When you learned to drive a car for the first time, remember how comforting it was to have an experienced driver beside you, able to anticipate the hazards and keep you on schedule?
That’s surely how the Expedition 38 crew feels about one of the voices “on the line” as two astronauts prepare to venture outside to replace a crippled ammonia pump. One of the “CapComs” or people communicating with the crew on Saturday, Monday and Wednesday will be astronaut Doug Wheelock — who just happens to be known for co-replacing a broken ammonia tank himself in 2010. (The other CapCom is Japanese astronaut Aki Hoshide, who will chat through robotic procedures with Koichi Wakata).
Wheelock is the visible edge of hundreds — likely thousands — of people working feverishly at NASA and its international partners this past week to get the spacewalks ready through pool simulations, a virtual reality lab and other means. Several backup and non-critical space station systems are offline because of that pump, which has to regulate temperatures properly for vital electronics to work.
“I am their choreographer,” Wheelock told Universe Today of his plan for the astronauts. While spacewalkers Mike Hopkins and Rick Mastracchio already know what they are supposed to do when, Wheelock said he will be “their eyes and ears on the timeline.” If something needs to be stopped or changed, he’ll help them figure out what to do next.

Wheelock and fellow astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson had to spring into action themselves in August 2010. A pump in the same location broke, forcing space station systems offline and requiring them to go outside a few days later. With astronaut Shannon Walker piloting Canadarm2, the astronauts accomplished their tasks in three spacewalks — but encountered obstacles along the way.
During the first spacewalk, as Wheelock disconnected lines from the broken pump, he not only faced a pipe that wouldn’t let go, but a shower of ammonia snowflakes. That was “what got me on the EVA [extra-vehicular activity],” he recalled. That’s why NASA plans to lower the line pressure on the cooling system before the astronauts head outside this time. Normally the lines are pressurized at 360 pounds per square inch, but they’ll be lowered to 120 psi through commands from the ground.
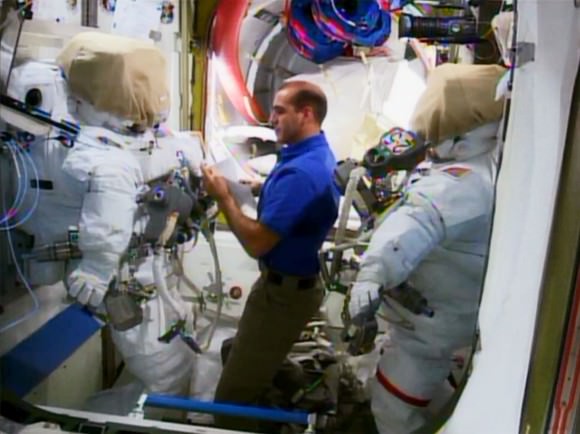
Other “lessons learned” are more recent. Italian astronaut Luca Parmitano was wearing a NASA spacesuit in July when he experienced a water leak in his helmet, putting him at risk and terminating the spacewalk early. This will be the first spacewalk since that time. NASA believes it has replaced the part of the suit that failed, but the agency has new backups in place. Hopkins and Mastracchio will have soaker pads in their helmets as well as a “snorkel”-like device, or tube that will let them breathe oxygen from a different part of the suit if water flows into the helmet again.

So what are some key parts of the spacewalks to look for? Wheelock identified a few spots.
‘HAP’ check. That soaker pad is called a “helmet absorption pad”, and as a matter of course the astronauts will be asked to verify that the pad is not wet at the same time that they also check their gloves for tears (another lesson learned from a past spacewalk.) So you will hear Wheelock calling “HAP check” from time to time to the crew.
Unlatching and latching the ammonia connectors on the pumps. Because this is when leaks are most likely to occur — posing a risk to Mastracchio, who is performing the work — Wheelock is going to do a “challenge and response” procedure. He will read up the step, the astronaut will verify it and will do the work. There will be “a lot more chatter on the [voice] loop” during those times, Wheelock said, with everyone on the ground watching through Mastracchio’s head camera feed (visible at the front of the room) to see what is happening. “There will be a lot of people standing in Mission Control at that point,” he joked, himself included.
Leak procedures. If ammonia does start to shower out, Mastracchio will quickly close the valve and wait a few minutes as it could be just residual ammonia in the line. If that doesn’t work out, Mastracchio is trained on a procedure to attach a device to the front end of the connector and move a lever that prevents a cavity in the line from filling with ammonia. Then he can open the valve again, bleed out the ammonia that’s left over and keep going.

Decontamination procedures. The ammonia makes a distinctive “ping” when it hits the helmet, says Wheelock (who yes, heard that happen himself.) You can also see ammonia on the suit, he said, as it looks a bit like candle wax and obscures the stitching. All of which to say, NASA has procedures in place if the agency suspects or can confirm large amounts of ammonia got on Mastracchio’s suit. (Small amounts would essentially fleck off in the sun.) Hopkins, who will be out of the line of fire, can do a thorough inspection of Mastracchio and scrape off any ammonia with a warm metal tool — without hurting the suit underneath. The astronauts could also do a “bakeout” in the airlock — 30 minutes if suspected, an hour if confirmed — where they will sit with the hatch open and wait for any ammonia to sublimate off the suit. Once they close the hatch, the astronauts can verify if the ammonia is gone using Drager tubes, which have gold crystals inside that turn “purpleish blue” in the presence of ammonia, Wheelock said.
Margin calls. Because NASA needs to make sure the astronauts have 30 to 60 minutes to decontaminate at the end of their spacewalks, officials will preserve a margin of oxygen available for the astronauts to walk through that work. So it’s possible the agency may terminate a spacewalk before all tasks are completed just because they need that bit of margin at the end.
To learn more, Wheelock has been answering questions occasionally on his Twitter account from followers, and you can read through what he posts when he finds the time. Universe Today will also cover the spacewalks (currently planned for Saturday, Monday and Wednesday) as they occur.