Some of the most amazing celestial sights are hidden from our view in the daytime sky. Or are they? We recently challenged readers to try and follow the planet Venus through inferior conjunction as it passed between the Earth and the Sun on January 11th. Unlike the previous pass on June 6th, 2012 when Venus made its last transit of the Sun for the 21st century, the 2014 solar conjunction offered an outstanding chance to trace Venus’s path just five degrees from the Sun from the dusk and into the dawn sky.
Expert astrophotographers Shahrin Ahmad based in Sri Damansara, Malaysia and Paul Stewart observing from New Zealand took up that daily challenge as Venus neared the limb of the Sun, with amazing results. Now, Shahrin has also produced an amazing time-lapse sequence of Venus passing through inferior conjunction.
You can actually see the illuminated “horns” of Venus as they thin, extend, and rotate around the limb as the planet passes the Sun.
And it’s what’s more incredible is that the capture was completed in the daytime. But such a feat isn’t for the unskilled. Shahrin told Universe Today of the special safety precautions he had to take to acquire Venus so close to the Sun:
“Since Venus was getting closer each day towards conjunction, I found it far too dangerous to find visually, either using the main telescope or the finderscope.”
Instead, Shahrin relies on computerized software named Cartes du Ciel to drive his Skywatcher EQ6 mount and pinpoint Venus in the daytime sky.
“The sky in Kuala Lumpur is never clear from here, thus it rarely appears dark blue, making it almost impossible to spot Venus visually, especially when it is less than 10 degrees from the Sun.”
Shahrin elaborated further on his special solar safety precautions:
“I always start with all covers in place and the solar filter on the main telescope. I will slew the telescope to the Sun, make some slight repositioning adjustments, and then synchronize the telescope to the new position. After ensuring the Sun is visible and centered on the computer screen, I slew to Venus. Once the mount has stopped in position, I remove the solar filter and replace it with a makeshift cardboard extender mounted on the existing dew-shield. This ensures that any direct sunlight is totally blocked from entering the optics.”
Shahrin notes that 90% of the time, Venus with appear on the computer screen after aligning. Otherwise, a brief spiral search of the field will slide it into view.
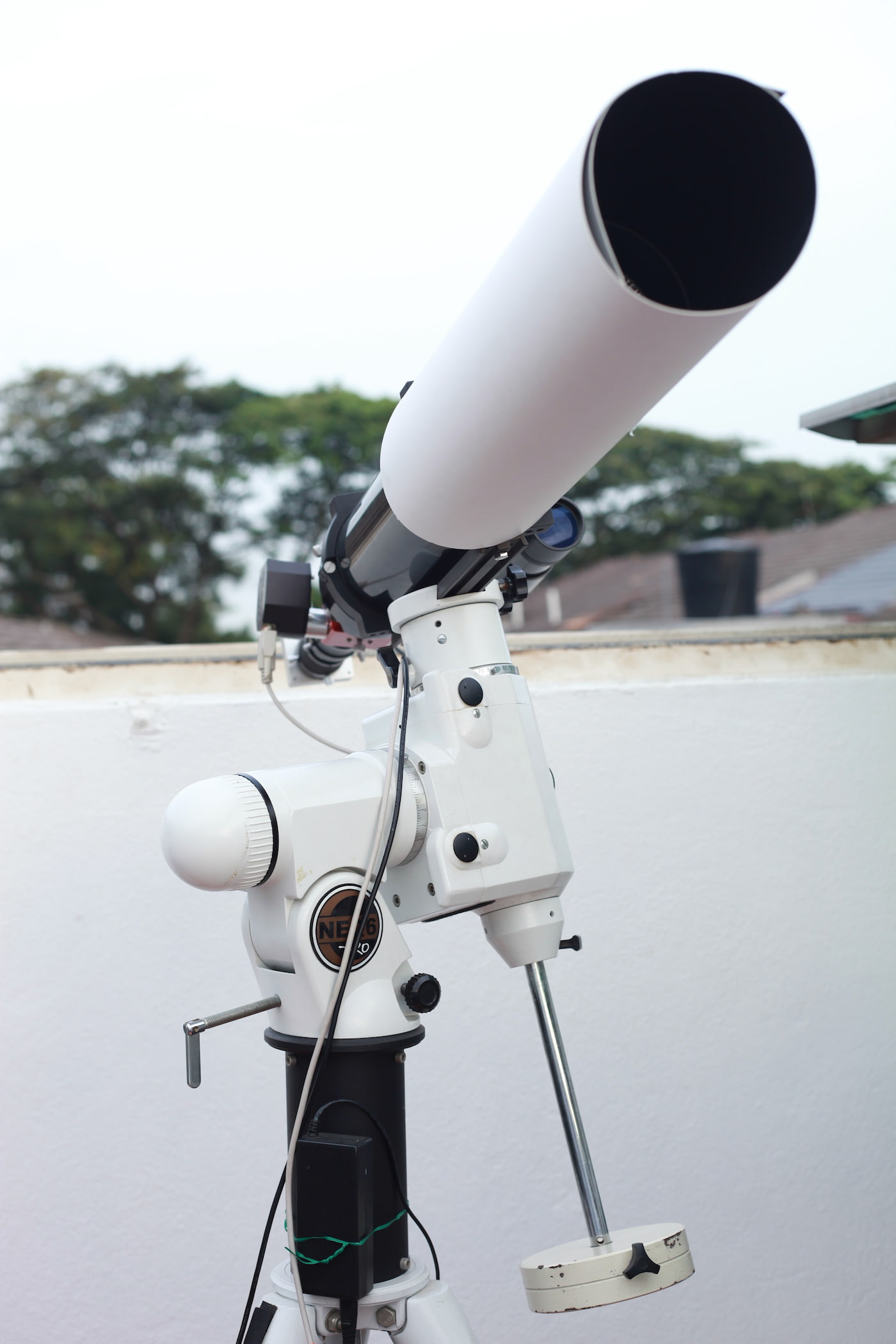
Shahrin observes from his ShahGazer Observatory, a roll-off-roof observatory just outside of Kuala Lumpur. He used the Skywatcher 120ED refractor pictured for the captures, with a 2x Barlow lens to achieve a focal length of 1800mm. Shahrin’s main camera is a QHY CCD IMG132e, and the rig is mounted on a Skywatcher EQ6.

“The experience of being able to track Venus approaching inferior conjunction over the Sun afterwards is exhilarating,” Shahrin told Universe Today. “It felt like watching and waiting for a total eclipse of the Sun, but in slow motion!”
Shahrin also counts himself lucky to have had a string of clear days leading up to and after inferior conjunction.
Shahrin’s capture of Venus 5 degrees from the Sun just 8 hours before inferior conjunction may also be a record. That’s a closer apparent separation than our visual sighting of Venus 7 hours and 45 minutes after inferior conjunction on January 16th 1998 as seen from North Pole Alaska, when the planet passed 5.5 degrees from the limb of the Sun.
“I’ve also noticed that in some of the photos, we can see a slight ‘glint’ of sunshine on part of Venus’ atmosphere,” Shahrin noted to Universe Today. “(This sighting) was actually confirmed by the RASC Edmonton Centre in Canada via their Twitter feed.”
An amazing capture, indeed. Venus is now back in the realm of visibility for us mere mortal backyard observers low in the dawn sky, shining at a brilliant magnitude -4.3. Expect it to vault up in a hurry for northern hemisphere observers as the favorable angle of the ecliptic will give it a boost in the dawn. Venus is also headed towards a spectacular 0.2 degree conjunction with Jupiter this summer on August 18th: expect UFO sightings to rise correspondingly. The Indian Army even briefly mistook the pair for Chinese spy drones early last year.
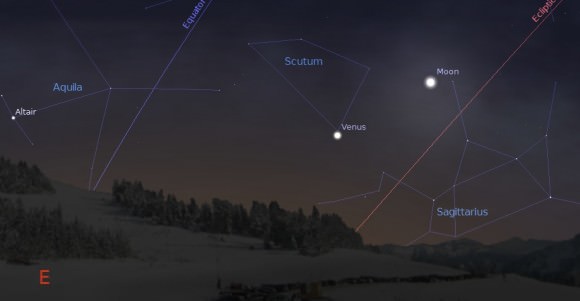
Venus will spend most of 2014 in the dawn sky and is headed for superior conjunction on October 25th, 2014. Venus spent a similar span in the dawn for the majority 2006, and will do so again in 2022. It’s all part of the 8-year cycle of Venus, a span over which apparitions of the planet roughly repeat. And the next shot we’ll have at inferior conjunction? That’ll be on August 15th, 2015 for favoring the southern hemisphere and March 25th, 2017 once again favoring the northern, when the planet very nearly passes as far from the Sun as it can appear at inferior conjunction at 8 degrees.
Congrats to Shahrin on his amazing capture!
-Follow the stargazing adventures of Sharin Ahmad on Google+ and as @shahgazer on Twitter
-Got pictures of Venus? Send ‘em in to Universe Today.