Few places in the solar system are better suited to a balloon than Titan. The combination of low gravity and high atmospheric density makes Saturn’s largest moon ideal for a lighter than “air” vehicle, and the idea to put one there has been around for at least two decades. So why haven’t we yet? The simple answer is the size of the necessary balloon is too large for the existing launch platforms. But a team from Boeing, the prime contractor on the Space Launch System (SLS), believes their new launch platform will be capable of getting a large balloon into orbit, along with its necessary scientific payload – and start unlocking the mysteries of this intriguing moon.
Continue reading “SLS Could Launch A Titan Balloon Mission”A Mission to Dive Titan’s Lakes – and Soar Between Them
Titan is one of the solar system’s most fascinating worlds for several reasons. It has something akin to a hydrological cycle, though powered by methane. It is the solar system’s second-largest moonMooner our own. It is the only other body with liquid lakes on its surface. That’s part of the reason it has attracted so much attention, including an upcoming mission known as Dragonfly that hopes to use its thick atmosphere to power a small helicopter. But some of the most interesting features on Titan are its lakes, and Dragonfly, given its means of locomotion, can’t do much with those other than look at them from afar. So another mission, initially conceived by James McKevitt, then an undergraduate at Loughborough University but now a PhD student at University College London would take a look at both their surface and underneath.
Continue reading “A Mission to Dive Titan’s Lakes – and Soar Between Them”Could Comets have Delivered the Building Blocks of Life to “Ocean Worlds” like Europa, Enceladus, and Titan too?
Throughout Earth’s history, the planet’s surface has been regularly impacted by comets, meteors, and the occasional large asteroid. While these events were often destructive, sometimes to the point of triggering a mass extinction, they may have also played an important role in the emergence of life on Earth. This is especially true of the Hadean Era (ca. 4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago) and the Late Heavy Bombardment, when Earth and other planets in the inner Solar System were impacted by a disproportionately high number of asteroids and comets.
These impactors are thought to have been how water was delivered to the inner Solar System and possibly the building blocks of life. But what of the many icy bodies in the outer Solar System, the natural satellites that orbit gas giants and have liquid water oceans in their interiors (i.e., Europa, Enceladus, Titan, and others)? According to a recent study led by researchers from Johns Hopkins University, impact events on these “Ocean Worlds” could have significantly contributed to surface and subsurface chemistry that could have led to the emergence of life.
Continue reading “Could Comets have Delivered the Building Blocks of Life to “Ocean Worlds” like Europa, Enceladus, and Titan too?”Experimental Radar Technique Reveals the Composition of Titan’s Seas

The Cassini-Huygens mission to Saturn generated so much data that giving it a definitive value is impossible. It’s sufficient to say that the amount is vast and that multiple scientific instruments generated it. One of those instruments was a radar designed to see through Titan’s thick atmosphere and catch a scientific glimpse of the moon’s extraordinary surface.
Scientists are still making new discoveries with all this data.
Continue reading “Experimental Radar Technique Reveals the Composition of Titan’s Seas”Planetary Protection: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?
Universe Today has recently investigated a plethora of scientific disciplines, including impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, comets, planetary atmospheres, planetary geophysics, cosmochemistry, meteorites, radio astronomy, extremophiles, organic chemistry, black holes, and cryovolcanism, while conveying their importance of how each of them continues to teach researchers and the public about our place in the vast universe.
Continue reading “Planetary Protection: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”Cryovolcanism: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?

Universe Today has had the privilege of spending the last several months venturing into a multitude of scientific disciplines, including impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, comets, planetary atmospheres, planetary geophysics, cosmochemistry, meteorites, radio astronomy, extremophiles, organic chemistry, and black holes, and their importance in helping teach scientists and the public about our place in the cosmos.
Continue reading “Cryovolcanism: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”The Ingenuity Team Downloads the Final Data from the Mars Helicopter. The Mission is Over
I really can’t believe that the Ingenuity helicopter on Mars took its maiden voyage in April 2021. On the 16th April 2024, engineers at NASA have received the final batch of data from the craft which marks the final task of the team. Ingenuity’s work is not over though as it will remain on the surface collecting data. For the engineers at NASA, they have their sights set on Dragonfly, a new helicopter destined for Titan.
Continue reading “The Ingenuity Team Downloads the Final Data from the Mars Helicopter. The Mission is Over”Are Titan's Dunes Made of Comet Dust?
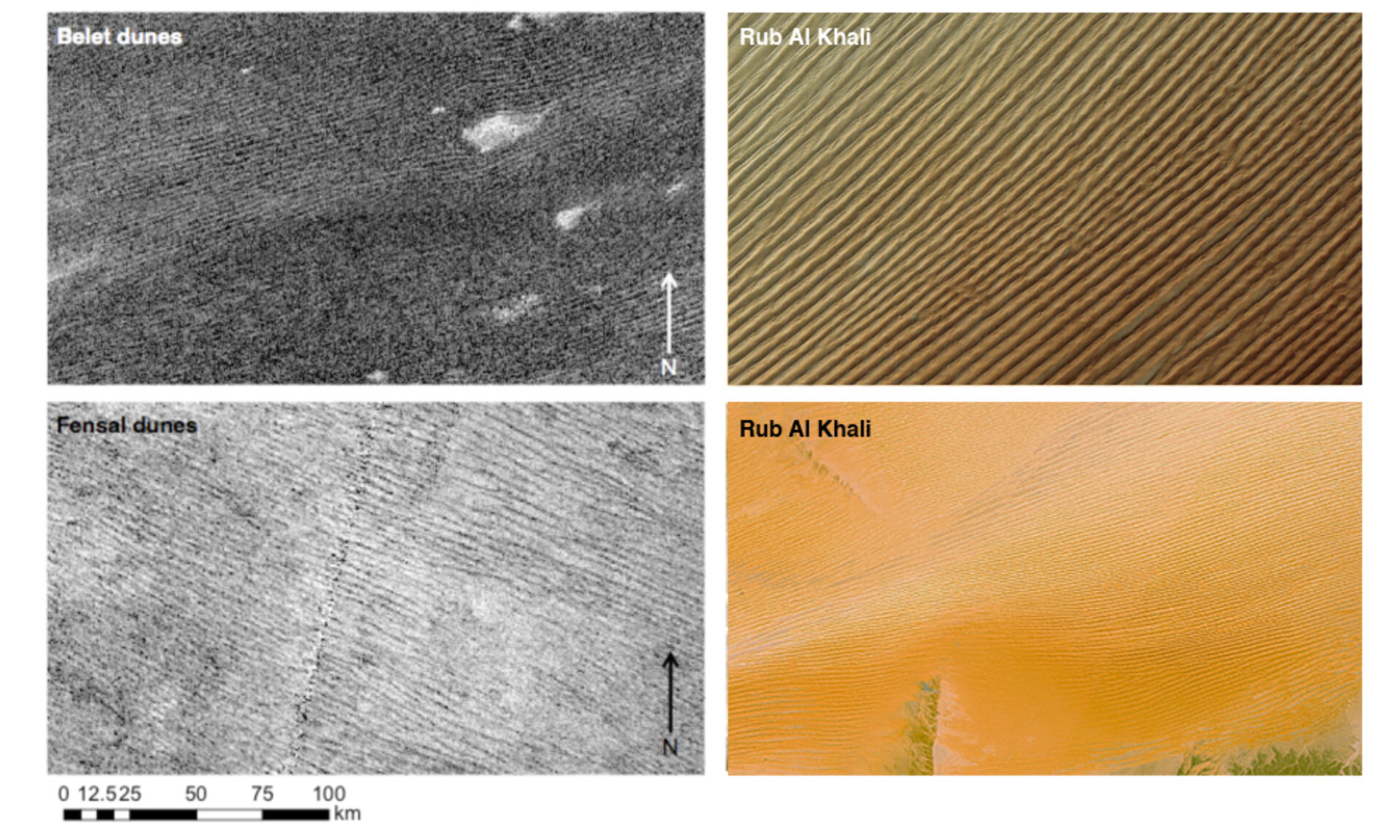
A new theory suggests that Titan’s majestic dune fields may have come from outer space. Researchers had always assumed that the sand making up Titan’s dunes was locally made, through erosion or condensed from atmospheric hydrocarbons. But researchers from the University of Colorado want to know: Could it have come from comets?
Continue reading “Are Titan's Dunes Made of Comet Dust?”Titan Probably Doesn’t Have the Amino Acids Needed for Life to Emerge

Does Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, possess the necessary ingredients for life to exist? This is what a recent study published in Astrobiology hopes to address as a team of international researchers led by Western University investigated if Titan, with its lakes of liquid methane and ethane, could possess the necessary organic materials, such as amino acids, that could be used to produce life on the small moon. This study holds the potential to help researchers and the public better understand the geochemical and biological processes necessary for life to emerge throughout the cosmos.
Continue reading “Titan Probably Doesn’t Have the Amino Acids Needed for Life to Emerge”How Did Life Get Started on Earth? Atmospheric Haze Might Have Been the Key
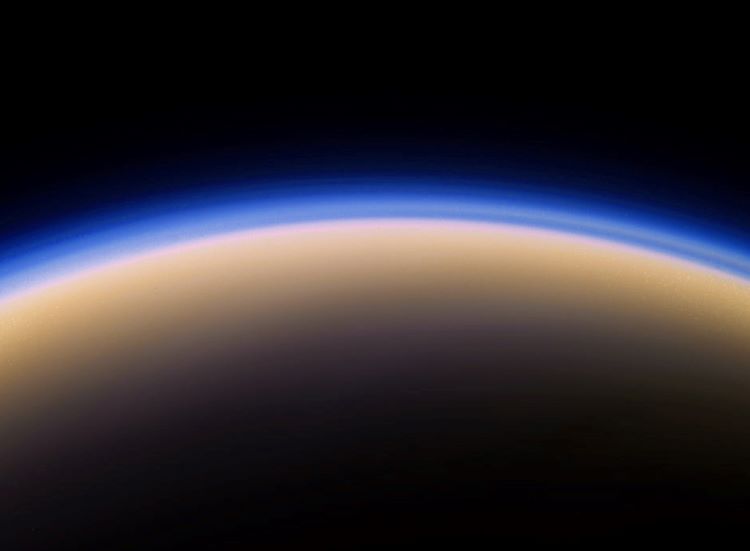

A recent study accepted to The Planetary Science Journal investigates how the organic hazes that existed on Earth between the planet’s initial formation and 500 million years afterwards, also known as Hadean geologic eon, could have contained the necessary building blocks for life, including nucleobases and amino acids. This study holds the potential to not only help scientists better understand the conditions on an early Earth, but also if these same conditions on Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, could produce the building blocks of life, as well.
Continue reading “How Did Life Get Started on Earth? Atmospheric Haze Might Have Been the Key”




