Ready for another Where In The Universe Challenge? Here’s #67! Take a look and see if you can name where in the Universe this image is from. Give yourself extra points if you can name the spacecraft responsible for the image. As usual, we’ll provide the image today, but won’t reveal the answer until tomorrow. This gives you a chance to mull over the image and provide your answer/guess in the comment section. Please, no links or extensive explanations of what you think this is — give everyone the chance to guess.
UPDATE: The answer has now been posted below.
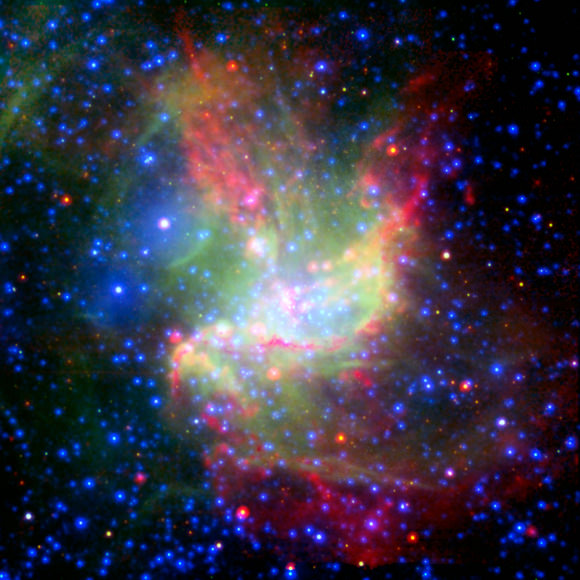
This colorful image is of NGC 346, the brightest star-forming region in the Small Magellanic cloud, a dwar galaxy that orbits the Milky Way at a distance of 210,000 light-years. It combines X-ray, infrared and visible light captured by ESA’s XMM-Newton X-ray observatory, NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory’s New Technology Telescope — so a composite from space- and ground-based telescopes.
This images was released in October 2008 and it provides a new information on how stars in the Universe form. This image shows that wind- and radiation-induced star formation are at play in the same cloud, telling astronomers that star formation is a complicated process comprising different competitive and collaborative mechanisms.
Learn more about his image here.
Thanks for participating in this week’s WITU challenge, and check back next week for another test of your visual knowledge of the cosmos!