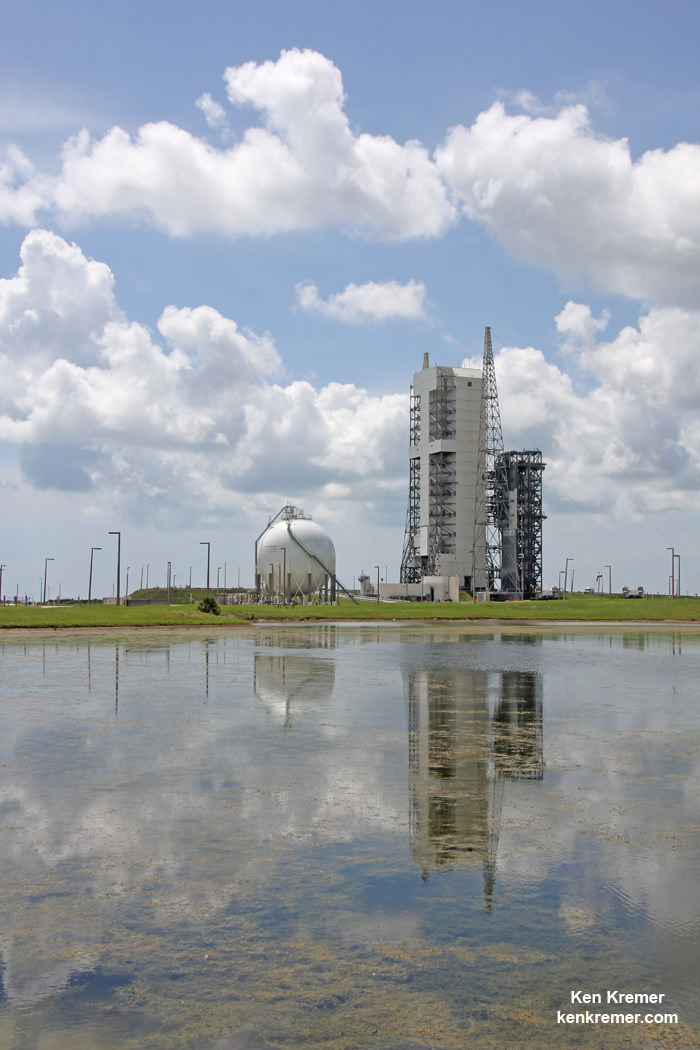
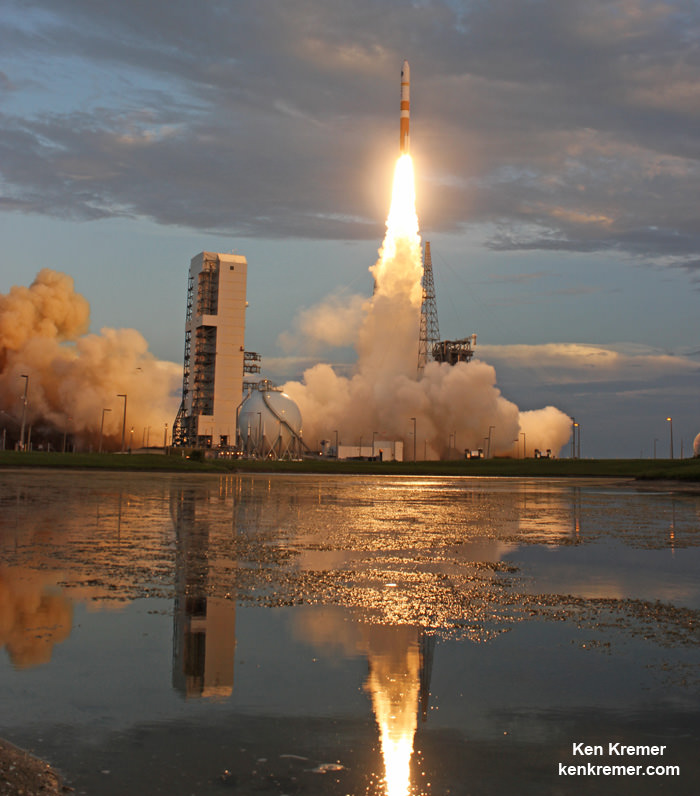
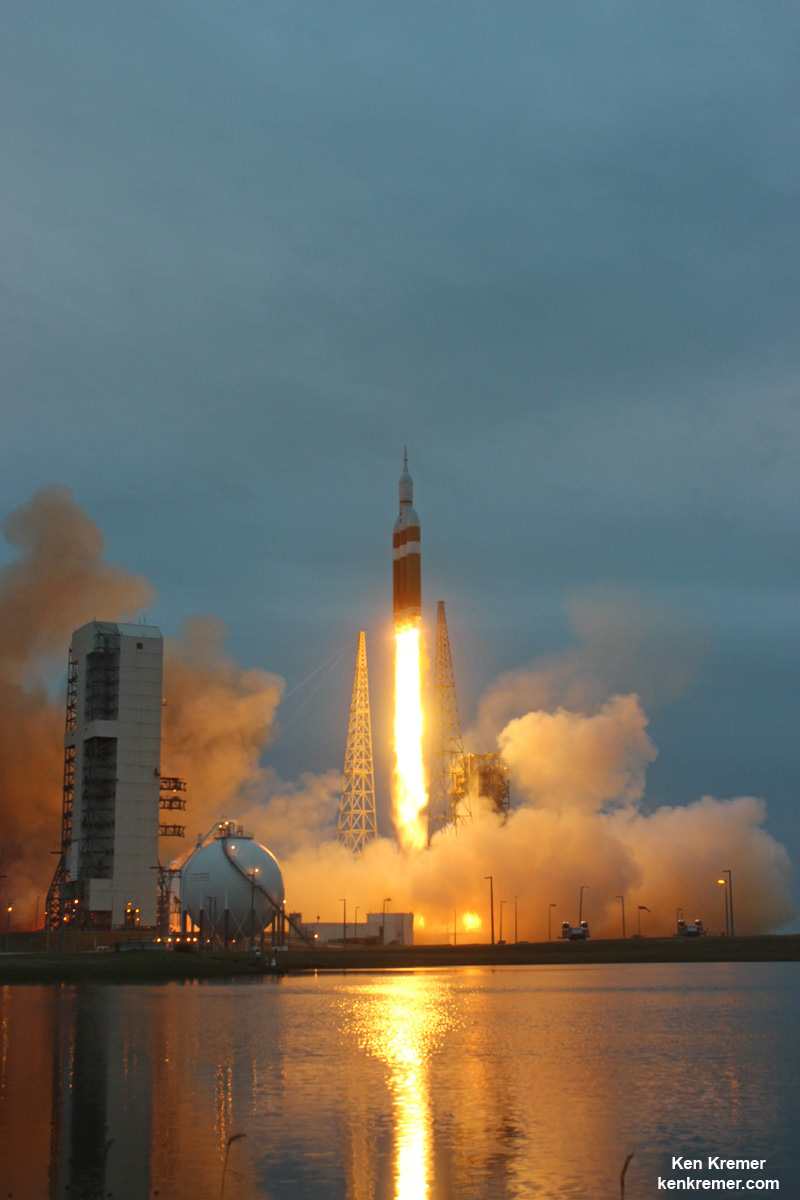
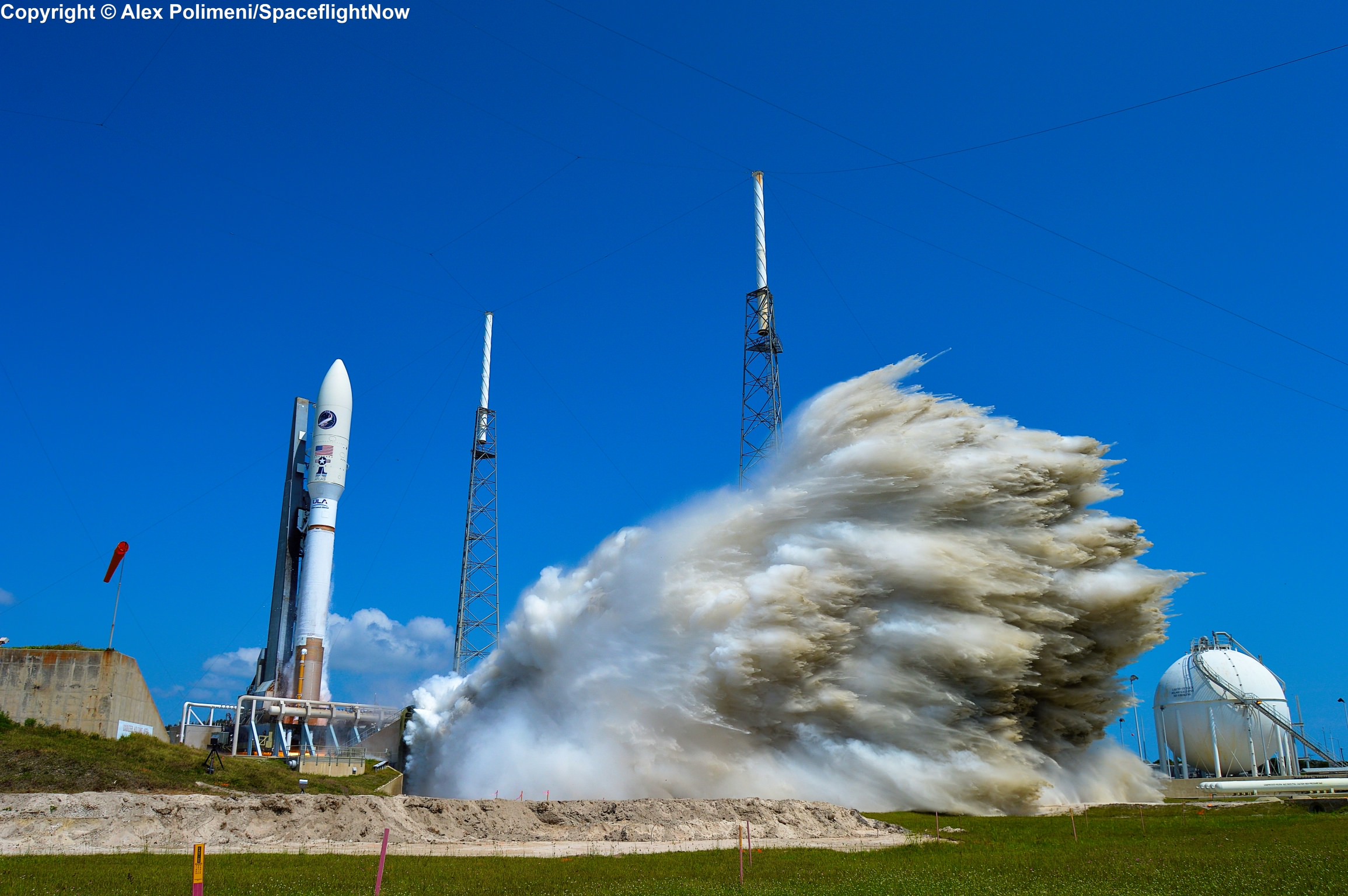
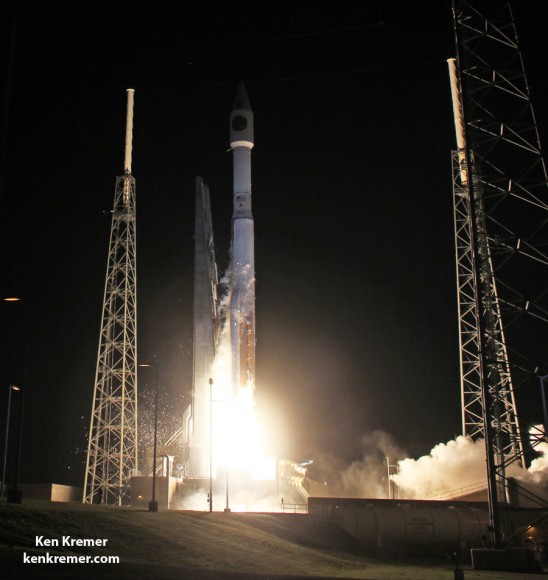
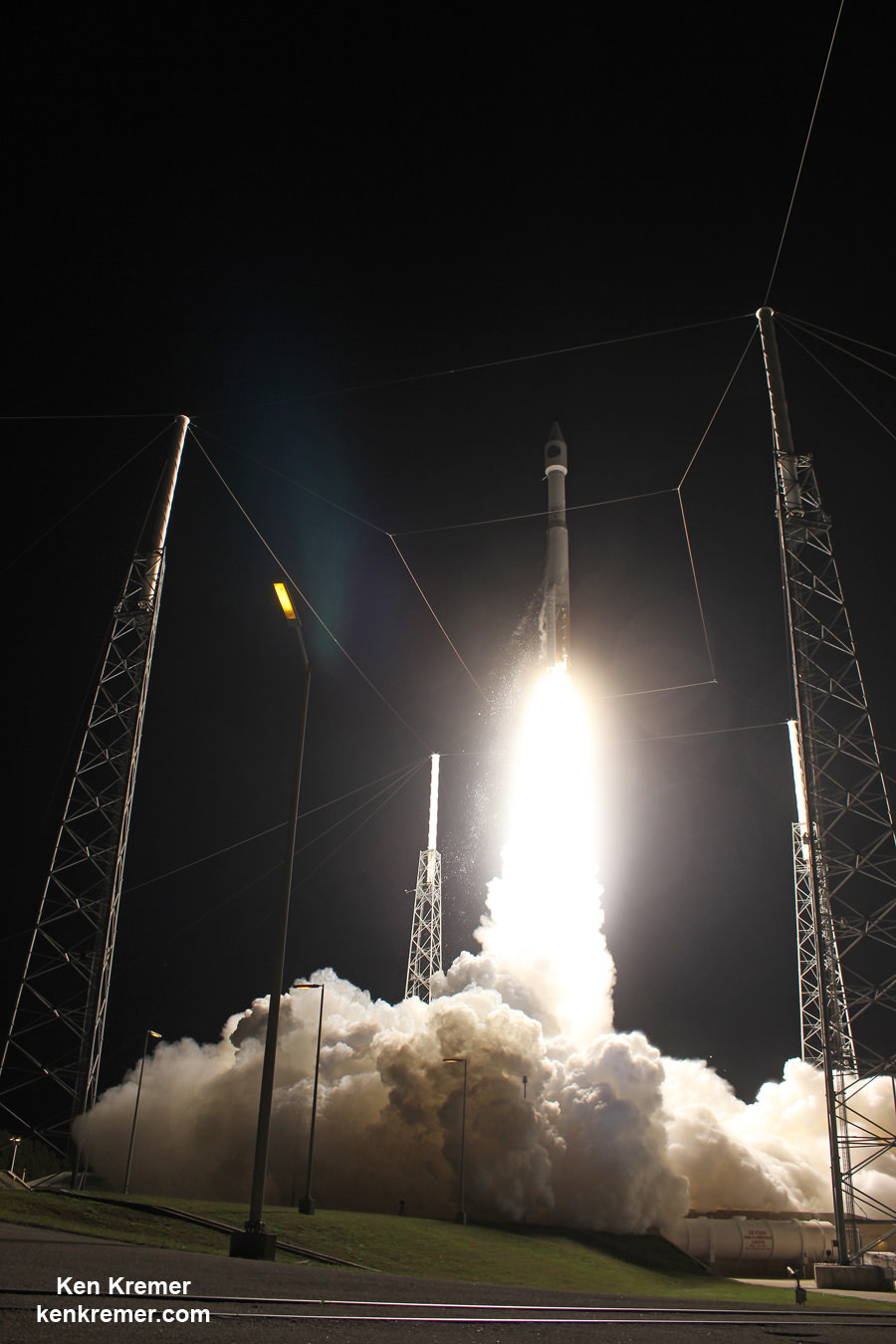
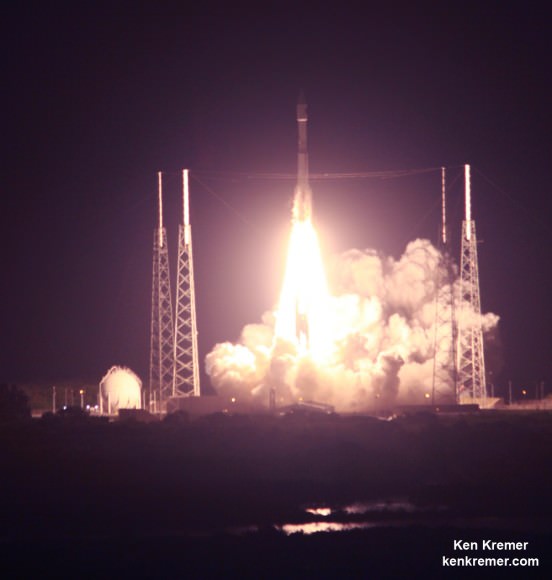
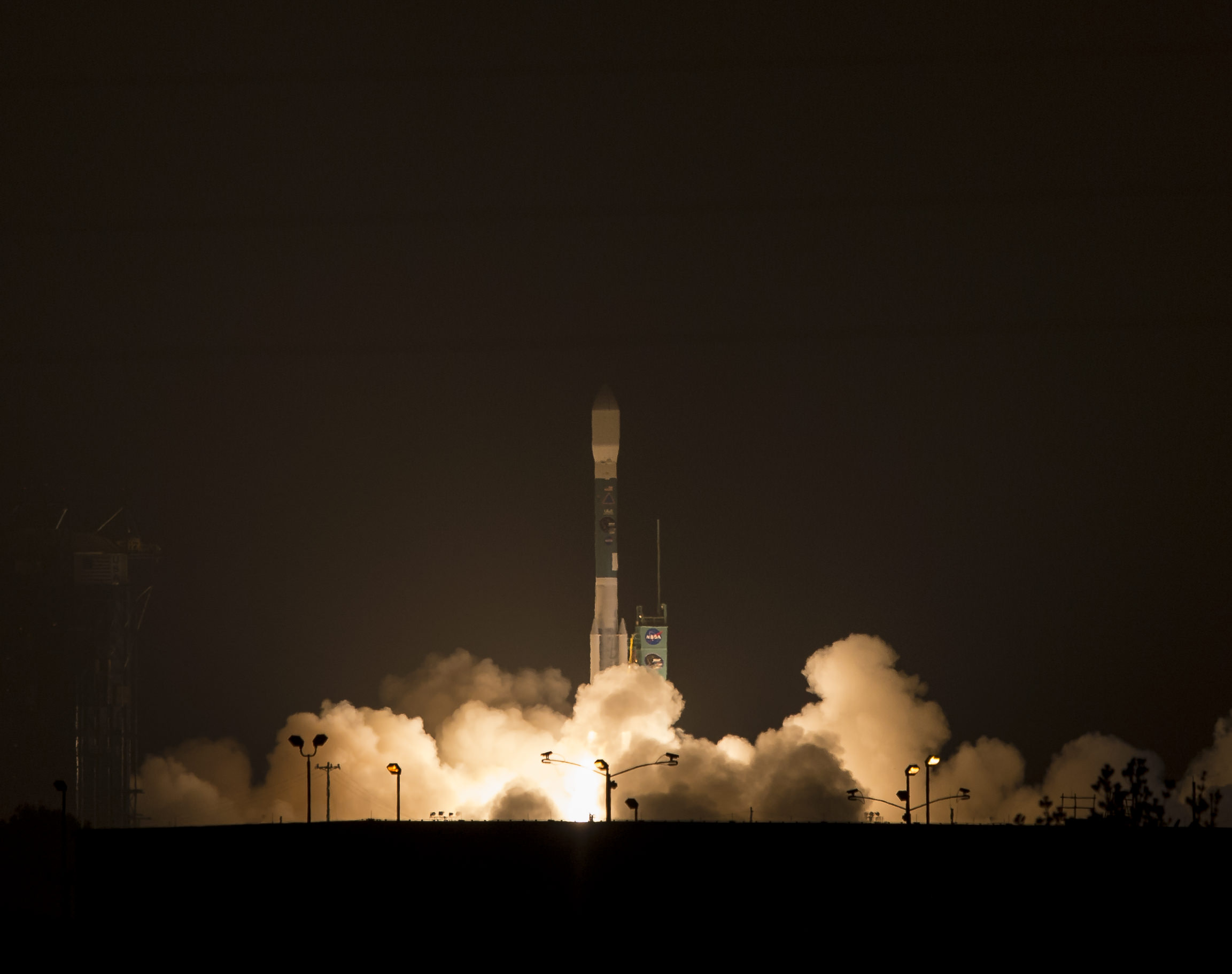
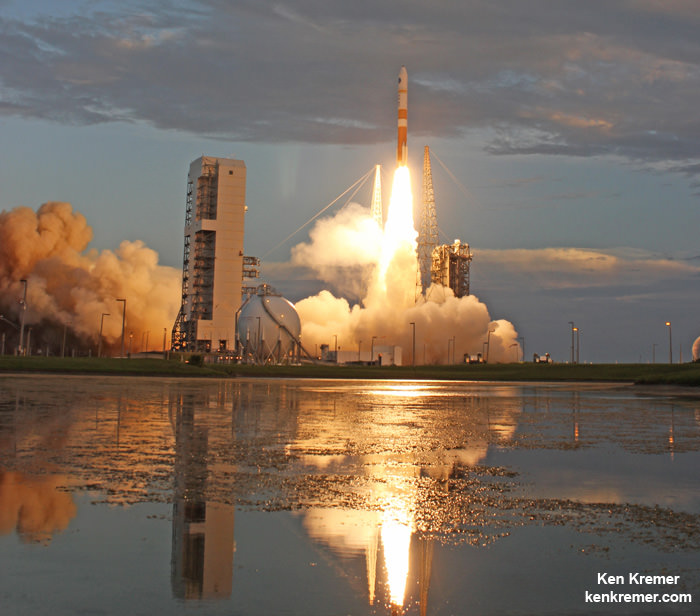
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, FL – An advanced military communications satellite that will significantly fortify tactical communications amongst U.S. and allied military forces took flight this evening, July 23, during a stunning sunset blastoff of a United Launch Alliance Delta IV rocket from the Florida space coast as threatening weather luckily skirted away from the launch site in the waning hours of the countdown.
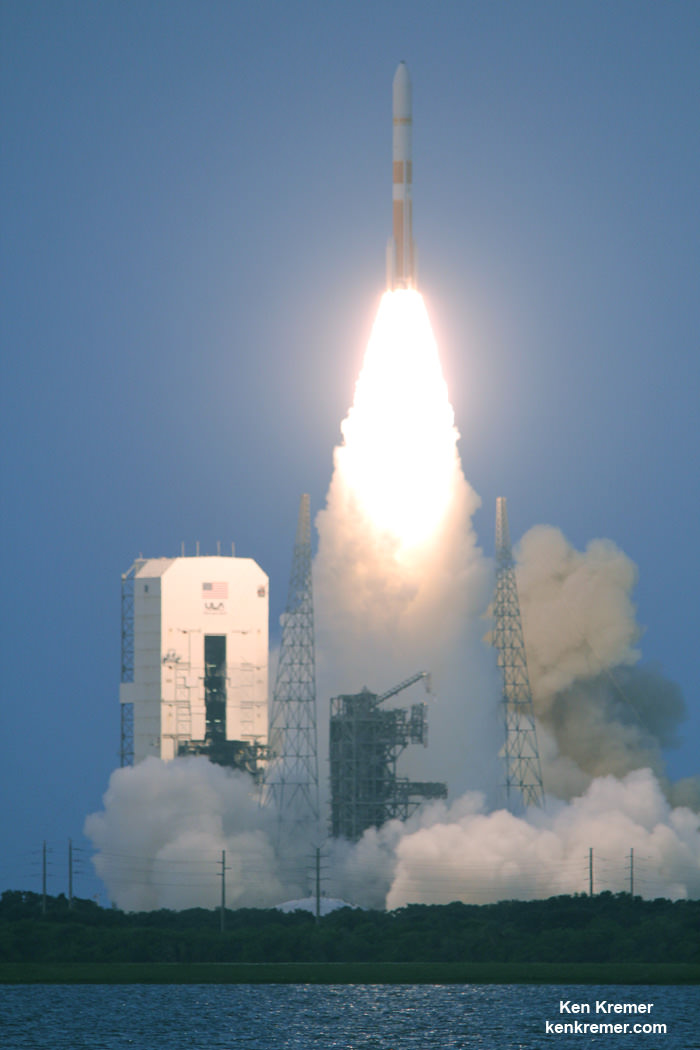
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV rocket successfully launched the Wideband Global SATCOM-7 (WGS-7) communications satellite for the U.S. Air Force at 8:07 p.m. EDT Thursday evening, July 23, from Space Launch Complex-37 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
The evening hues in the sunset skies over the launch pad region were stellar and wowed spectators all along the space coast region.
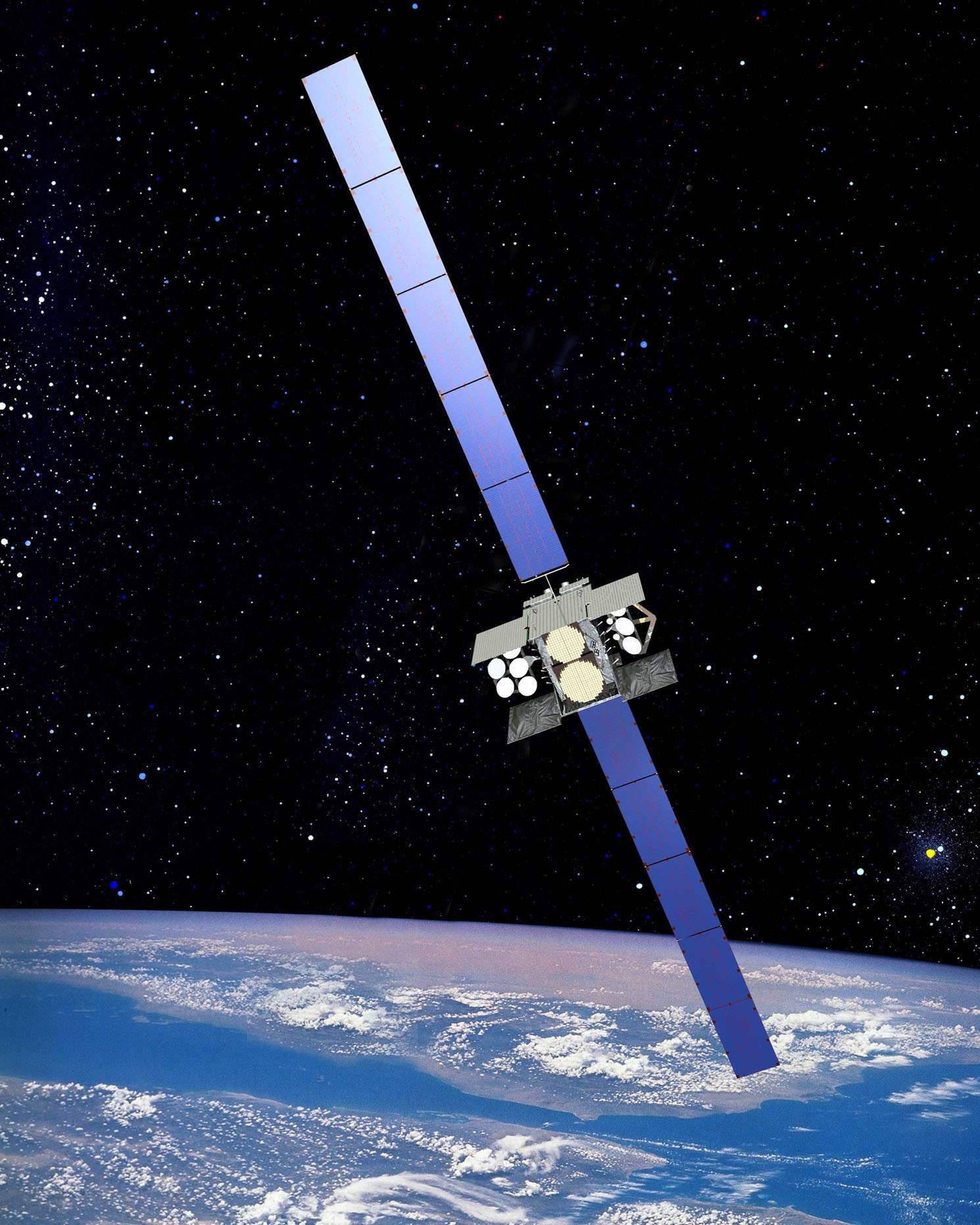
The Wideband Global SATCOM system provides “anytime, anywhere communication” for allied military forces “through broadcast, multicast and point to point connections,” according to ULA.

The $570 million WGS 7 satellite is part of a significant upgraded constellation of high capacity communications satellites providing enhanced communications capabilities to American and allied troops in the field for the coming two decades.
“WGS provides essential communications services, allowing Combatant Commanders to exert command and control of their tactical forces, from peace time to military operations.”
Following a one day launch postponement forced by drenching rainstorms, widespread thunderstorms and heavy winds on Wednesday, the initial outlook for Thursdays weather looked at first like it would repeat the dismal weather conditions in the central Florida region and cause another scrub.
Luckily the forecast storms relented and heavy rains and thunder passed through the launch pad area earlier enough in the day that technicians for rocket provider ULA were able to fuel the rocket as planned with cryogenic propellants starting around four hours before the liftoff.
WGS-7 is the seventh in a series of high capacity that will broaden tactical communications for U.S. and allied forces at both a significantly higher capacity and lower cost.
The Boeing built WGS-7 will provide the U.S. and allied militaries with 17 percent more secure communications bandwidth. It is also the only military satellite communications system that can support simultaneous X and Ka band communications.
“Every WGS that we deliver increases the ability of U.S. and allied forces to reliably transmit vital information,” said Dan Hart, Boeing vice president, Government Satellite Systems.
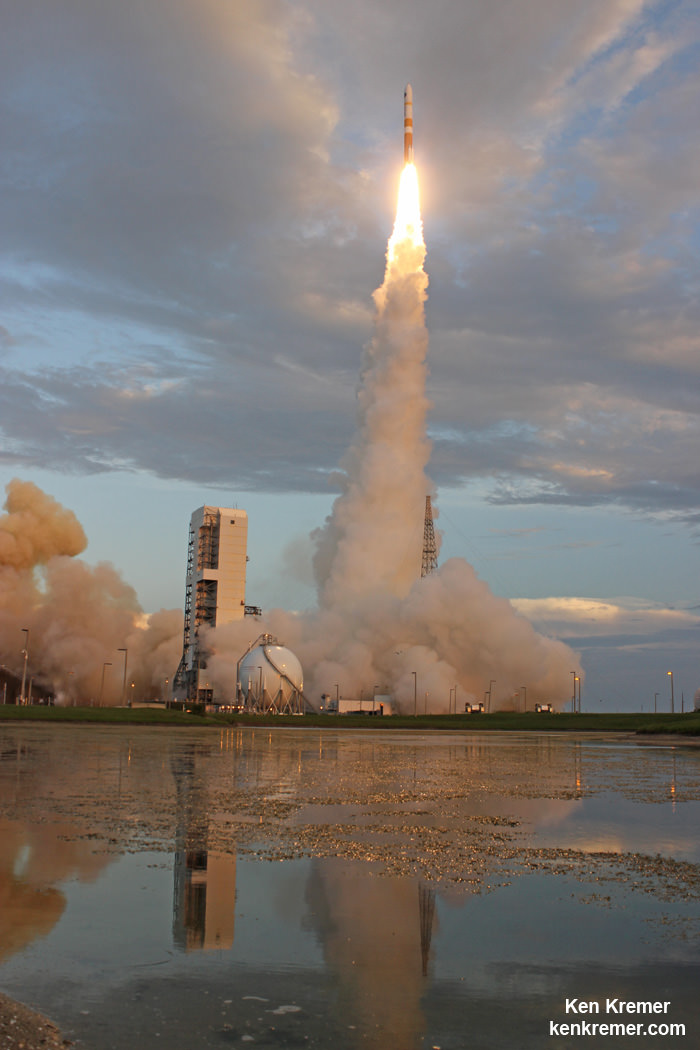

It sent signals confirming its health soon after launch.
Altogether Boeing is manufacturing 10 WGS satellites for the U.S. Air Force.
The WGS payload bandwidth will be enhanced even more for the last three satellites in the WGS series. To further improve connectivity the payload bandwidth will double for WGS-8.
Boeing also promises big cost reductions on the last four WGS satellites by instituting additional commercial manufacturing procedures.
“By utilizing commercial processes, we are able to offer greater capacity at a lower spacecraft cost, resulting in more than $150 million in savings for WGS-7 through WGS-10,” noted Hart.
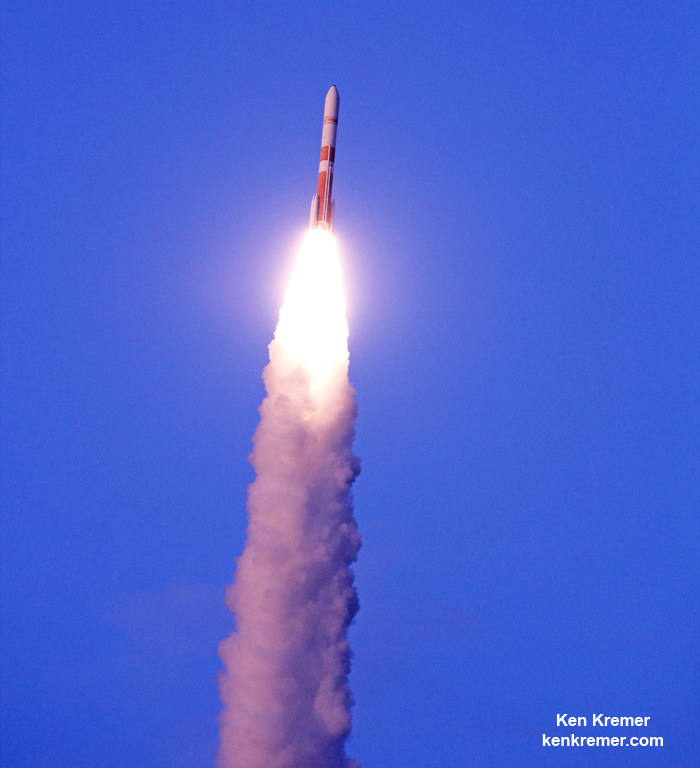

Tonight’s spectacular liftoff was the second successful ULA launch in just eight days from Cape Canaveral. Last week a ULA Atlas V launched the latest GPS satellite for the USAF.
The WGS launch also marked ULA’s seventh launch in 2015. Overall this was ULA’s 98th successful one-at-a-time launch since the company was formed in December 2006 as a joint venture between Lockheed and Boeing.

“Kudos to the Air Force and all of our mission partners on today’s successful launch and orbital delivery of the WGS-7 satellite. The ULA team is honored work with these premier U.S. government and industry mission teammates and to contribute to the WGS enhanced communications capabilities to the warfighter,” said Jim Sponnick, ULA vice president, Atlas and Delta Programs.
“The team continues to emphasize reliability, and one launch at a time focus on mission success to meet our customer’s needs.”
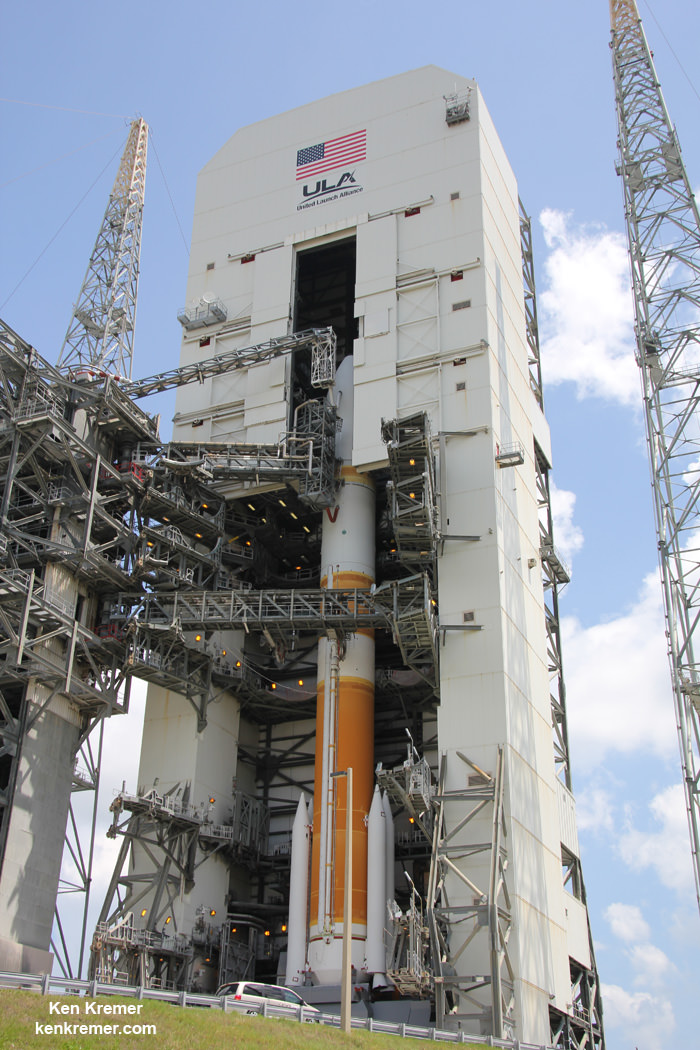

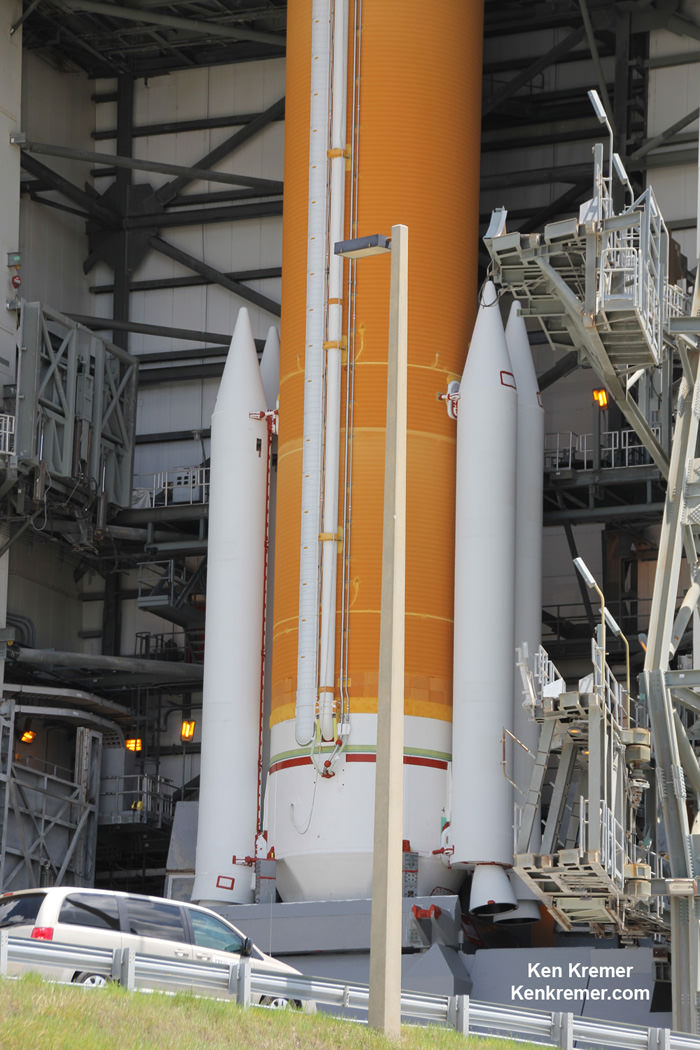
The Delta IV Medium+ rocket launched in a 5,4 configuration with a 5-meter diameter composite payload fairing built by Orbital ATK and with four solid rocket motors augmenting the first stage common booster core powered by a single RS-68A main engine. Each of the 60 inch diameter GEM-60 solids from Orbital ATK produces about 200,000 lbs of thrust.
This was the first flight of the Delta IV with the newly upgraded RS-68 engine.
The Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-68A first stage main engine burns cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen which generates about 702,000 lbf of thrust at sea level. The upper stage was powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10B-2 engine
“The modified nozzle on the RS-68A supports a 17% increase in engine performance,” Andrew Haaland of Orbital ATK told Universe today at the media viewing site.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.