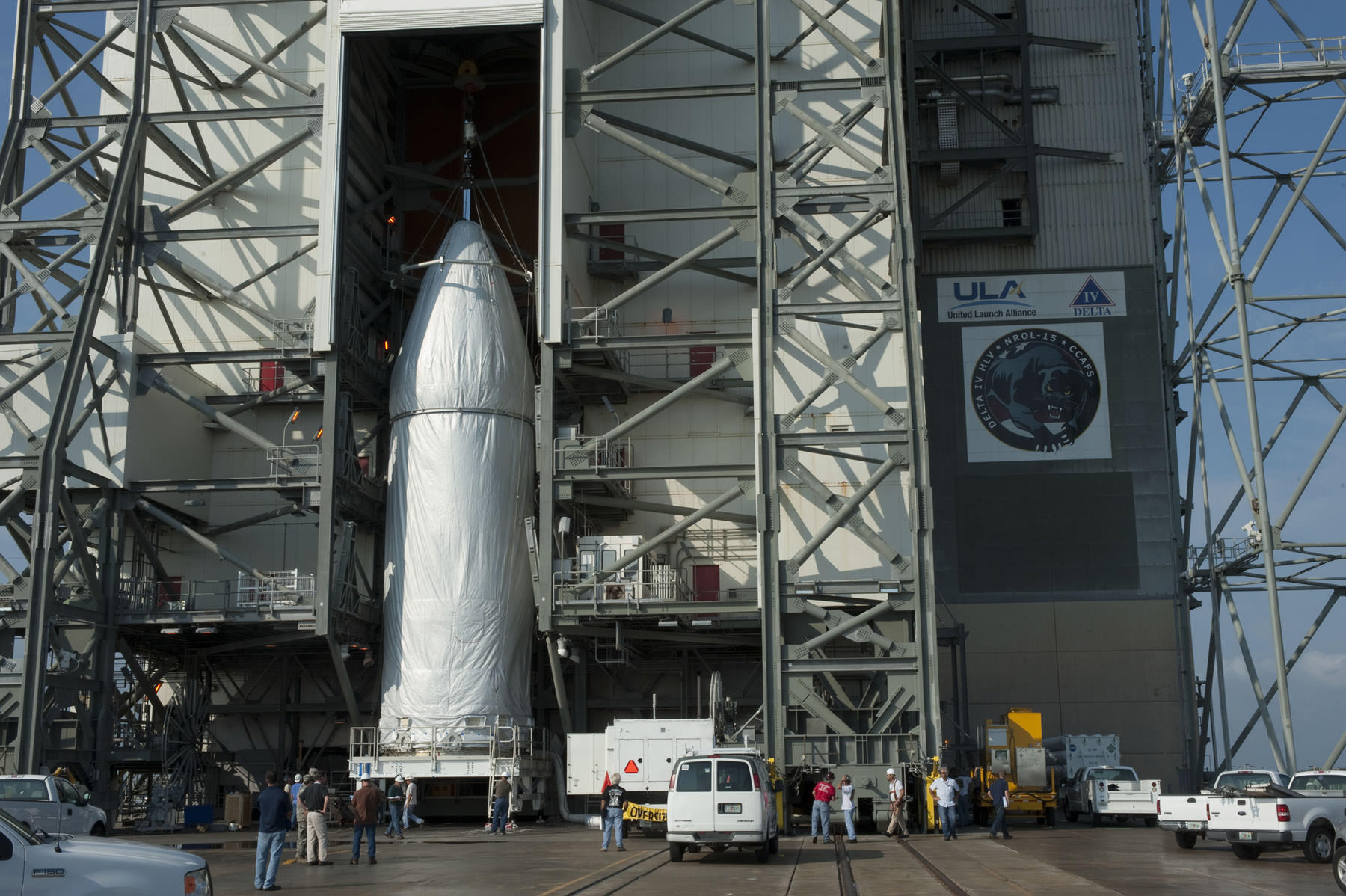
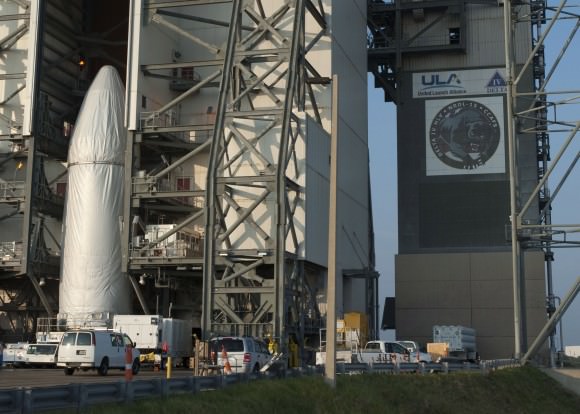
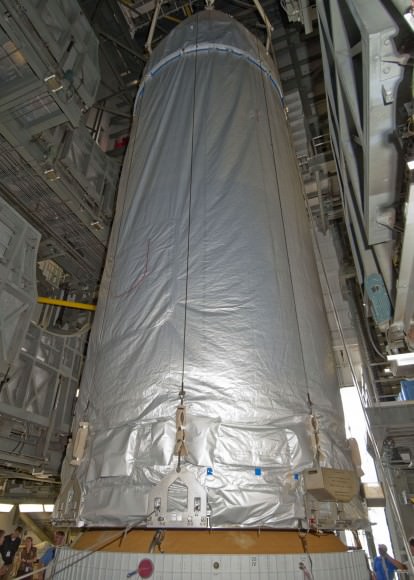
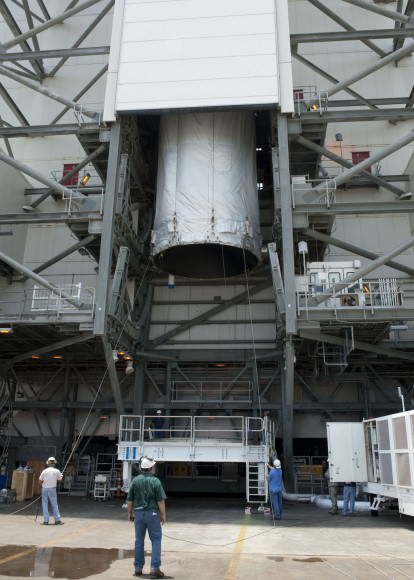
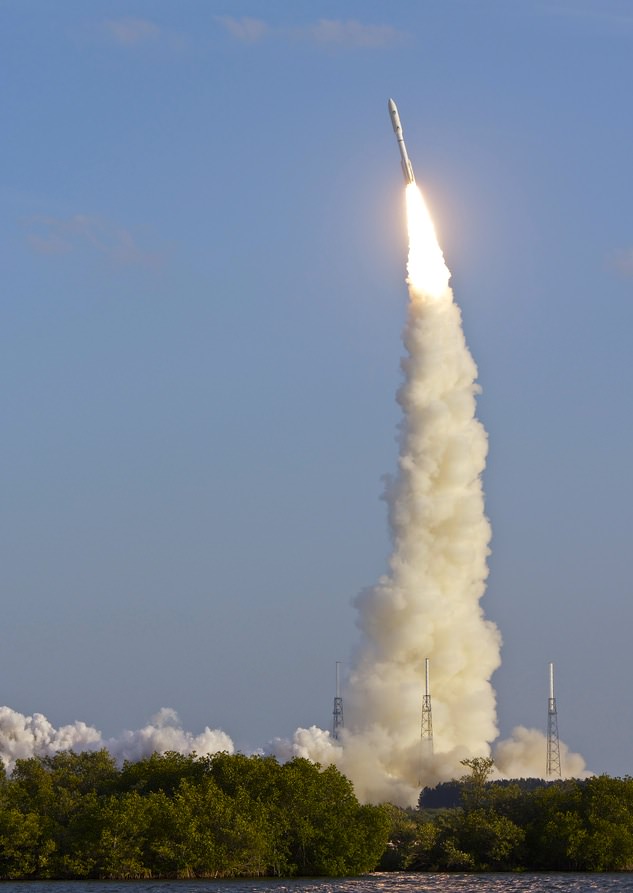
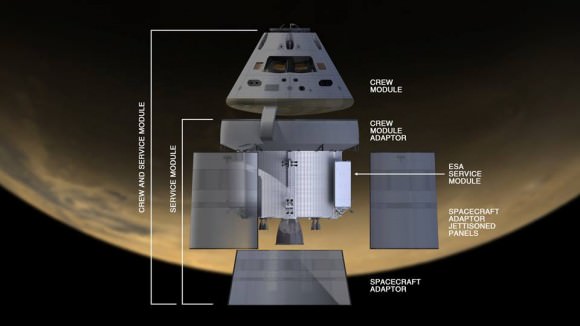
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, FL – Production and assembly of virtually all of the key hardware elements for NASA’s eagerly anticipated Orion EFT-1 uncrewed test flight are either complete or nearing completion at the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral.
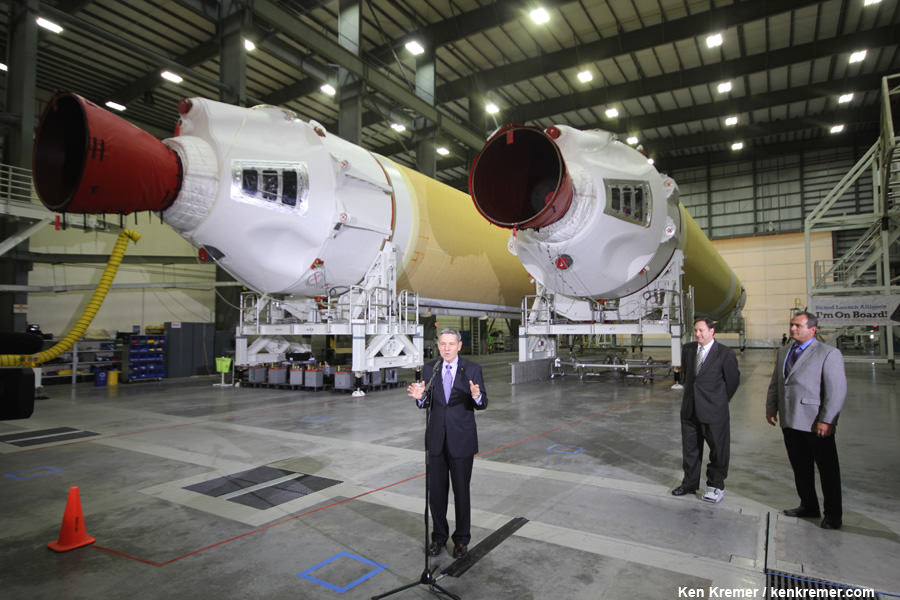
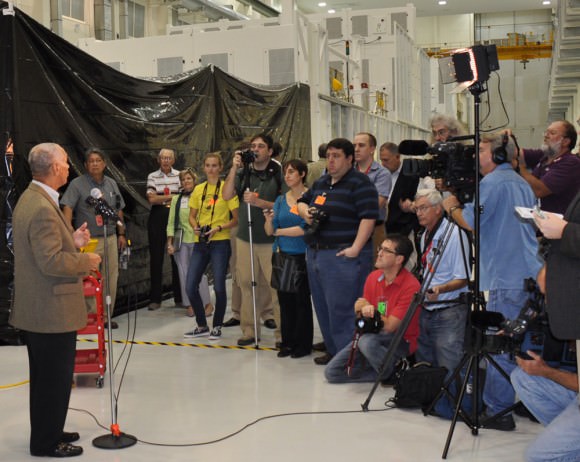
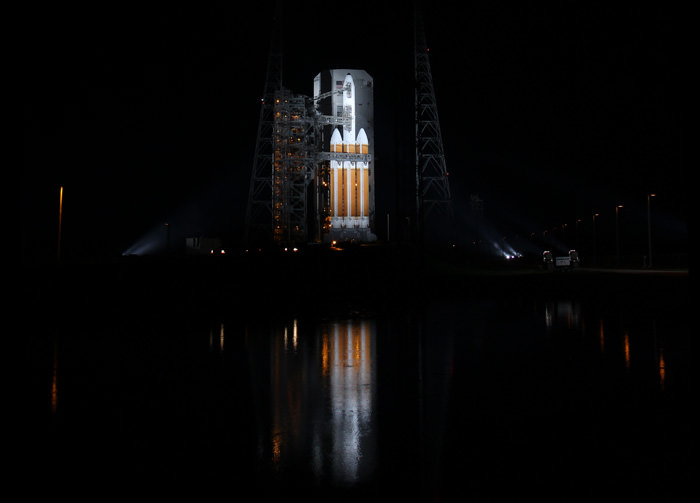
Two of the three first stage boosters comprising the mammoth Delta IV Heavy rocket that will propel Orion to high Earth orbit have arrived at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, and were unveiled this week by top NASA managers at a media briefing attended by Universe Today.
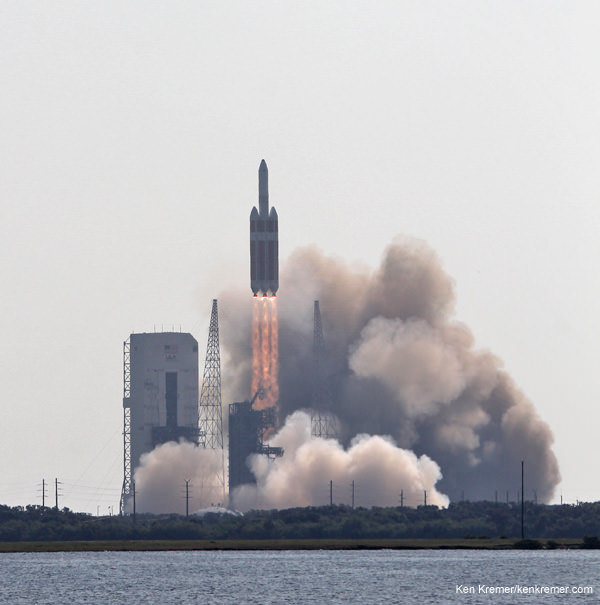
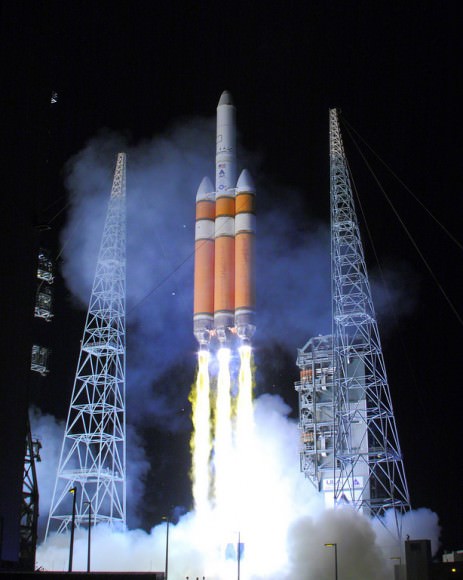
The triple barreled Delta IV Heavy rocket is currently the most powerful rocket in America’s fleet and the only one capable of launching the Orion EFT-1 capsule to its intended orbit of 3600 miles altitude above Earth.
Due to urgent US national security requirements, the maiden blastoff of the unmanned Orion pathfinder capsule – that will one day send humans back to the Moon and beyond Earth’s realm – has just been postponed about three months from September to December 2014 in order to make way for the accelerated launch of recently declassified US Air Force Space Surveillance satellites – as I reported here.

The center and starboard side boosters recently arrived at the Cape aboard a barge from Decatur, Alabama where they were manufactured by United Launch Alliance (ULA).
The remaining port side booster and the Centaur upper stage are due to be shipped by ULA to Cape Canaveral in April.
“It’s great to see Orion, the next step in our journey of exploration, said NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot. “And it’s very exciting to see the engines integrated into the booster.”
“This mission is a stepping stone on NASA’s journey to Mars. The EFT-1 mission is so important to NASA. We will test the capsule with a reentry velocity of about 85% of what expect on returning [astronauts] from Mars.”
“We will test the heat shield, the separation of the fairing and exercise over 50% of the eventual software and electronic systems inside the Orion spacecraft. We will also test the recovery systems coming back into the Pacific Ocean.”
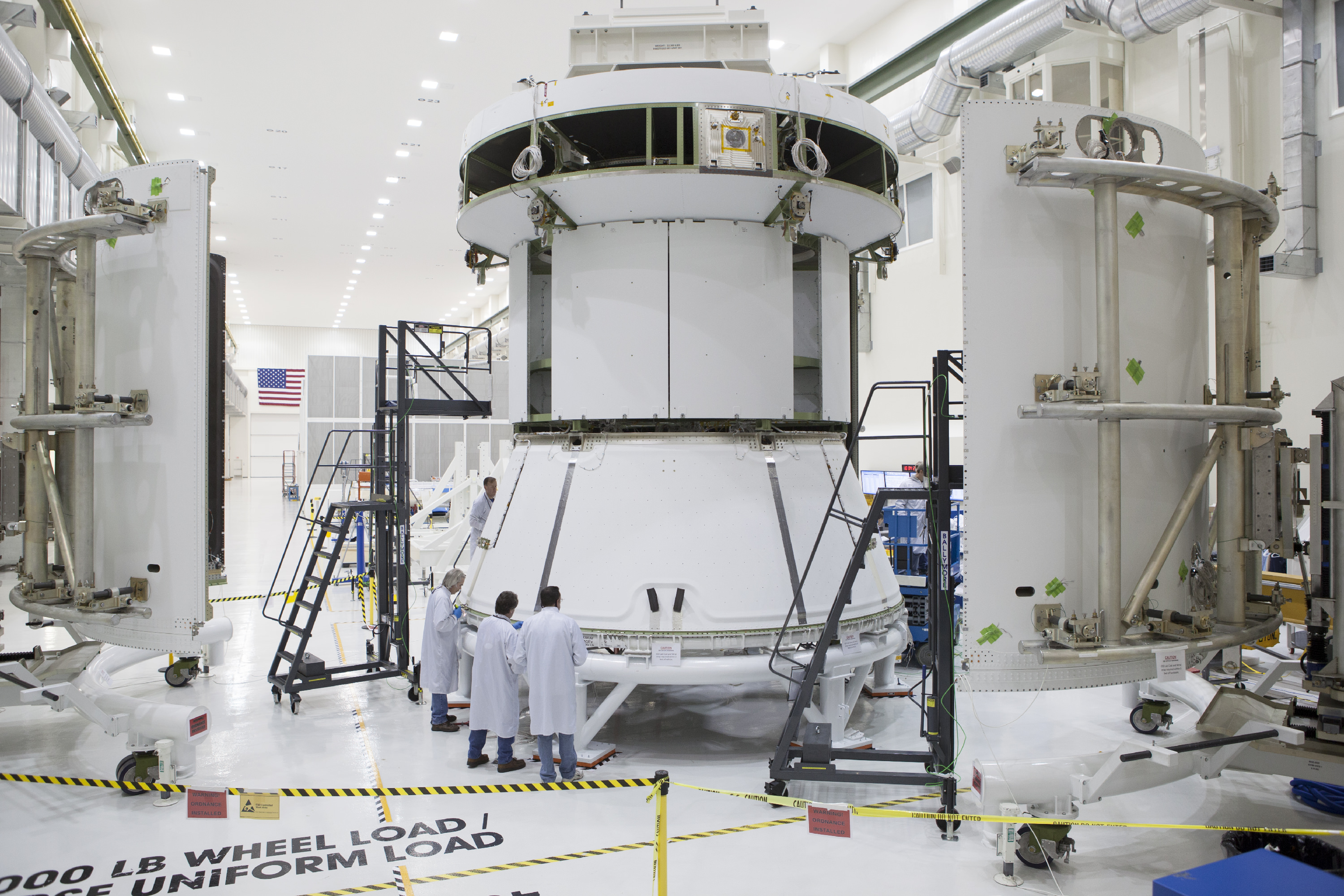
Despite the EFT-1 launch postponement, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana said technicians for prime contractor Lockheed Martin are pressing forward and continue to work around the clock at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in order to still be ready in time to launch by the original launch window that opens in mid- September 2014.
“The contractor teams are working to get the Orion spacecraft done on time for the December 2017 launch,” said former shuttle commander Cabana.
“They are working seven days a week in the Operations and Checkout High Bay facility to get the vehicle ready to roll out for the EFT-1 mission and be mounted on top of the Delta IV Heavy.”
“I can assure you the Orion will be ready to go on time, as soon as we get our opportunity to launch that vehicle on its first flight test and that is pretty darn amazing.”
“It’s great to see all the hardware and boosters that will take Orion to orbit.”
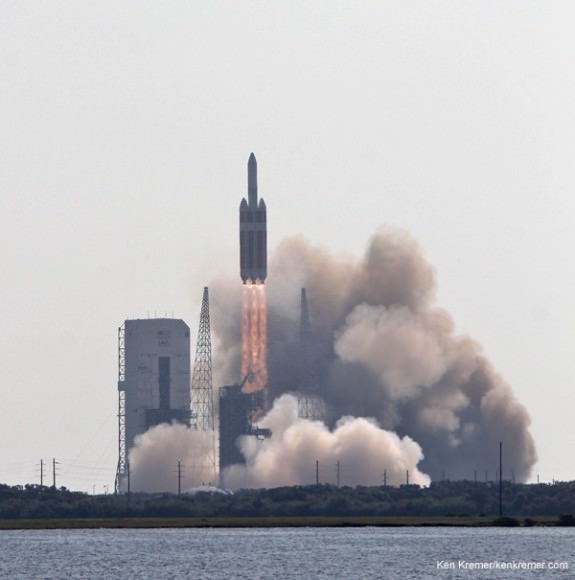

Universe Today also confirmed with Cabana that NASA will absolutely not delay any Orion processing and assembly activities.
“Our plan is to have the Orion spacecraft ready because we want to get EFT-1 out so we can start getting the hardware in for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) and start processing for that vehicle that will launch on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in 2017,” Cabana told me standing besides the Delta IV boosters inside the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral.

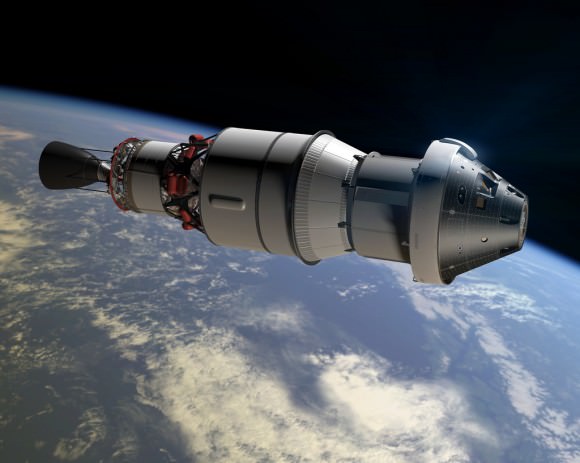
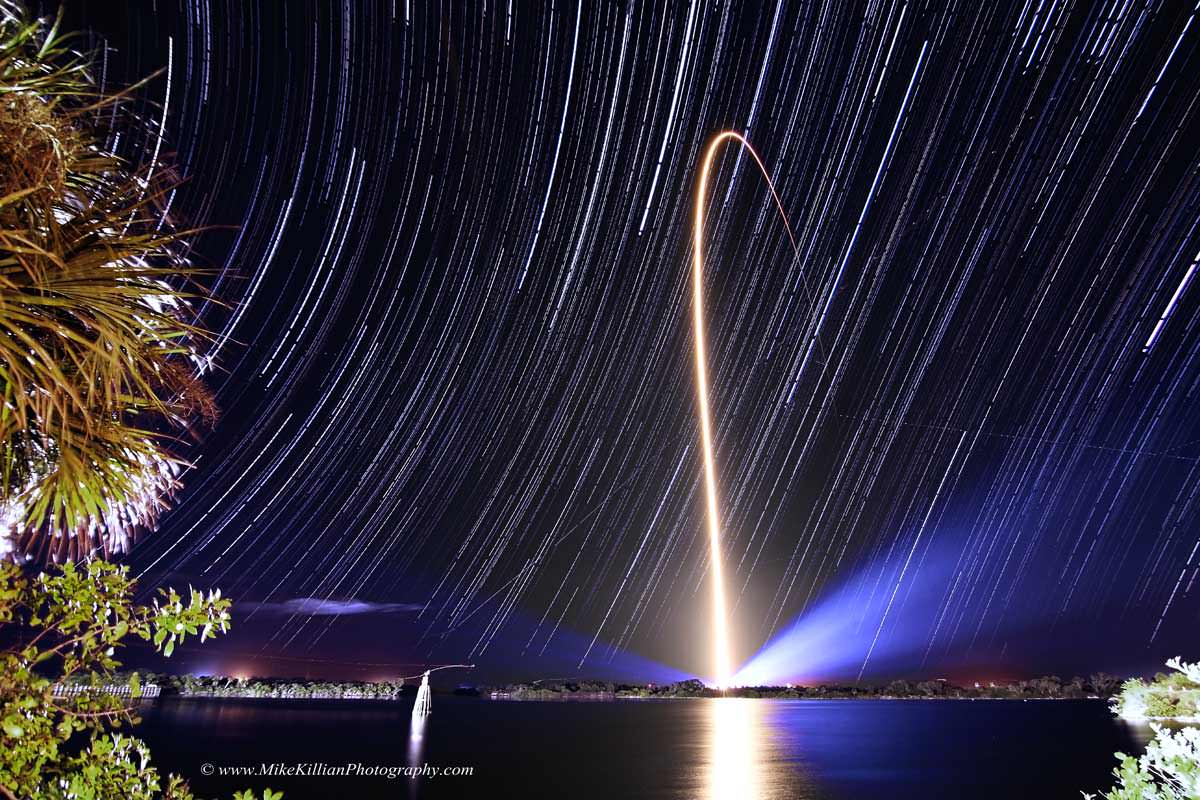
The two-orbit, four- hour EFT-1 flight will lift the Orion spacecraft and its attached second stage to an orbital altitude of 3,600 miles, about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) – and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
Although the mission will only last a few hours it will be high enough to send the vehicle plunging back into the atmosphere and a Pacific Ocean splashdown to test the craft and its heat shield at deep-space reentry speeds of 20,000 mph and endure temperatures of 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit – like those of the Apollo moon landing missions.
The EFT-1 mission will provide engineers with critical data about Orion’s heat shield, flight systems and capabilities to validate designs of the spacecraft, inform design decisions, validate existing computer models and guide new approaches to space systems development. All these measurements will aid in reducing the risks and costs of subsequent Orion flights before it begins carrying humans to new destinations in the solar system.
“Orion EFT-1 is really exciting as the first step on the path of humans to Mars,” said Lightfoot. It’s a stepping stone to get to Mars.”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, Chang’e-3, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, LADEE, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.
Learn more at Ken’s upcoming presentations at the NEAF astro/space convention, NY on April 12/13 and at Washington Crossing State Park, NJ on April 6. Also evenings at the Quality Inn Kennedy Space Center, Titusville, FL, March 24/25 and March 29/30