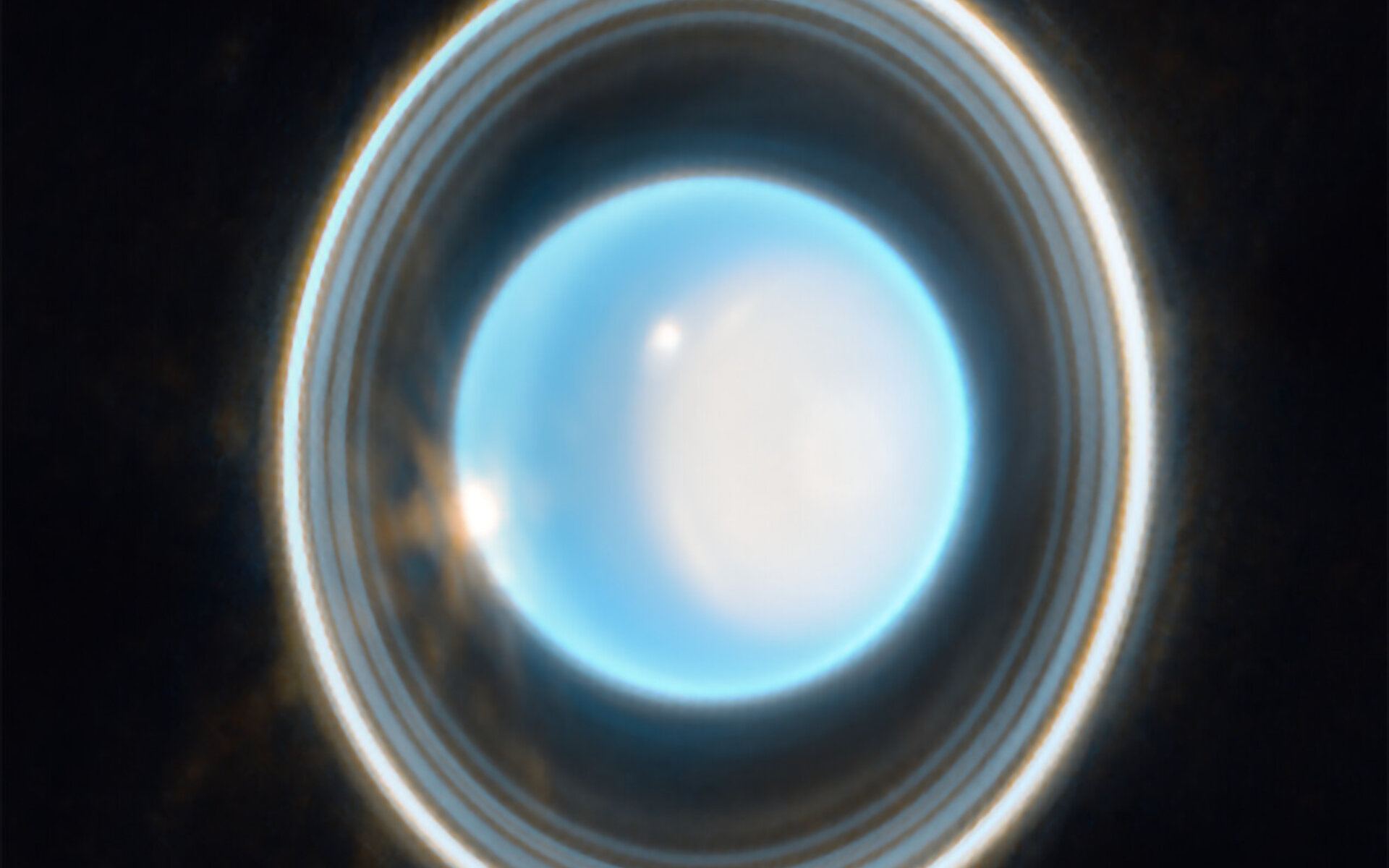
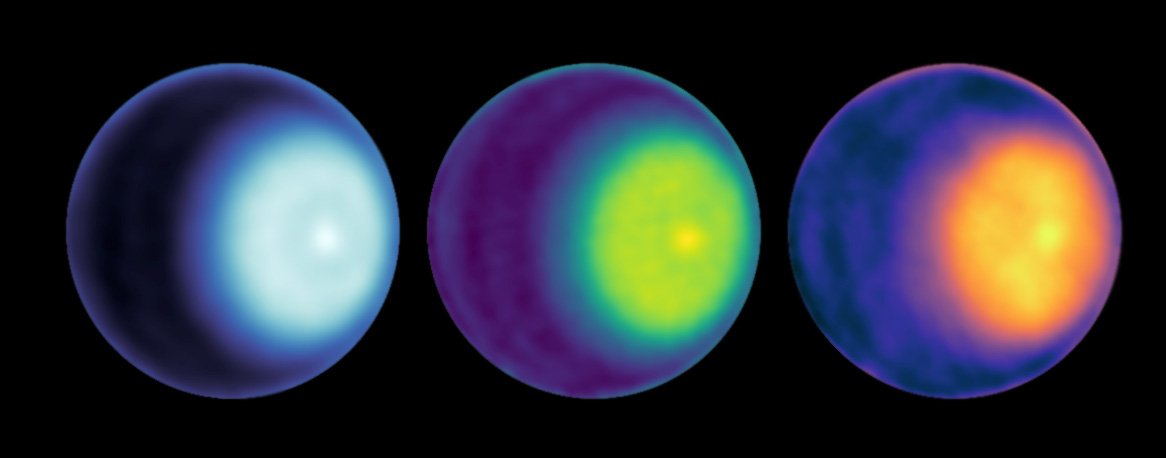
In our search for exoplanets, we’ve found that many of them fall into certain types or categories, such as Hot Jupiters, Super-Earths, and Ice Giants. While we don’t have any examples of the first two in our solar system, we do have two Ice Giants: Uranus and Neptune. They are mid-size gas planets formed in the cold outer regions of the solar system. Because of this, they are rich in water and other volatile compounds, and they are very different from large gas giants such as Jupiter. We still have a great deal to learn about these worlds, but what we’ve discovered so far has been surprising, such as the nature of their magnetic fields.
Continue reading “What's Inside Uranus and Neptune? A New Way to Find Out”What's Inside Uranus and Neptune? A New Way to Find Out