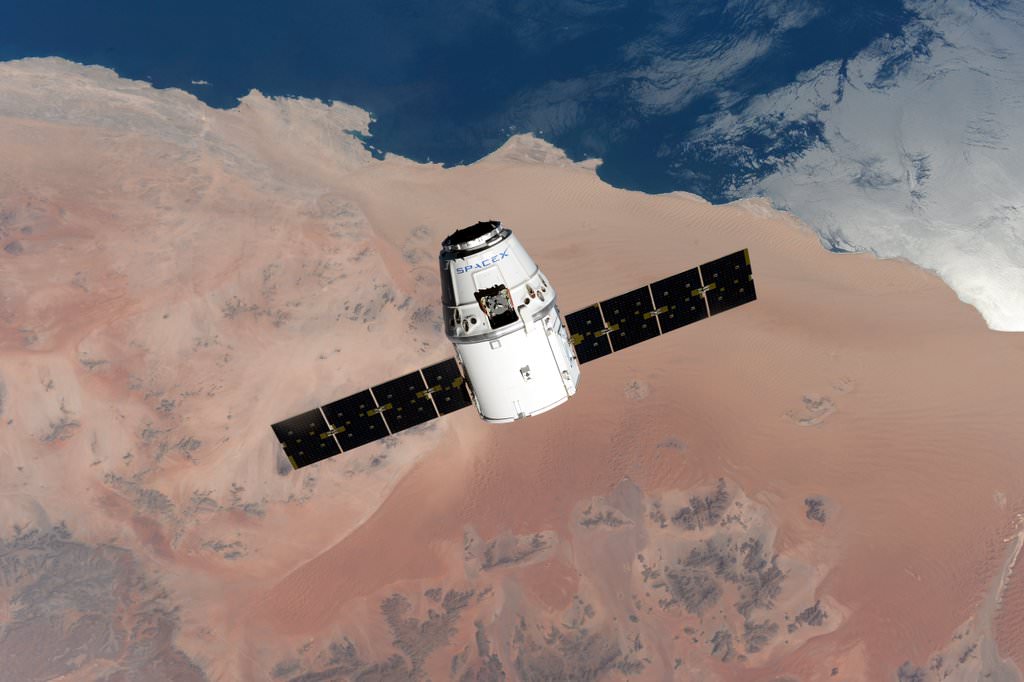
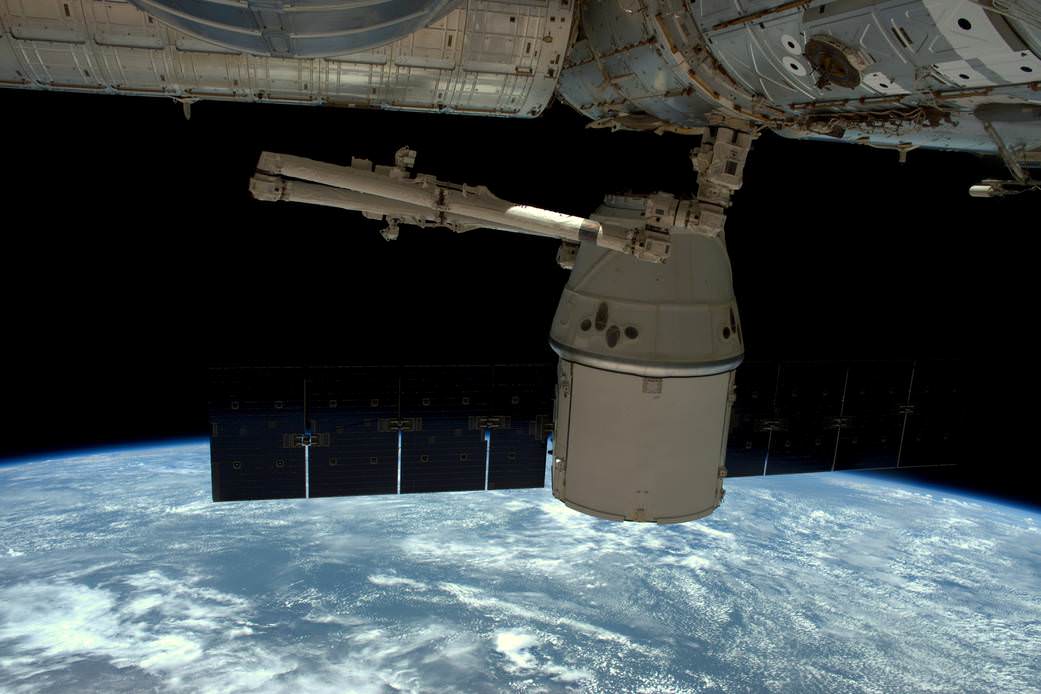
A SpaceX cargo Dragon spacecraft loaded with nearly two tons of critical NASA science and technology experiments and equipment returned to Earth this afternoon, Wednesday, May 11, safely splashing down in the Pacific Ocean – and bringing about a successful conclusion to its mission to the International Space Station (ISS) that also brought aloft a new room for the resident crew.
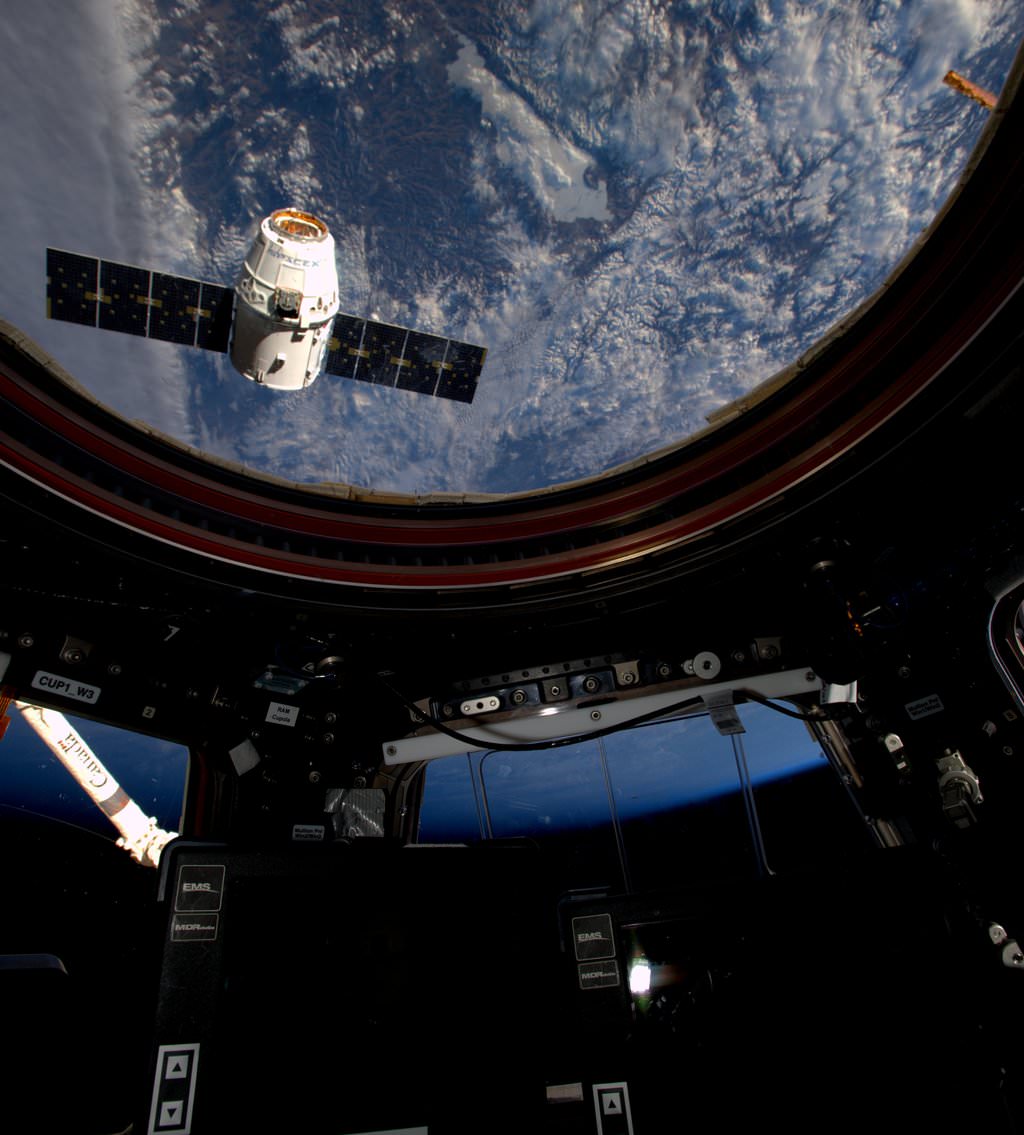
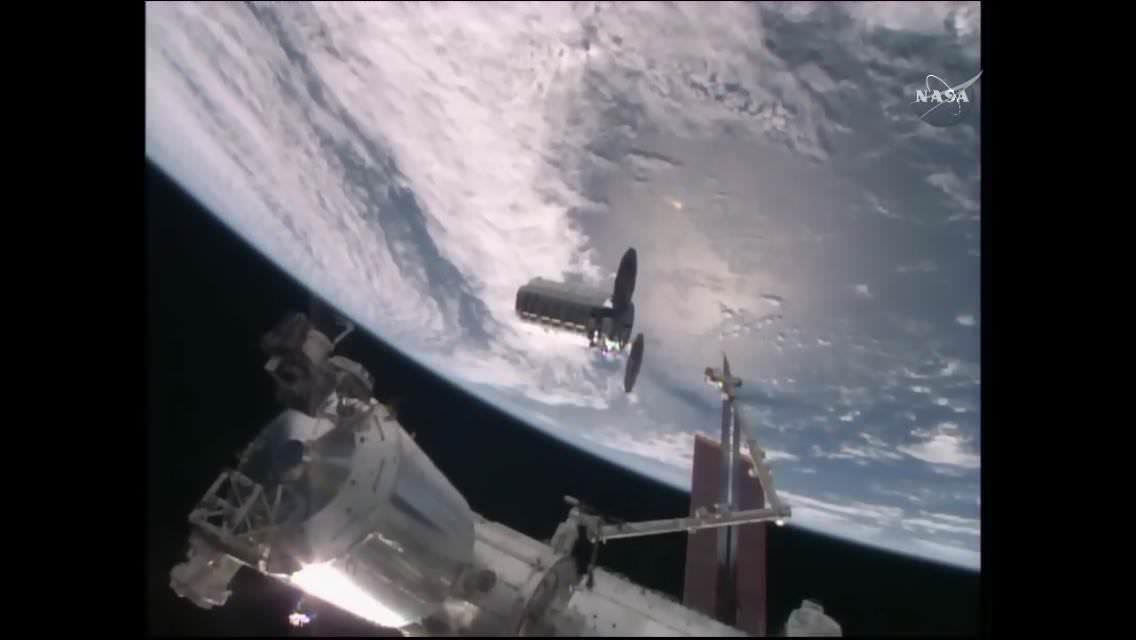
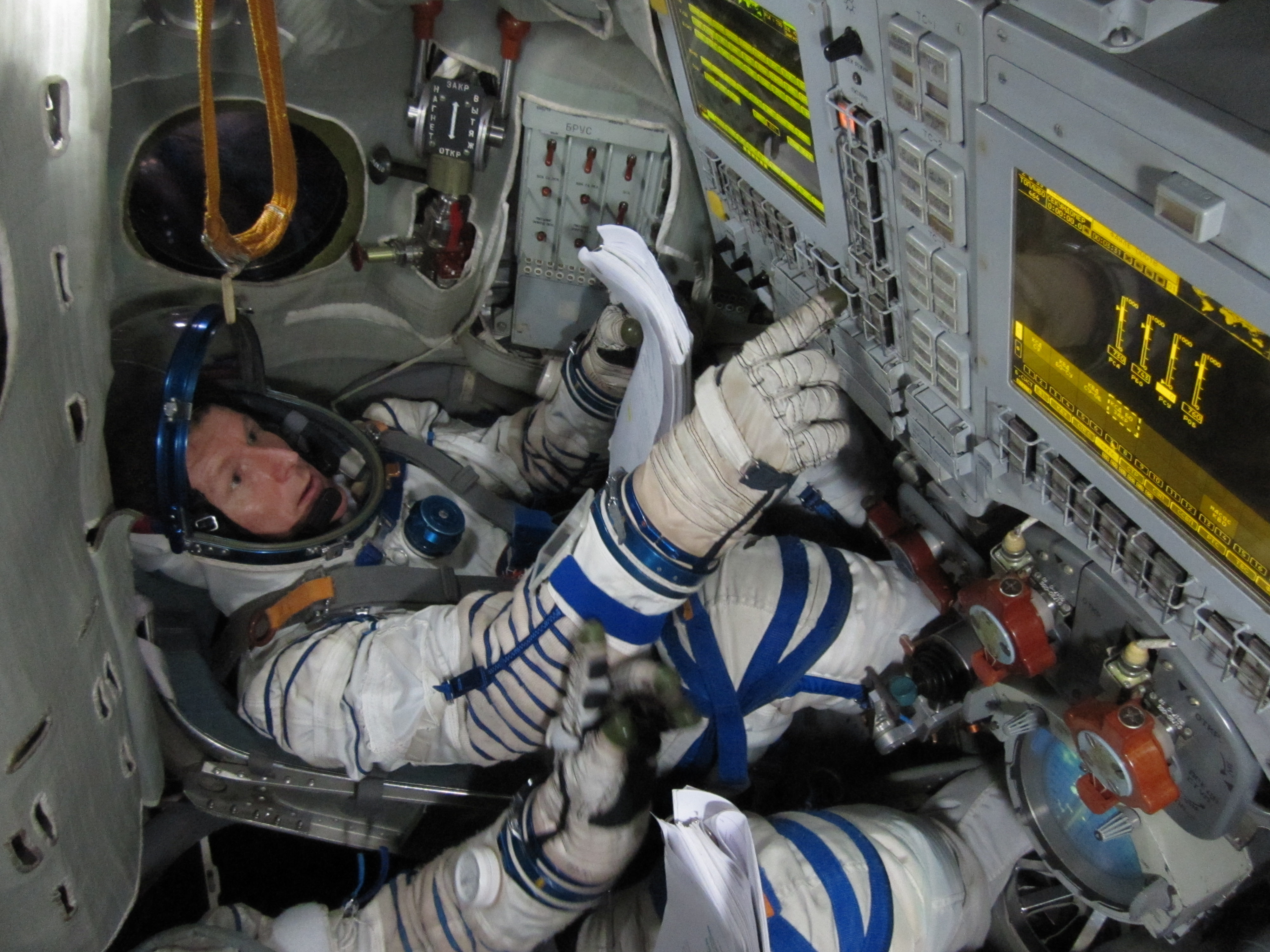
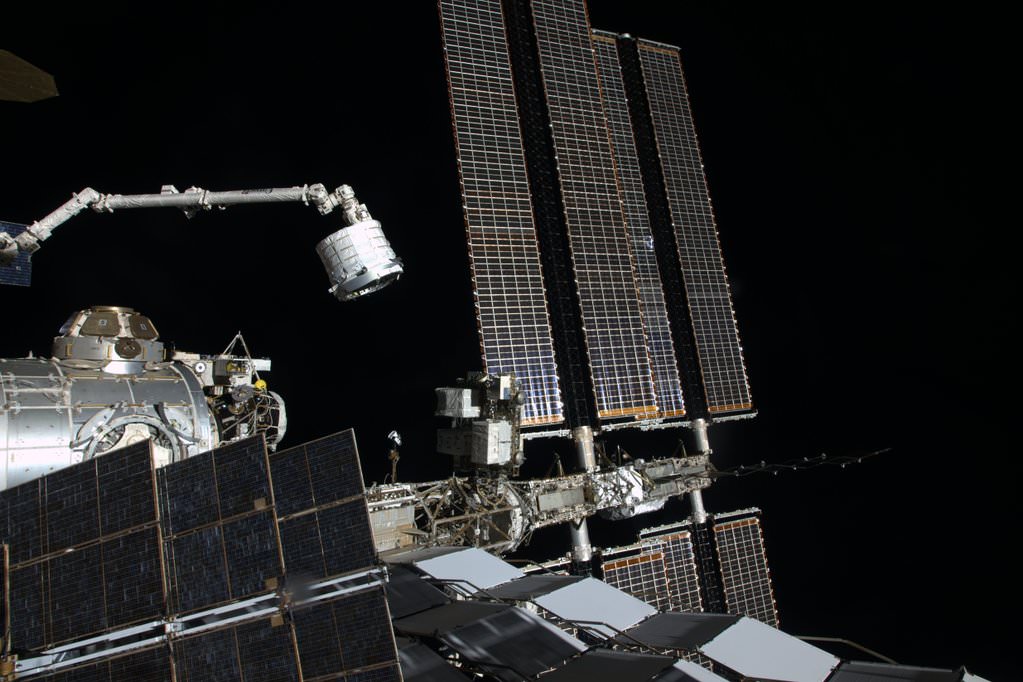
Following a month long stay at the orbiting outpost, the unmanned Dragon was released from the grip of the stations Canadian-built robotic arm at 9:19 a.m. EDT by European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Tim Peake.
After being detached from its berthing port at the Earth-facing port on the stations Harmony module by ground controllers, Peake commanded the snares at the terminus of the 57 foot long (19 meter long) Canadarm2 to open – as the station was soaring some 260 miles (418 kilometers) over the coast of Australia southwest of Adelaide.
Dragon backed away and soon departed after executing a series of three departure burns and maneuvers to move beyond the 656-foot (200-meter) “keep out sphere” around the station.

“The Dragon spacecraft has served us well, and it’s good to see it departing full of science, and we wish it a safe recovery back to planet Earth,” Peake said.
Dragon fired its braking thrusters to initiate reentry back into the Earth’s atmosphere, and survived the scorching 3000+ degree F temperatures for the plummet back home.
A few hours after departing the ISS, Dragon splashed down in the Pacific Ocean at 2:51 p.m. EDT today, descending under a trio of huge orange and white main parachutes about 261 miles southwest of Long Beach, California.
“Good splashdown of Dragon confirmed, carrying thousands of pounds of @NASA science and research cargo back from the @Space_Station,” SpaceX notified via Twitter.
It was loaded with more than 3,700 pounds of NASA cargo, science and technology demonstration samples including a final batch of human research samples from former NASA astronaut Scott Kelly’s historic one-year mission that concluded in March.
“Thanks @SpaceX for getting our science safely back to Earth! Very important research,” tweeted Kelly soon after the ocean splashdown.
Among the study samples returned are those involving Biochemical Profile, Cardio Ox, Fluid Shifts, Microbiome, Salivary Markers and the Twins Study.
The goal of Kelly’s one-year mission was to support NASA’s plans for a human ‘Journey to mars’ in the 2030s. Now back on the ground Kelly continues to support the studies as a human guinea pig providing additional samples to learn how the human body adjusts to weightlessness, isolation, radiation and the stress of long-duration spaceflight.
Among the other items returned was a faulty spacesuit worn by NASA astronaut Tim Kopra. It will be analyzed by engineers to try and determine why a small water bubble formed inside Kopra’s helmet during his spacewalk in January that forced it to end prematurely as a safety precaution.
Dragon was plucked from the ocean by SpaceX contracted recovery ships and is now on its way to port in Long Beach, California.
“Dragon recovery team on site after nominal splashdown in Pacific,” said SpaceX.
“Some cargo will be removed and returned to NASA, and then be prepared for shipment to SpaceX’s test facility in McGregor, Texas, for processing,” says NASA.
Currently Dragon is the only station resupply craft capable of returning significant quantities of cargo and science samples to Earth.
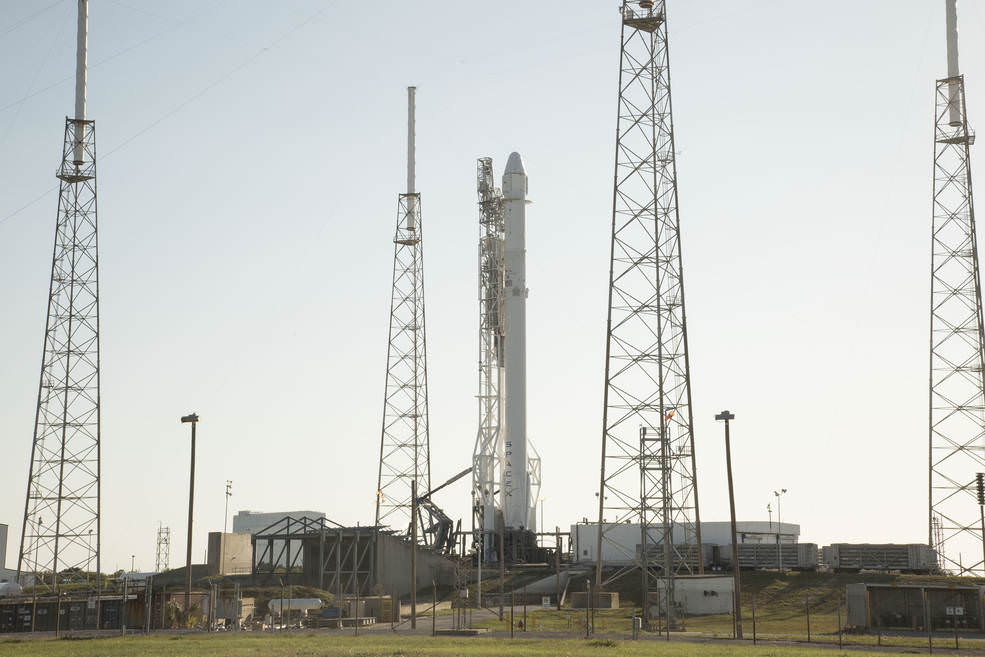
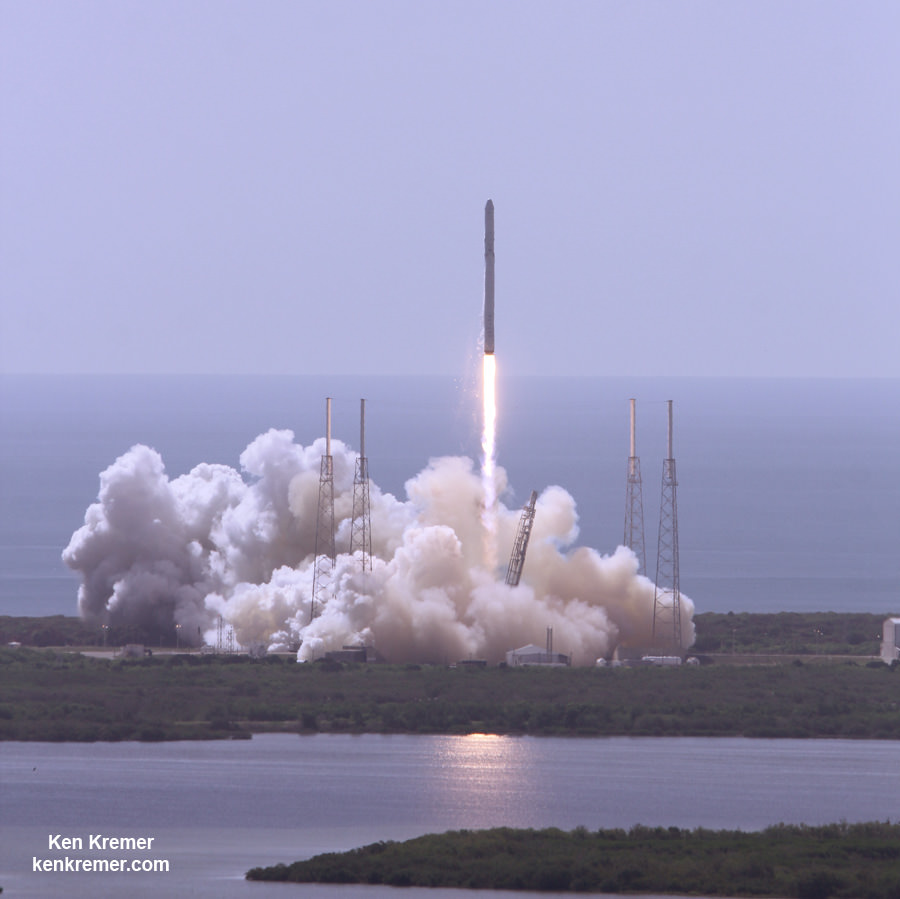
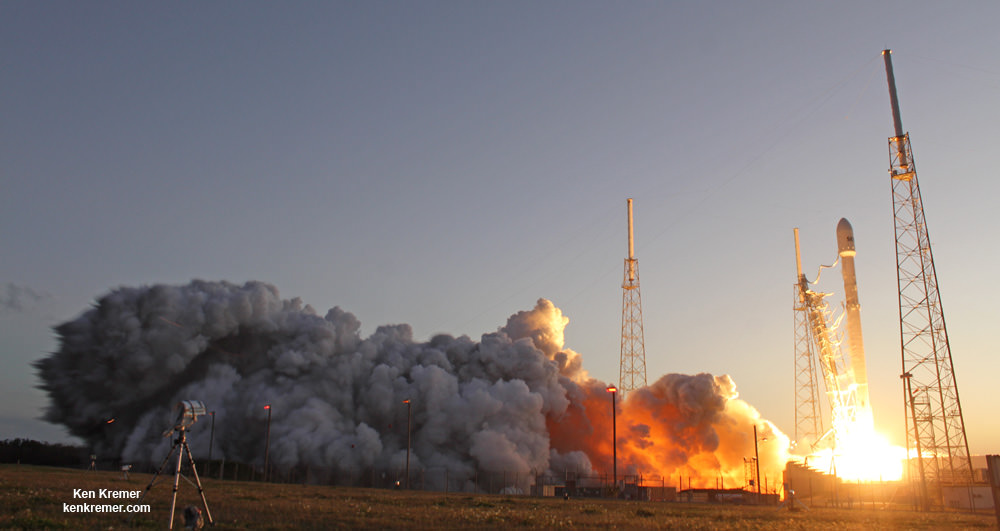
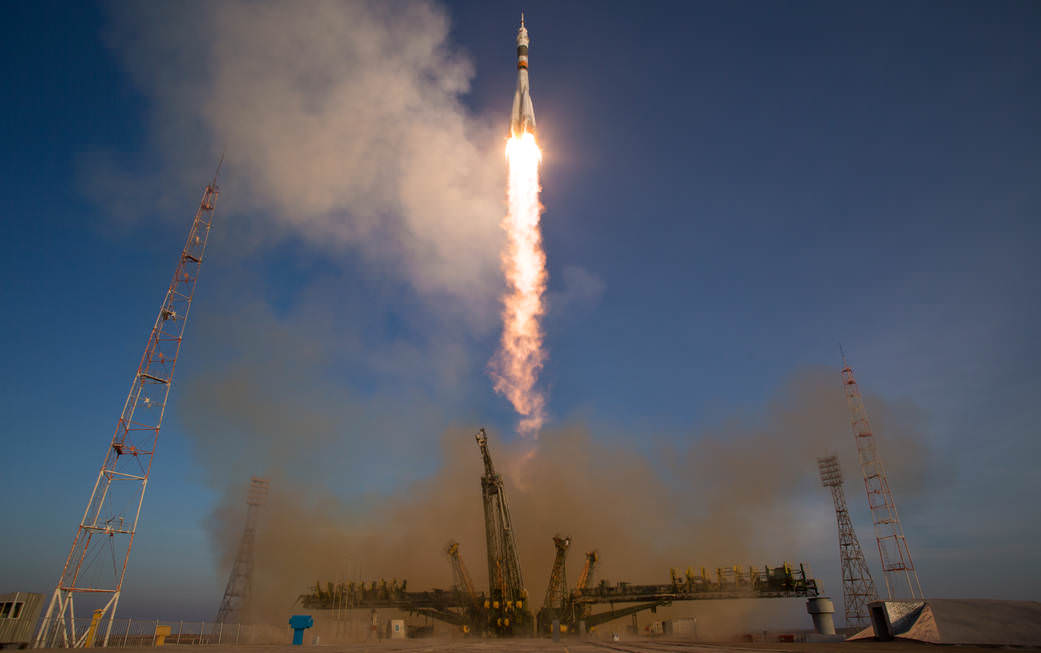
The Dragon CRS-8 cargo delivery mission began with a spectacular blastoff atop an upgraded version of the two stage SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, boasting over 1.5 million pounds of thrust on Friday, April 8 at 4:43 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The primary goal of the Falcon 9 launch was carrying the SpaceX Dragon CRS-8 cargo freighter to low Earth orbit on a commercial resupply delivery mission for NASA to the International Space Station (ISS).
Relive the launch via this video of the SpaceX Falcon 9/Dragon CRS-8 liftoff from my video camera placed at the pad:
Video Caption: Spectacular blastoff of SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Dragon CRS-8 cargo freighter bound for the International Space Station (ISS) from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL at 4:43 p.m. EST on April 8, 2016. Up close movie captured by Mobius remote video camera placed at launch pad. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
The SpaceX commercial cargo freighter was jam packed with more than three and a half tons of research experiments, essential crew supplies and a new experimental inflatable habitat for it deliver run.
After a two day orbital chase it reached the ISS and the gleeful multinational crew of six astronauts and cosmonauts on Sunday, April 10.
Expedition 47 crew members Jeff Williams and Tim Kopra of NASA, Tim Peake of ESA (European Space Agency) and cosmonauts Yuri Malenchenko, Alexey Ovchinin and Oleg Skripochka of Roscosmos are currently living aboard the orbiting laboratory.
CRS-8 counts as the company’s eighth flight to deliver supplies, science experiments and technology demonstrations to the ISS for the crews of Expeditions 47 and 48 to support dozens of the approximately 250 science and research investigations in progress.
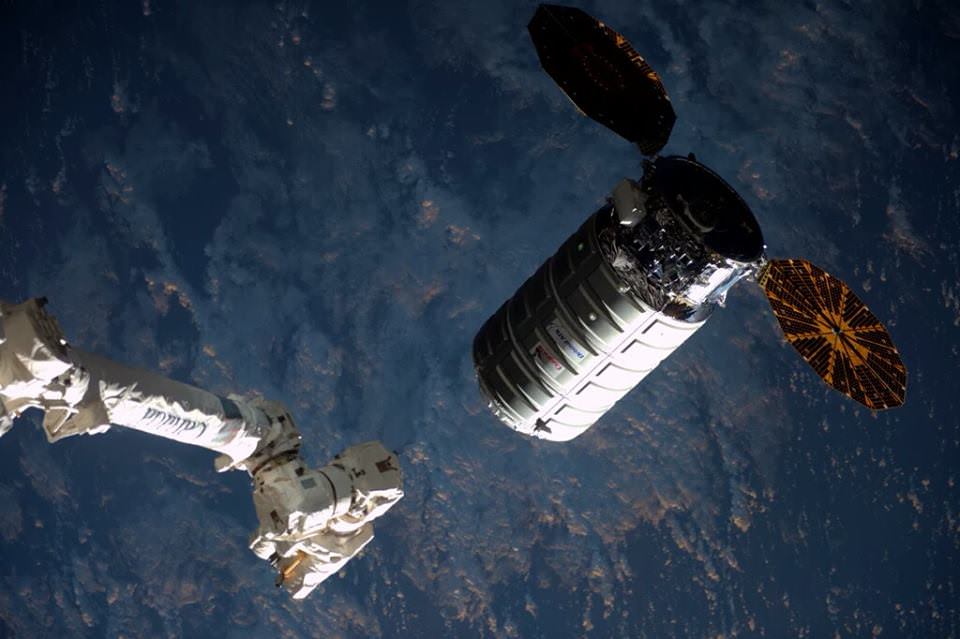
In a historic first, the arrival of the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft marked the first time that two American cargo ships are simultaneously docked to the ISS. The Orbital ATK Cygnus CRS-6 cargo freighter arrived two weeks earlier on March 26 and is now installed at a neighboring docking port on the Unity module.
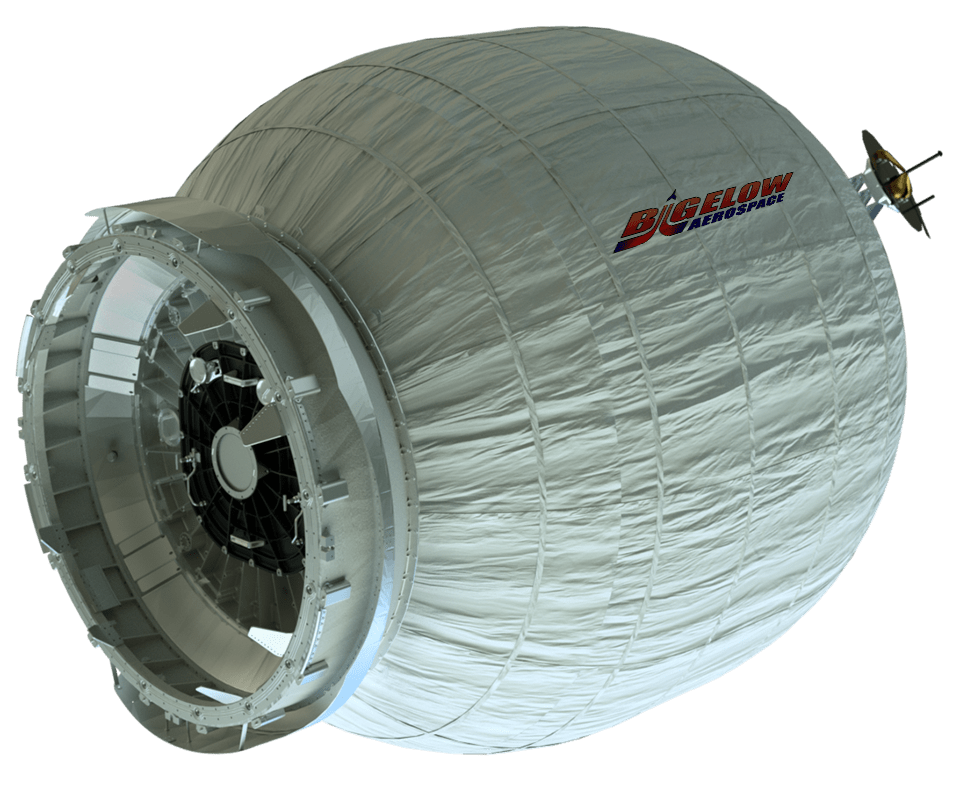
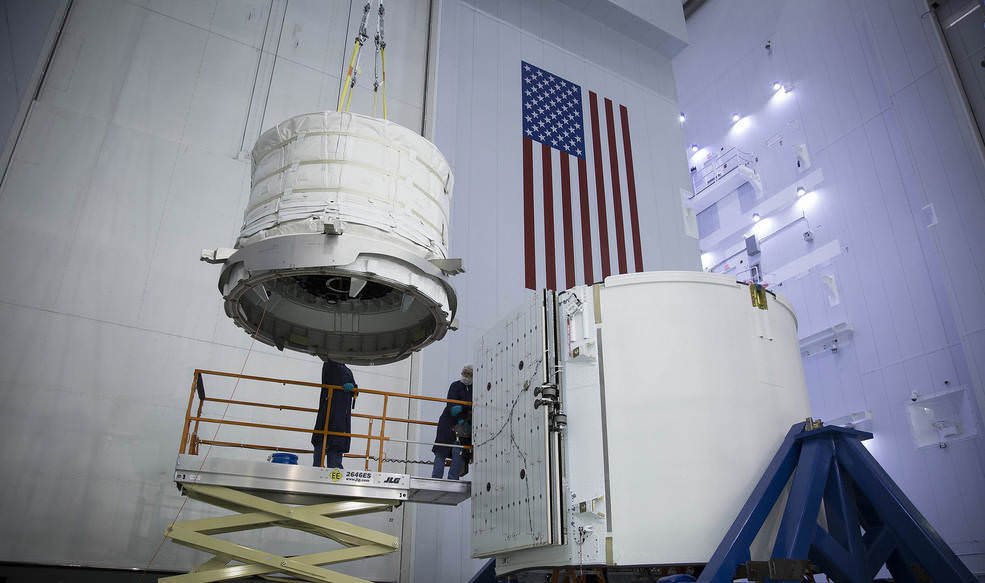
The Dragon spacecraft delivered almost 7,000 pounds of cargo, including the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), to the orbital laboratory which was carried to orbit inside the Dragon’s unpressurized truck section.
BEAM is a prototype inflatable habitat that the crew plucked from the Dragon’s truck with the robotic arm for installation on a side port of the Tranquility module on April 16.

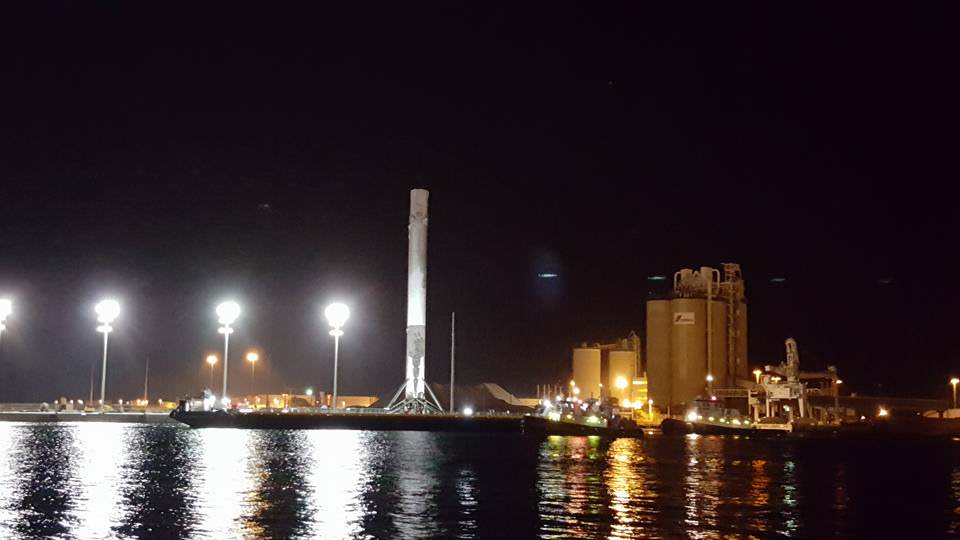
Minutes after the successful April 8 launch, SpaceX accomplished their secondary goal – history’s first upright touchdown of a just flown rocket onto a droneship at sea.
The recovered booster arrived back at Port Canaveral a few days later and was transported back to the firms processing hanger at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) for testing and eventual reflight.

The next NASA contracted cargo launch to the ISS by SpaceX is currently slated for late June from Cape Canaveral.
The next Orbital ATK Cygnus cargo launch is slated for July from NASA Wallops.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
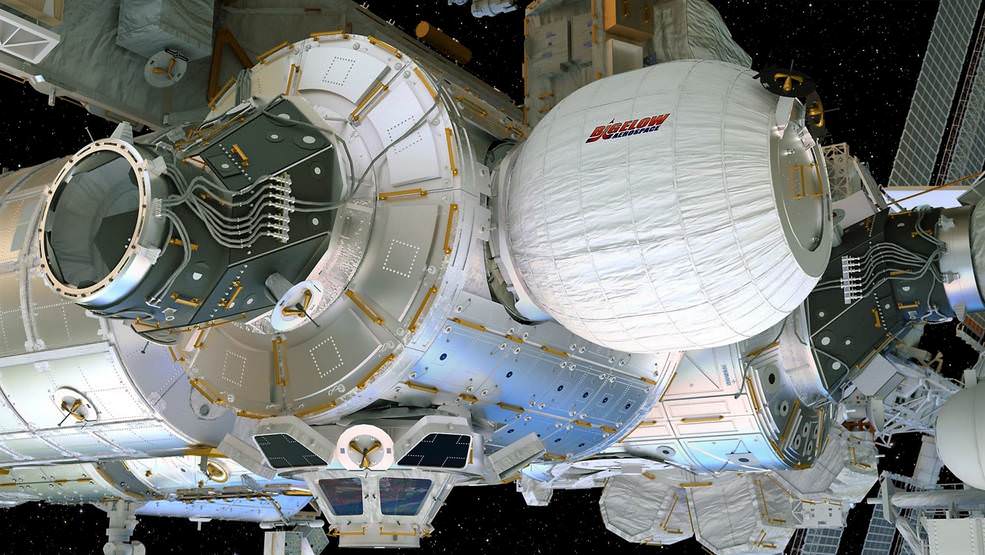

Credits: Bigelow Aerospace