How do you measure an object’s weight from a distance? You could guess at its distance and therefore derive its size. Maybe you could further speculate about its density, which would eventually lead to an estimated weight. But these are far from the exact empirical studies that astrophysicists would like to have when trying to understand the weight of stars. Now, for the first time ever, scientists have empirically discovered the weight of a distant single star, and they did so using gravitational lensing.
Continue reading “The Mass of a Single Star (other than the Sun) has Been Directly Measured for the First Time”Two Stars Orbiting Each Other Every 51 Minutes. This Can’t End Well
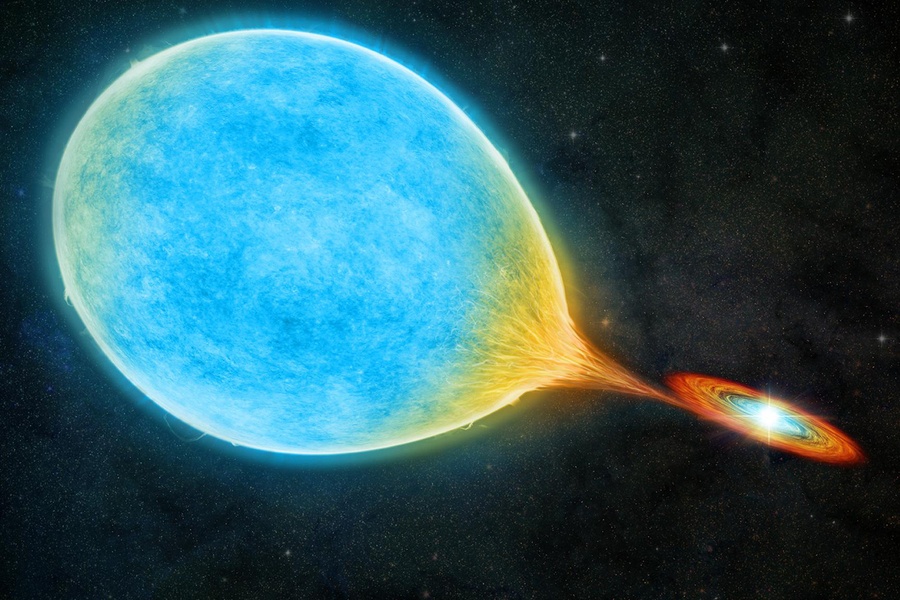

We don’t have to worry too much about our Sun. It can burn our skin, and it can emit potent doses of charged material—called Solar storms—that can damage electrical systems. But the Sun is alone up there, making things simpler and more predictable.
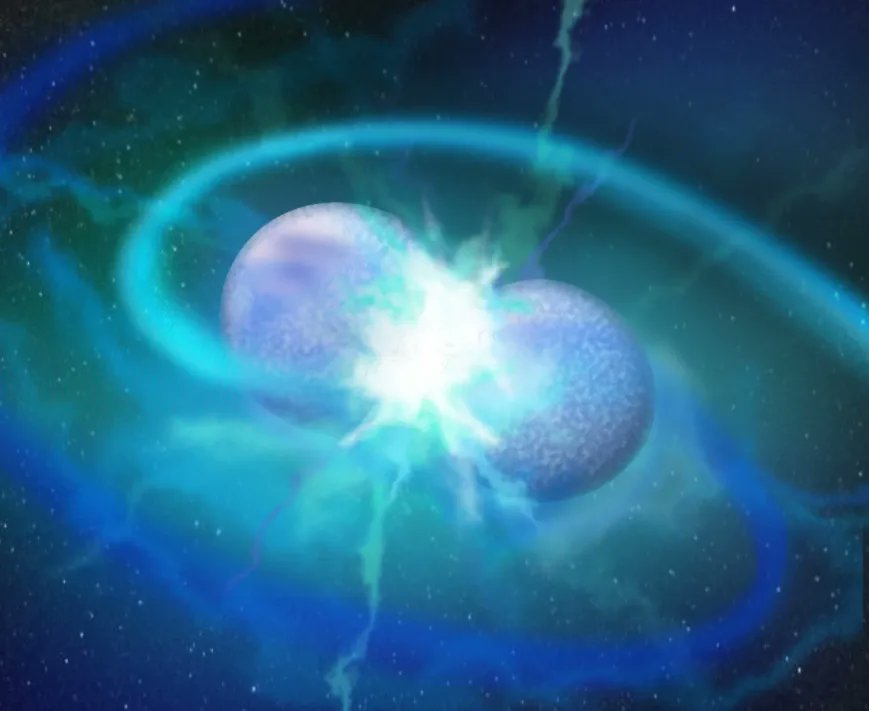
Other stars are locked in relationships with one another as binary pairs. A new study found a binary pair of stars that are so close to each other they orbit every 51 minutes, the shortest orbit ever seen in a binary system. Their proximity to one another spells trouble.
Continue reading “Two Stars Orbiting Each Other Every 51 Minutes. This Can’t End Well”Astronomers Finally Catch a Nova Detonating on a White Dwarf as it's Happening
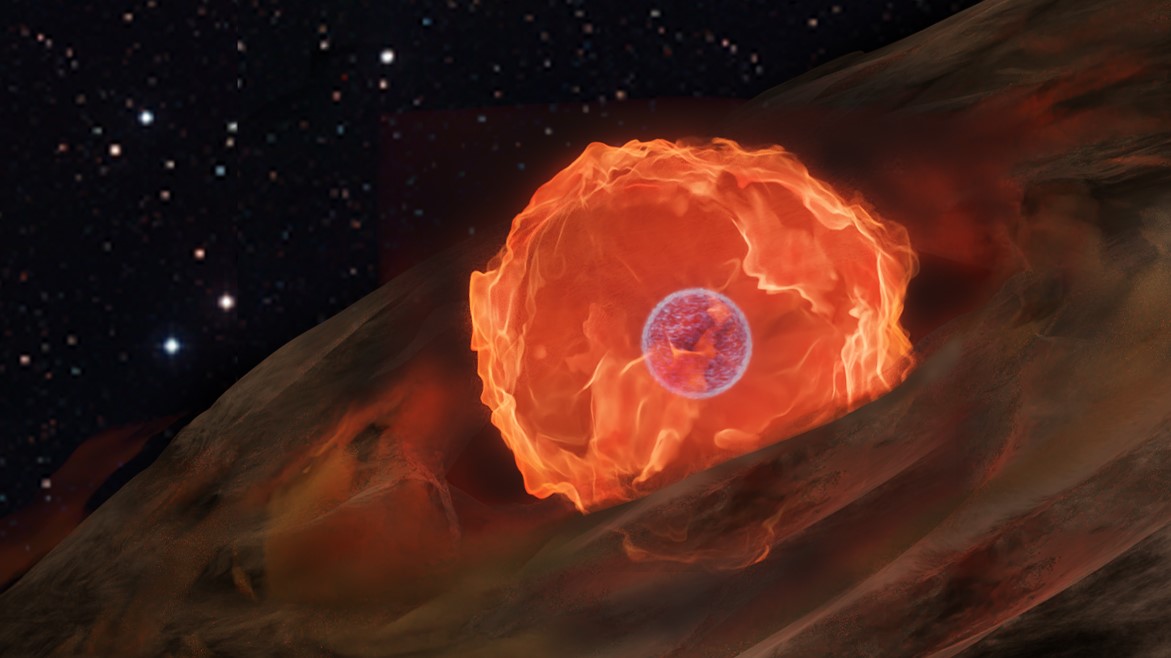
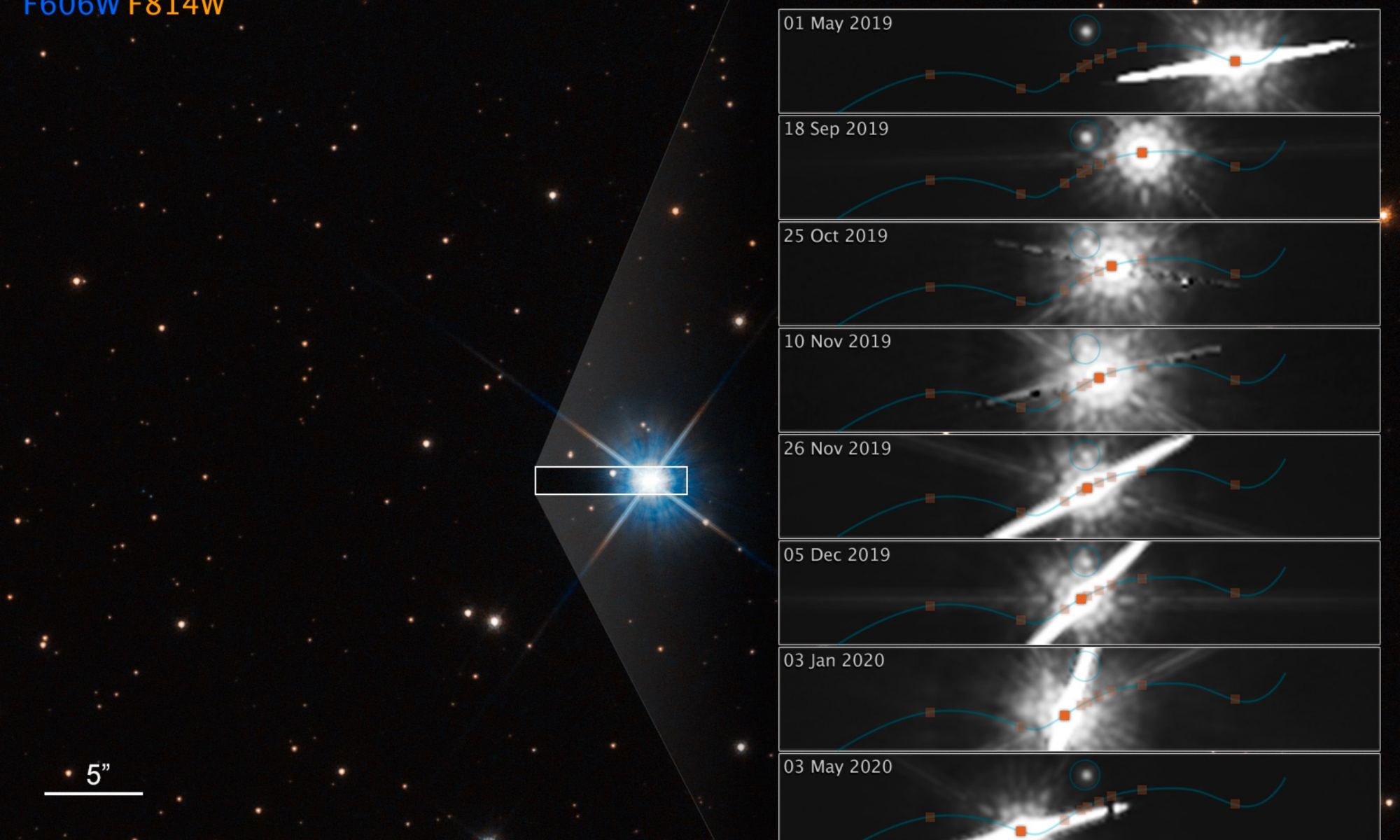
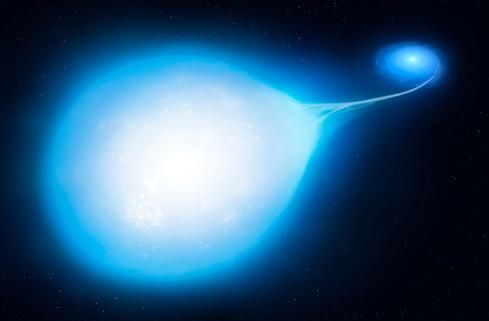
On July 7, 2020, the X-ray instrument eROSITA captured an astronomical event that – until then – had only been theorized and never seen. It saw the detonation of a nova on a white dwarf star, which produced a so-called fireball explosion of X-rays.
“It was to some extent a fortunate coincidence, really,” said Ole König from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), who led the team of scientists who have published a new paper on the discovery. “These X-ray flashes last only a few hours and are almost impossible to predict, but the observational instrument must be pointed directly at the explosion at exactly the right time.”
Continue reading “Astronomers Finally Catch a Nova Detonating on a White Dwarf as it's Happening”If There are Dyson Spheres Around White Dwarfs, We Should be Able to Detect Them
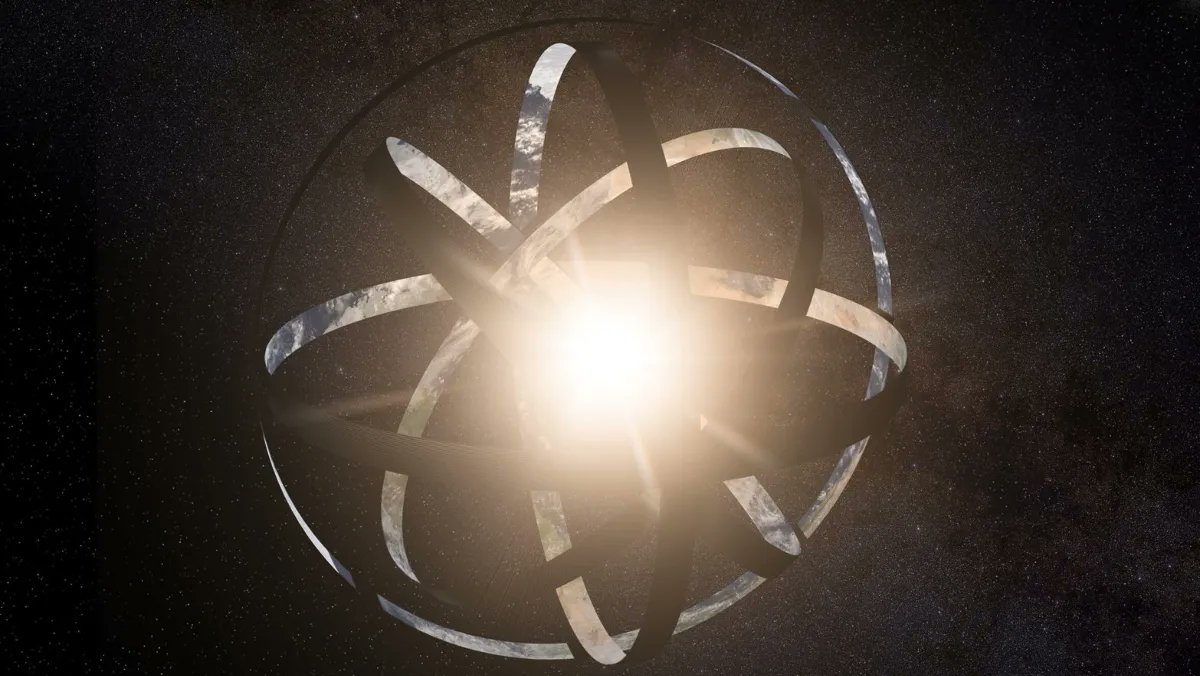
Searching for Dyson spheres, rings, or swarms remains a preoccupation of many astronomers. If there are any out there, they will eventually be found, and the person or research team to do so will go down in history for making one of the most momentous discoveries in the history of humanity. If you’re interested in claiming that accolade for yourself, an excellent place to look may be around white dwarfs. At least, that’s the theory put forward in a new paper by Benjamin Zuckerman, a now-retired professor of astrophysics at UCLA.
Continue reading “If There are Dyson Spheres Around White Dwarfs, We Should be Able to Detect Them”A New Kind of Stellar Explosion Has Been Discovered: Micronovae
The most energetic explosions in the Universe come from stars called supernovae. These galactic bombs have the energy of about 1028 mega-tons. After they detonate, the only thing left behind is either a neutron star or black hole. Another type of stellar explosion is known as a nova which has much less energy and covers the surface of a white dwarf.
Now, a team of astronomers recently discovered a new type of stellar explosion akin to supernovae and novae but with much less energy, and they’re calling it a micronova.
Continue reading “A New Kind of Stellar Explosion Has Been Discovered: Micronovae”Astronomers Discover a Strange new Star That Might be From the Collision Between two Dead Stars
With how many stars there are in our galaxy, there are sure to be plenty of different types of them. But they still continue to amaze us with their differences and constantly challenge our models on how exactly they form. Now a new class of stars was discovered by Dr. Klaus Werner of the University of Tübingen, and they are covered in different materials than expected.
Continue reading “Astronomers Discover a Strange new Star That Might be From the Collision Between two Dead Stars”Planet Found in the Habitable Zone of a White Dwarf

Most stars will end their lives as white dwarfs. White dwarfs are the remnant cores of once-luminous stars like our Sun, but they’ve left their lives of fusion behind and no longer generate heat. They’re destined to glow with only their residual energy for billions of years before they eventually fade to black.
Could life eke out an existence on a planet huddled up to one of these fading spectres?
Continue reading “Planet Found in the Habitable Zone of a White Dwarf”Astronomers Discover a Totally New Kind of Nebula
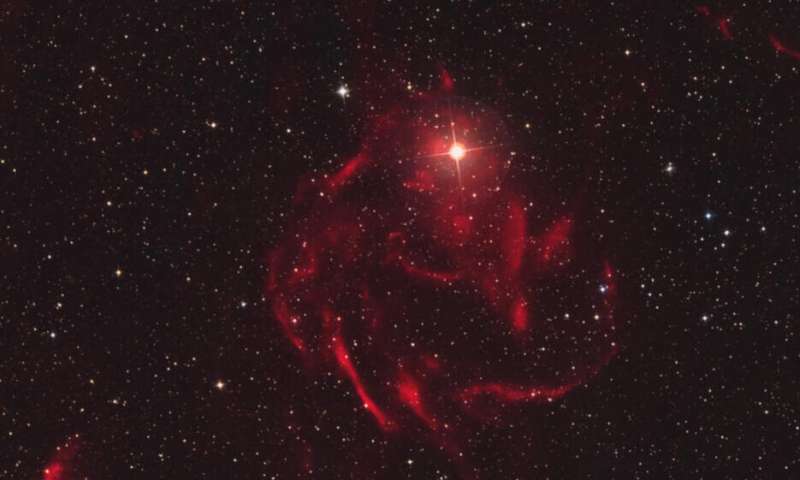

Most Universe Today readers are familiar with nebulae. They’re gaseous structures lit up with radiation from nearby stars, and they’re some of nature’s most beautiful forms.
With the help of amateur astronomers who laid the groundwork, an international team of astronomers have discovered a new type of nebulae around binary stars that they’re calling galactic emission nebulae.
Continue reading “Astronomers Discover a Totally New Kind of Nebula”White Dwarfs can Continue Burning Hydrogen, Even After They’re Dead
White dwarfs are supposed to be dead remnants of stars, doomed to simply fade away into the background. But new observations show that some are able to maintain some semblance of life by wrapping themselves in a layer of fusing hydrogen.
Continue reading “White Dwarfs can Continue Burning Hydrogen, Even After They’re Dead”From the way These Stars Look, a Supernova is Inevitable
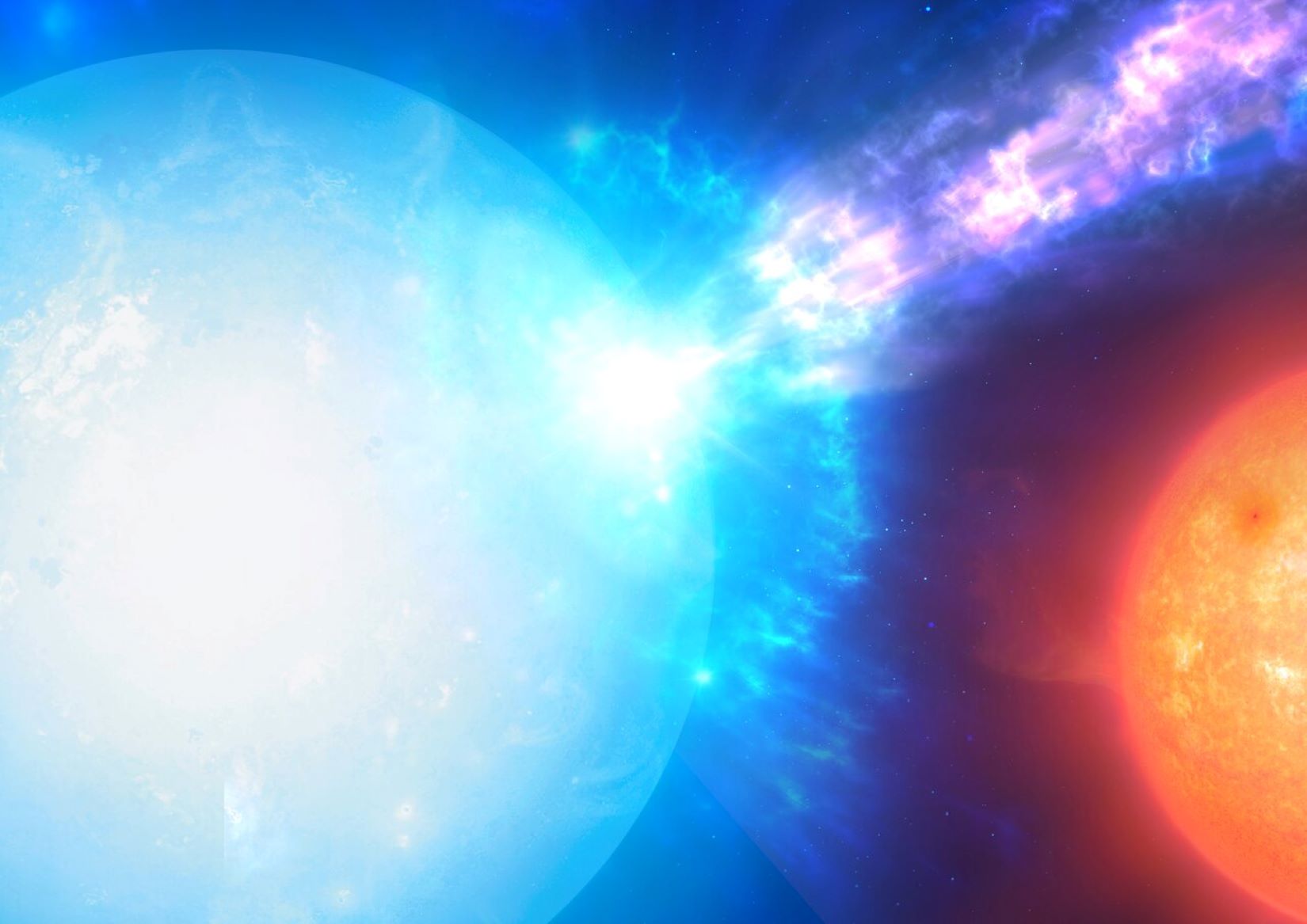
Sometimes loud explosions are easier to deal with when you know they’re coming. They are also easier to watch out for. So when astronomers from the University of Warwick found a rare tear-drop shaped star, known as HD265435, they knew they were looking at a potential new supernova waiting to happen. The only caveat – it might not actually happen until 70 million years from now.
Continue reading “From the way These Stars Look, a Supernova is Inevitable”