So, did this past weekend’s shift back to Standard Time for most of North America throw you for a loop? Coming the day after Halloween, 2015 was the earliest we can now shift back off Daylight Saving Time. Sunday won’t fall on November 1st again until 2020. Expect evenings get darker sooner for northern hemisphere residents, while the planetary action remains in the dawn sky.
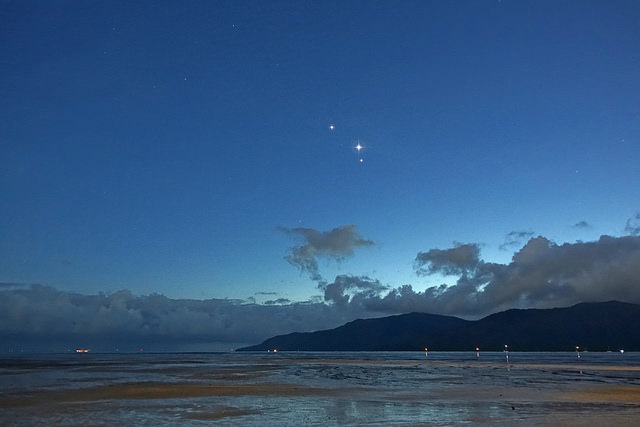
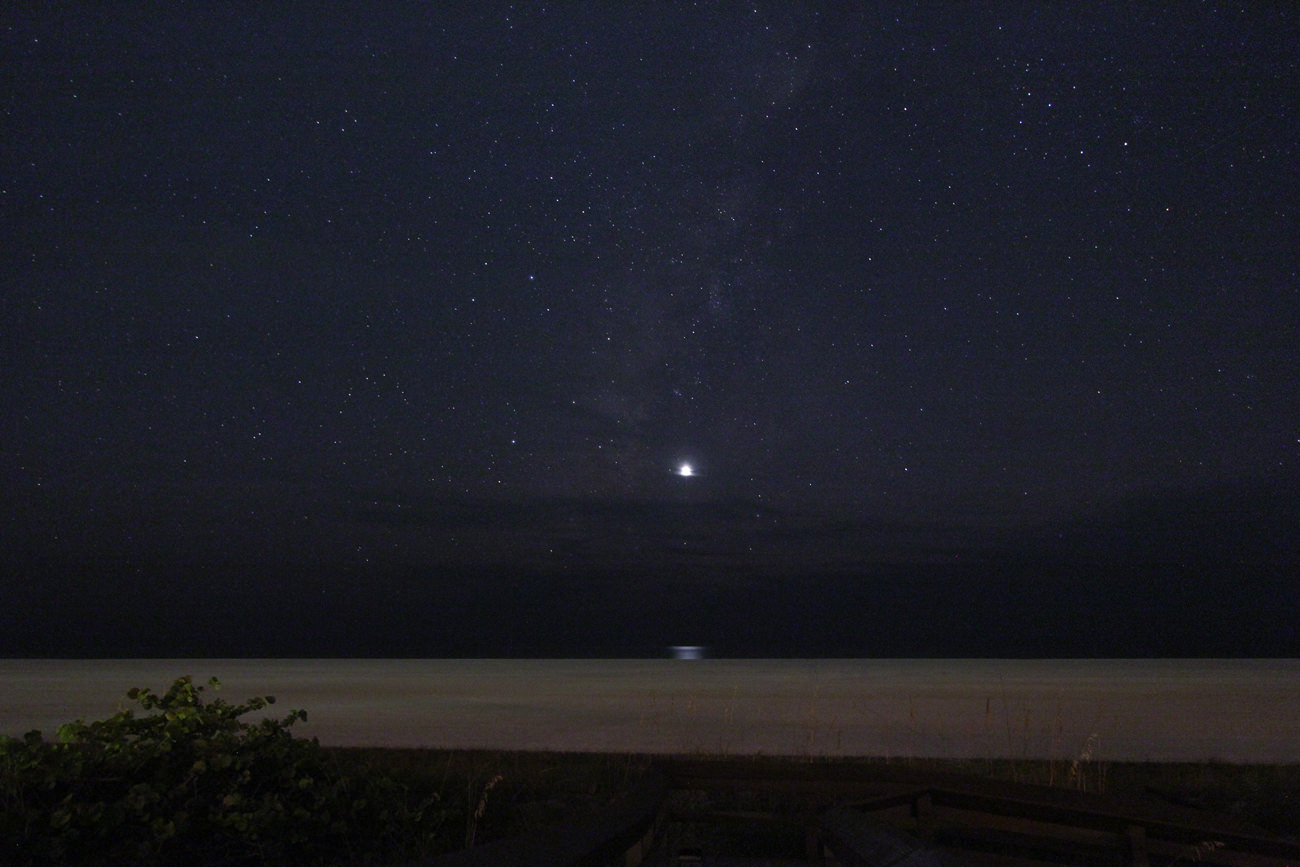
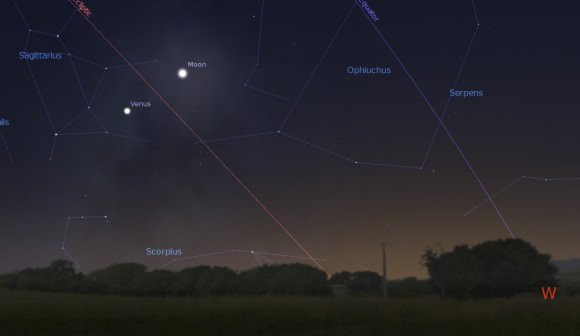
Though Mercury has exited the morning twilight stage, the planets Jupiter, Venus and Mars continue to put on a fine show, joined by the waning crescent Moon later this week. The action starts today on November 3rd, which finds +1.9 magnitude Mars passing just 0.68 degrees (40’, just over the apparent diameter of a Full Moon) from brilliant -3.9 magnitude Venus. Though the two nearest planets to the Earth appear to meet up in the dawn sky, Mars is actually 2.5 times more distant than Venus, which sits 74.4 million miles (124 million kilometres) from the Earth. Venus exhibits a 57% illuminated gibbous phase 21” across this week, versus Mars’ paltry 4.5” disc.
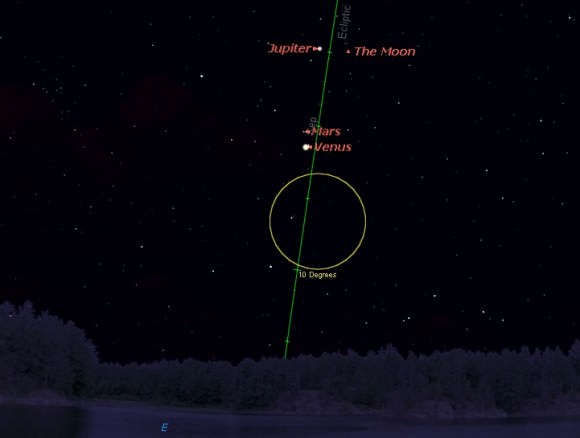
Watch the scene shift, as the Moon joins the dance this weekend. The mornings of Friday, November 6th and Saturday, November 7th are key, as the Moon passes just two degrees from the Jupiter and Mars pair and just over one degree from Venus worldwide. Similar close pairings of the Moon and Venus adorn many national flags, possibly inspired by a close grouping of Venus and the Moon witnessed by skywatchers of yore.
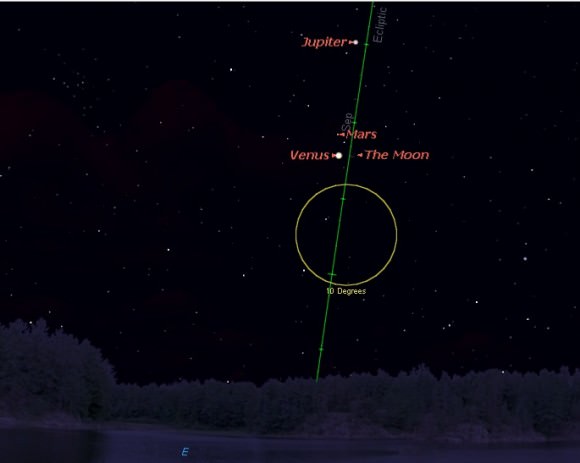
Saturday November 7th is also a fine time to try your hand at seeing Venus in the daytime, using the nearby crescent Moon as a guide. The Moon will be only four days from New, and the pair will be 46 degrees west of the Sun, an optimal situation as Venus just passed greatest western elongation 46.4 degrees west of the Sun on October 26th.
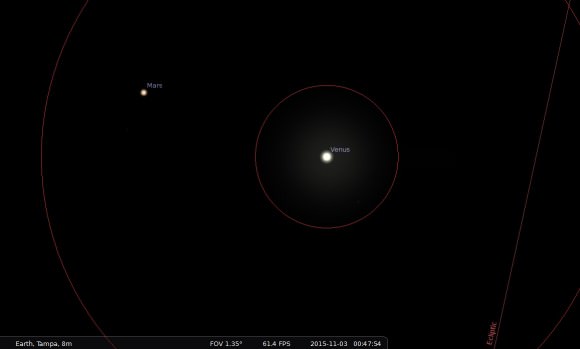
Though Venus may seem like a difficult daytime object, it’s actually intrinsically brighter than the Moon per square arc second. Difficulty finding it stems from seeing it against a low contrast blue daytime sky, its small size, and lack of context and depth. The larger but dimmer Moon actually serves as a good anchor to complete this feat of visual athletics.

Looking for more? Comet C/2013 US10 Catalina will join the planetary lineup next lunation ‘round, hopefully shining at magnitude +5 as it glides past Venus and the Moon on December 7th. Karl Battams at the U.S. Naval Research Labs has confirmed that Comet US10 Catalina—which reaches perihelion this month on November 15th –should also briefly graze the field of view for SOHO’s LASCO C3 camera on November 7th.
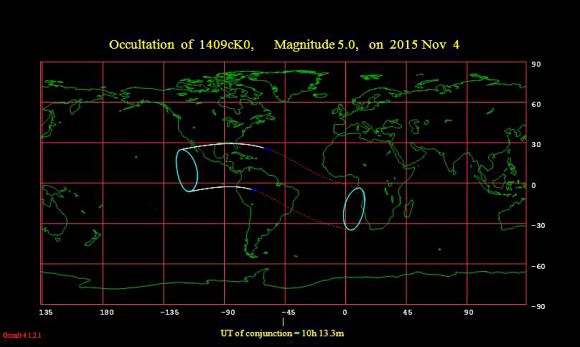
There’s also a few notable lunar occultations this week. The Moon also occults the +5 magnitude star Chi Leonis for viewers around the Gulf of Mexico on November 4th, including a dramatic grazing event for Northern Florida. The Moon also occults the +3.5 magnitude star Omicron Leonis on Nov 4th for Alaska as well.
See a bright star near the Venus this week? It’s none other than +3.6 magnitude Beta Virginis (Zavijava). The star passes 15’ from Venus on the morning of November 6th. Stick around ‘til 2069, and you can actually witness Venus occult Beta Virginis. Between Beta Virginis and Mars, Venus has the appearance this week of having the large pseudo-moon it never possessed. From Venus, our Moon would appear near magnitude +0.4 with a disk 6.4” this week, and range 12’ from the Earth.
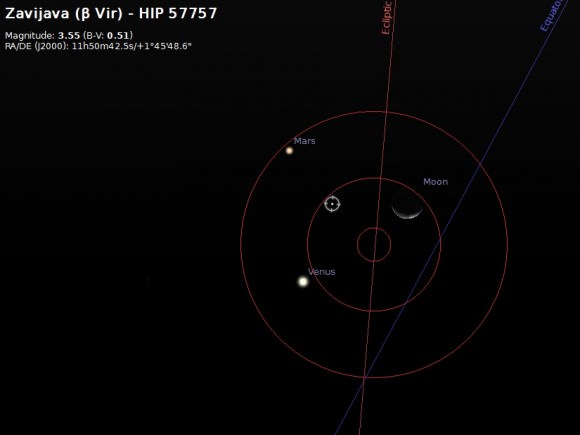
Now for the wow factor. All of these disparate objects merely lie along our Earthbound line of sight this week. Traveling at the speed of light (186,282 miles or 299,792 kilometers a second), the Moon lies just over a second away. Venus, Mars and Jupiter are next, at 6, 18, and 49 light minutes out, respectively… and Beta Virginis? It lies 36 light years distant.
This pass of the Moon also sets us up for an occultation of Mars and a dramatic daytime occultation of Venus for North America during the next lunation…
More to come!
-Got pictures of the planetary grouping this week with the Moon? Be sure to send ’em in to Universe Today and our Flickr forum.