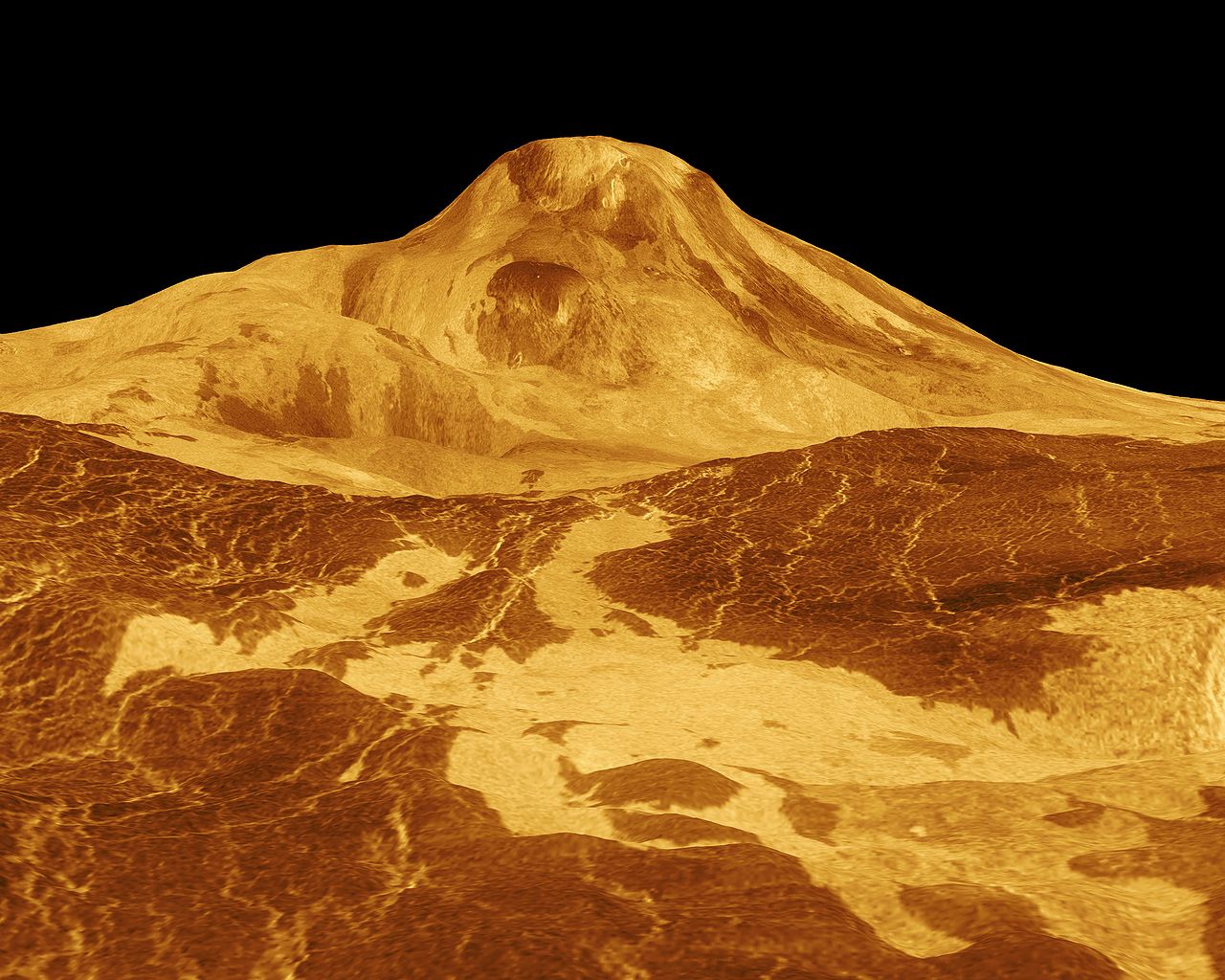
Ever since the announcement last September that astronomers found evidence of phosphine in the clouds of Venus, the planet has been getting a lot of attention. It’s not surprising. Phosphine is a potential biosignature: On Earth, it is produced by microbial life. Might a similar biological process be taking place in the skies of our sister planet? It’s a tantalizing prospect, and is definitely worth examining closely, but it’s too early to be sure. Microbes aren’t the only way to get phosphine. A new paper published on July 12th in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science suggests that volcanism might instead be to blame for the strange chemistry in the Venusian cloud tops.
Continue reading “Volcanic Activity on Venus Could Explain Phosphine”Venus’ Surface Tectonics is More Like Pack ice on Earth
Planets move in mysterious ways. Or at least their surfaces do. Earth famously has a system of tectonic plates that drives the movement of its crust. Those plate tectonics are ultimately driven by the flow of material in the mantle – the layer directly below the crust. Now, scientists have found a slightly different deformation mechanic on our nearest sister planet – Venus.
Continue reading “Venus’ Surface Tectonics is More Like Pack ice on Earth”Bad News, Life Probably can’t Exist on Venus. Good News, it Could be in Jupiter’s Clouds
For decades, scientists engaged in the search for life in the Universe (aka. astrobiology) have focused on searching for life on other Earth-like planets. These included terrestrial (aka. rocky) planets beyond our Solar System (extrasolar planets) and ones here at home. Beyond Earth, Mars is considered to be the most habitable planet next to Earth, and scientists have also theorized that life could exist (in microbial form) in the cloud tops of Venus.
In all cases, a major focal point is whether or not planets have large bodies of water on their surfaces (or did in the past). However, a new study led by a research team from the UK and German (with support from NASA) has shown that the existence of life may have less to do with the quantity of water and more to with the presence of atmospheric water molecules. As a result, we may have better luck finding life on Jupiter’s turbulent cloud deck than Venus’.
Continue reading “Bad News, Life Probably can’t Exist on Venus. Good News, it Could be in Jupiter’s Clouds”NASA Orders Up a Double Shot of Venus Missions Amid Questions About Life
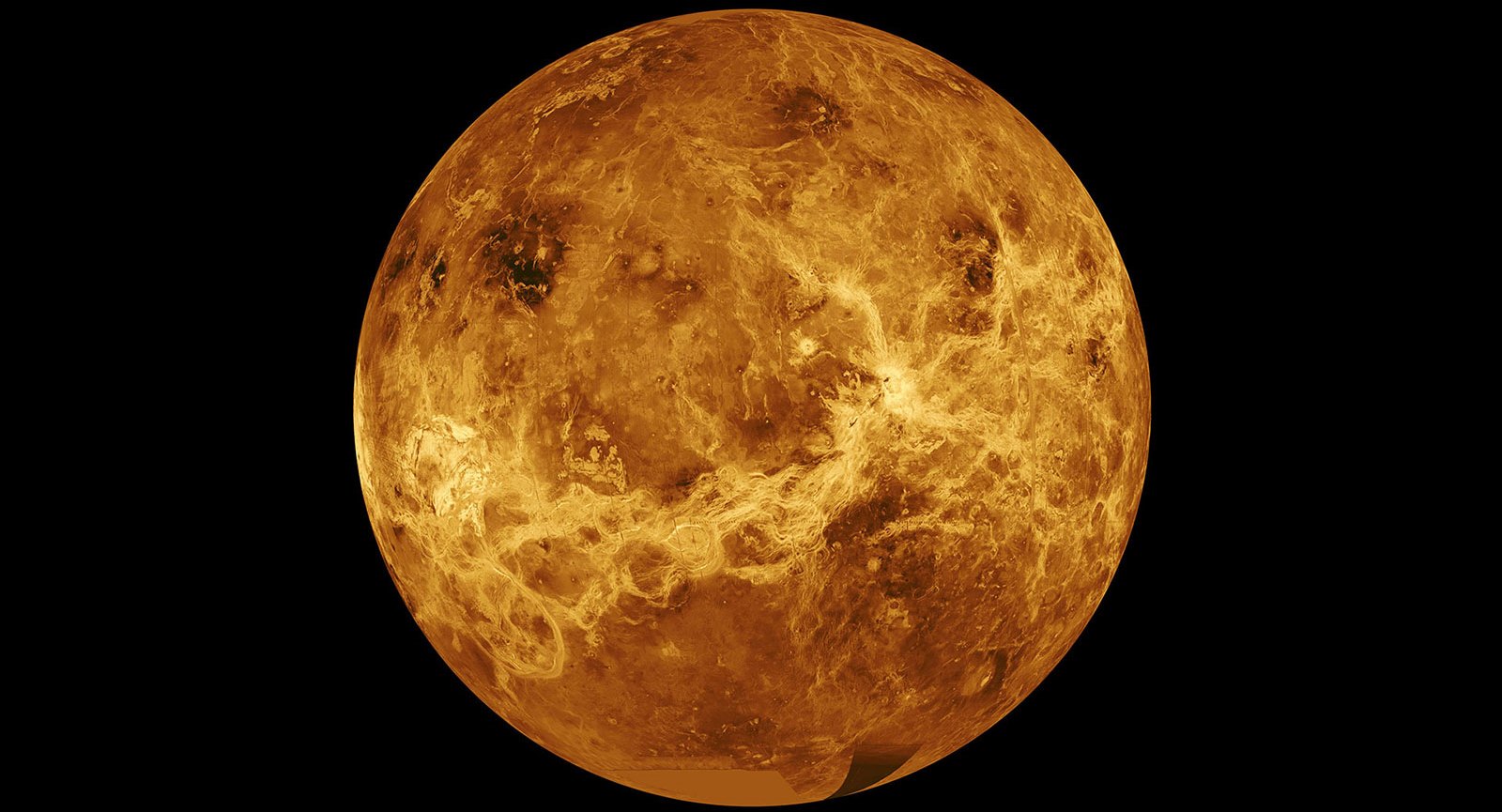

NASA’s planetary science program is making a big bet on Venus, after decades of putting its chips on Mars in the search for hints of past or present life out there in the solar system.
The bet comes in the form of a double dose of development funding for Discovery Program missions, amounting to as much as $1 billion. Both DAVINCI+ and VERITAS were selected from a field of four finalists in a competitive process — leaving behind missions aimed at studying Jupiter’s moon Io and Neptune’s moon Triton.
“These two sister missions are both aimed to understand how Venus became an inferno-like world capable of melting lead at the surface,” NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said June 2 in his first “State of NASA” address. “They will offer the entire science community the chance to investigate a planet we haven’t been to in more than 30 years.”
Lessons from Venus, which underwent a runaway greenhouse effect early in its existence, could improve scientists’ understanding of our own planet’s changing climate. The missions could also address one of the biggest questions about the second rock from the Sun: whether life could exist in the upper reaches of its cloud layer.
Continue reading “NASA Orders Up a Double Shot of Venus Missions Amid Questions About Life”What we’ve Learned About Venus From the Parker Solar Probe
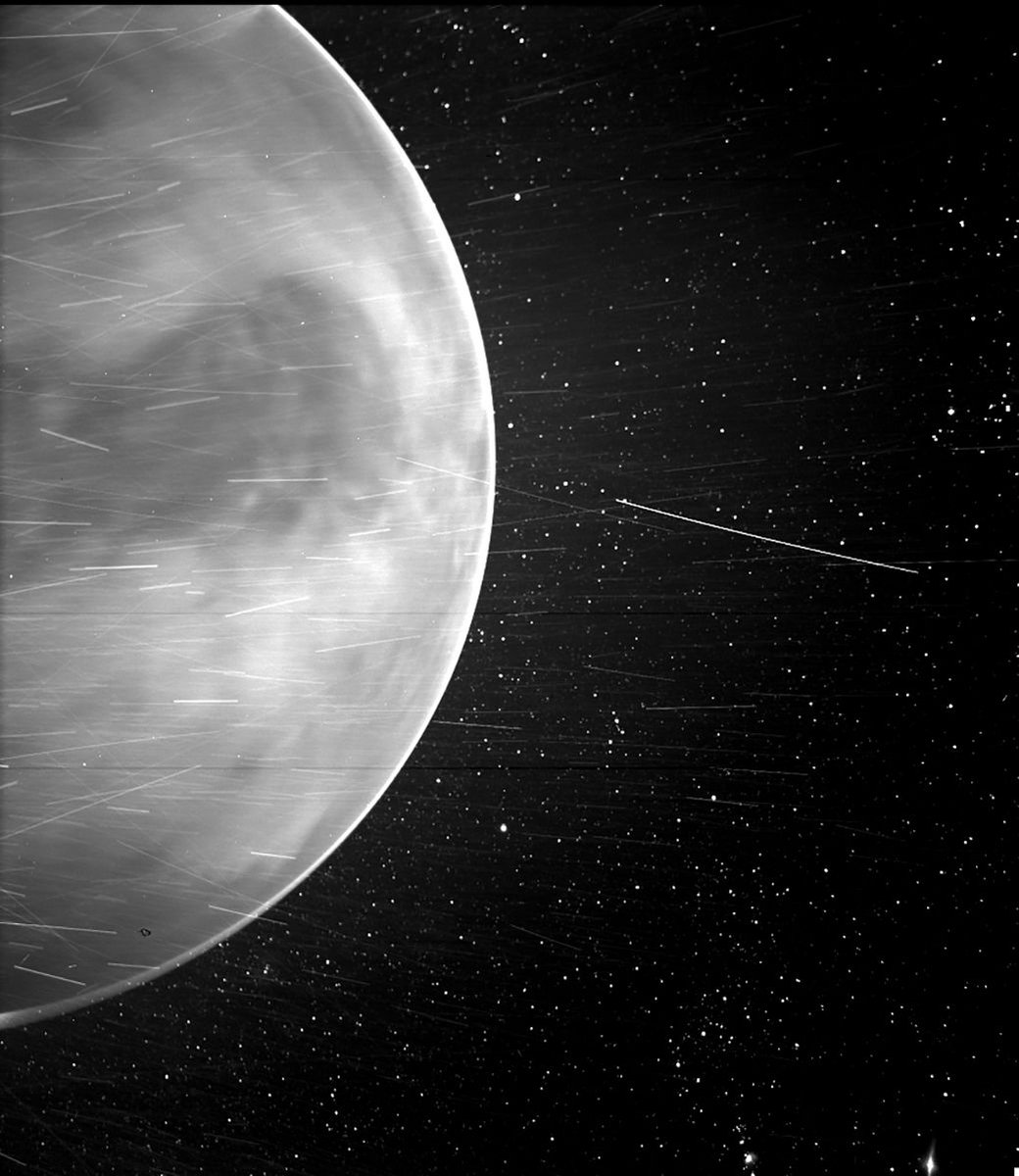
The Parker Solar Probe has been getting in a lot of extracurricular activity lately. Originally designed to observe the Sun, the probe has been taking full advantage of its path through the solar system. In addition to snapping pictures of comets, the probe has repeatedly focused on Venus, including capturing an image peering underneath the cloud cover of the notoriously hot world. Now a team led by Glyn Collinson of Goddard Space Flight Center found another serendipitous discovery in the data Parker collected during its latest flyby in the summer of 2020 – the probe actually flew through Venus’ upper atmosphere, and that atmosphere appeared different than it was almost 30 years ago.
Continue reading “What we’ve Learned About Venus From the Parker Solar Probe”How Long is a Day on Venus? We Finally Know the Exact Answer
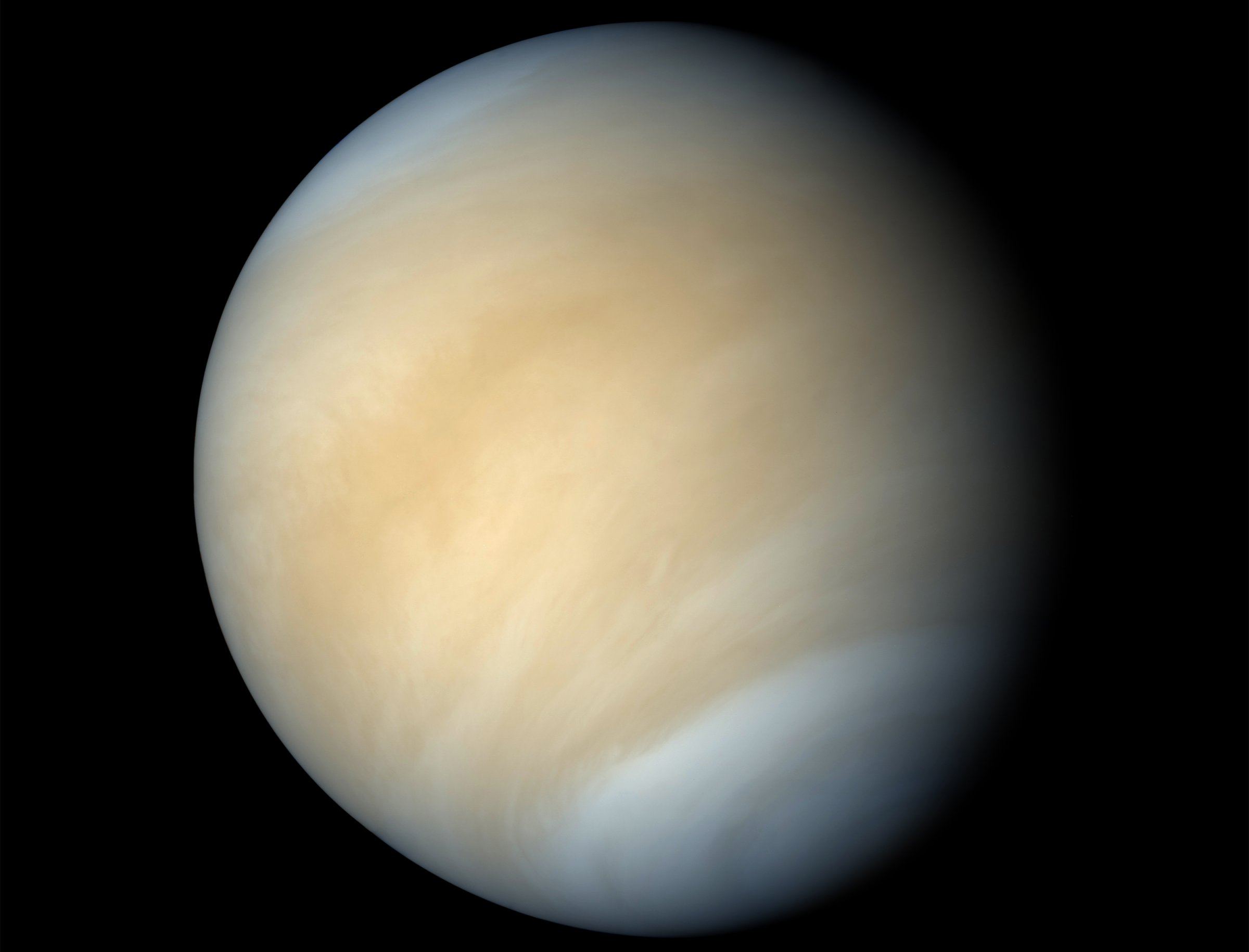

Venus, aka. Earth’s “Sister Planet,” has always been shrouded in mystery for astronomers. Despite being planet Earth’s closest neighbor, scientists remained ignorant of what Venus’ surface even looked like for well into the 20th century, thanks to its incredibly dense and opaque atmosphere. Even in the age of robotic space exploration, its surface has been all but inaccessible to probes and landers.
And so the mysteries of Venus have endured, not the least of which has to do with some of its most basic characteristics – like its internal mass distribution and variations in the length of a day. Thanks to observations conducted by a team led from UCLA, who repeatedly bounced radar off the planet’s surface for the past 15 years, scientists now know the precise length of a day on Venus, the tilt of its axis, and the size of its core.
Continue reading “How Long is a Day on Venus? We Finally Know the Exact Answer”Parker Solar Probe Captured Images of Venus on its way to the Sun
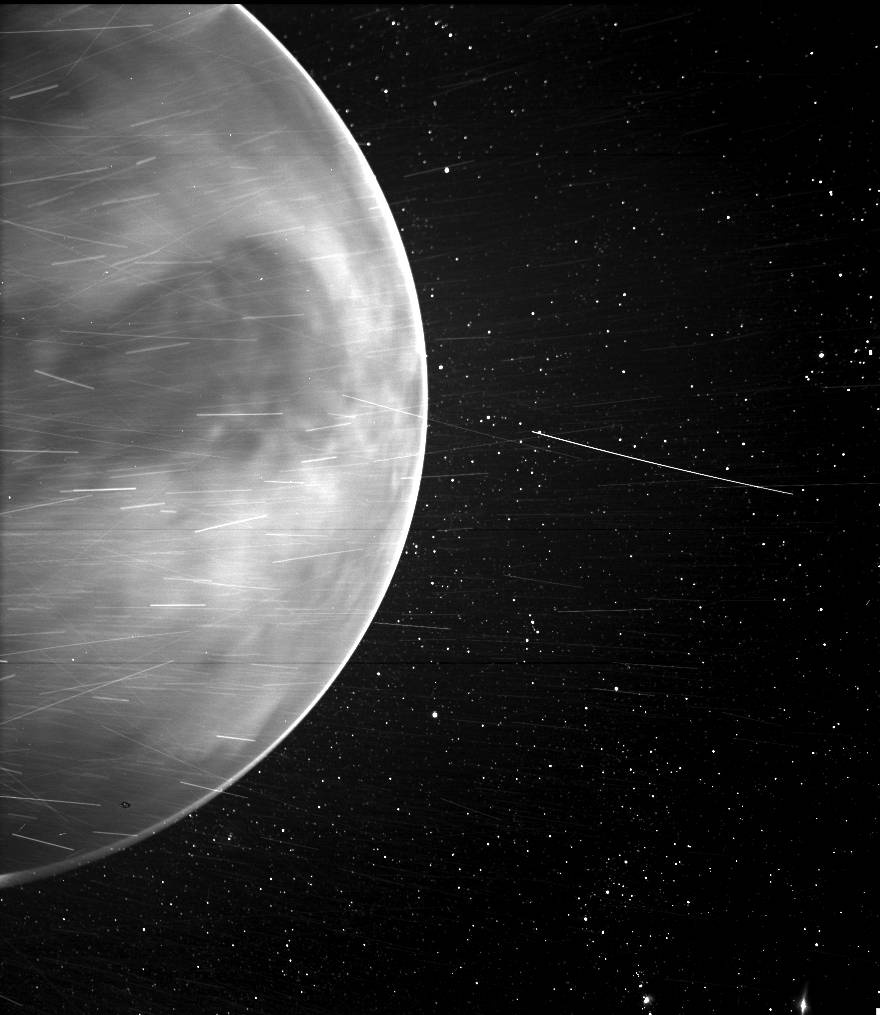

Last summer, the Parker Solar Probe flew past Venus on its way to fly closer to the Sun. In a bit of a surprise, one of the spacecraft’s cameras, the Wide-field Imager for Parker Solar Probe, or WISPR, captured a striking image of the planet’s nightside from 7,693 miles (12380 km) away.
The surprise of the image was that WISPR – a visible light camera – seemingly captured Venus’ surface in infrared light.
Continue reading “Parker Solar Probe Captured Images of Venus on its way to the Sun”What Looked Like Phosphine On Venus Might Actually Just Be Sulfur Dioxide
There’s nothing like a good old fashioned science fight. When the discovery being challenged is one of the most public and intriguing of the last year, it’s bound to be even more interesting. A team of scientists, led by Andrew Lincowski and Victoria Meadows at the University of Washington (UW), and involving members from a variety of NASA labs and other universities, has challenged the discovery of phosphine in the atmosphere of Venus that was first announced last year. Their explanation is much simpler: it was most likely sulfur dioxide, one of the most abundant materials already known to be in Venus’ atmosphere.
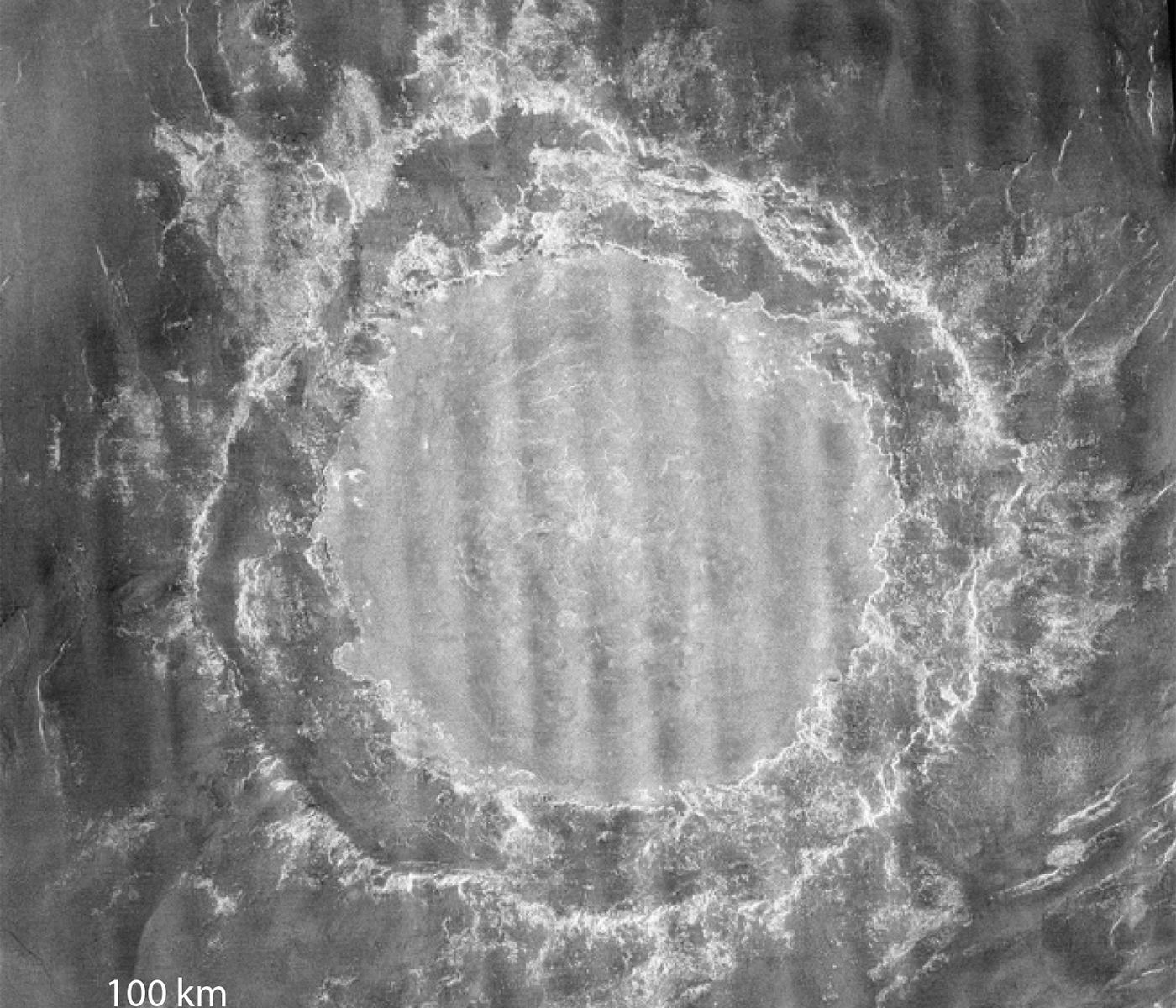
Continue reading “What Looked Like Phosphine On Venus Might Actually Just Be Sulfur Dioxide”A Crater on Venus Indicates the Planet Hasn’t Been Volcanic for a Long Time
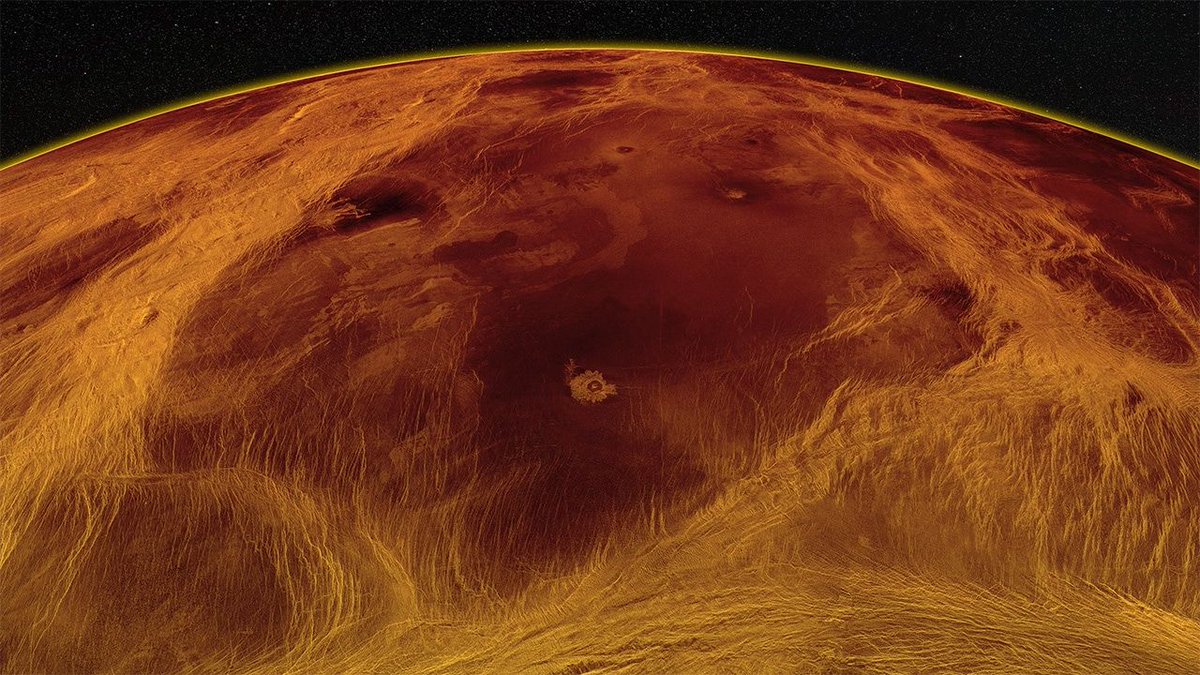
Venus may not have had Earth-like tectonic plates or volcanism for the last billion years, according to a new study. A deep look at a giant impact crater on Venus suggests the planet hasn’t experienced any tectonic activity in the recent past, and might be covered with a in a single outer plate. If so, this would essentially rule out any recent volcanic activity on the planet that many consider Earth’s twin.
Continue reading “A Crater on Venus Indicates the Planet Hasn’t Been Volcanic for a Long Time”Solar Orbiter Caught Venus, Earth and Mars in One of its Photos

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is heading towards the center of the Solar System, with the goal of capturing the closest images ever taken of our Sun. But during its flight, the spacecraft turned back to look towards home. It captured Venus, Earth, and Mars together, as seen from about 155.7 million miles (250.6 million kilometers) away.
Continue reading “Solar Orbiter Caught Venus, Earth and Mars in One of its Photos”