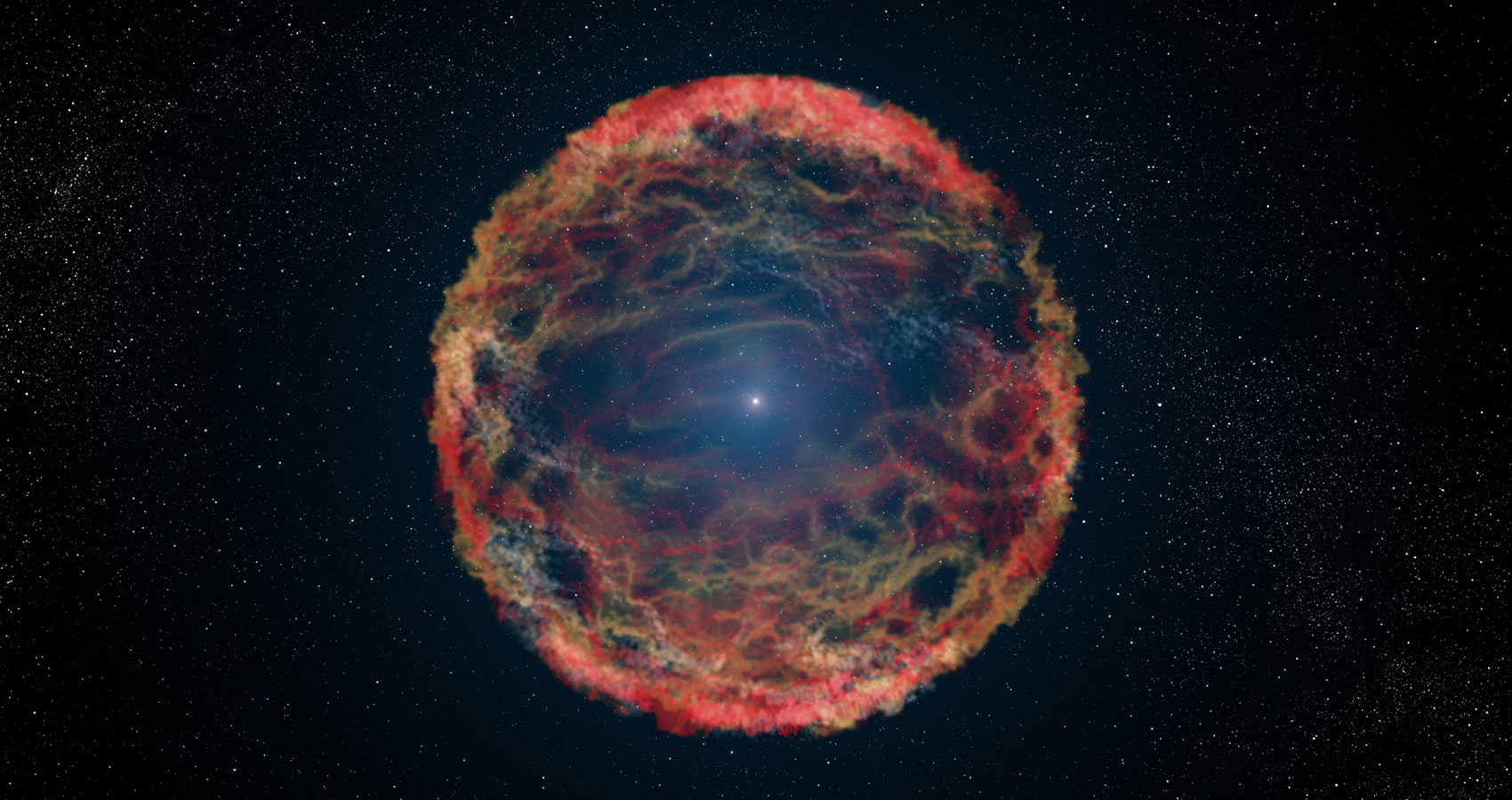
Type Ia supernovae are an important tool for modern astronomy. They are thought to occur when a white dwarf star captures mass beyond the Chandrasekhar limit, triggering a cataclysmic explosion. Because that limit is the same for all white dwarfs, Type Ia supernovae all have about the same maximum brightness. Thus, they can be used as standard candles to determine galactic distances. Observations of Type Ia supernova led to the discovery of dark energy and that cosmic expansion is accelerating.
Continue reading “White Dwarf Measured Before it Exploded as a Supernova”How can White Dwarfs Produce Such Powerful Magnetic Fields?
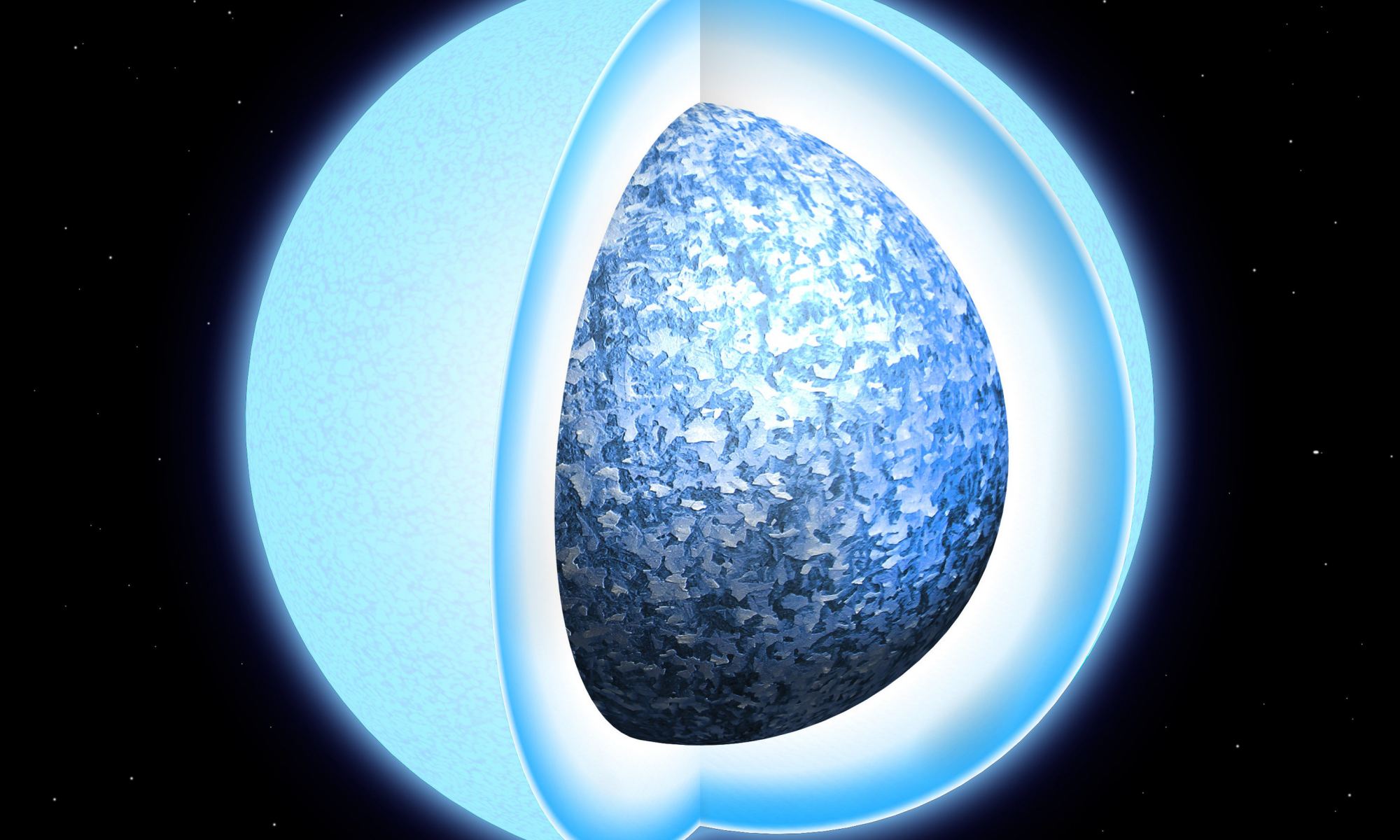
White dwarfs have some surprisingly strong magnetic fields, and one team of astronomers may have finally found the reason why. When they cool, they can activate a dynamo mechanism similar to what powers the Earth’s magnetic field.
Continue reading “How can White Dwarfs Produce Such Powerful Magnetic Fields?”White Dwarf Atmospheres Might Contain the Pulverized Crusts of Their Dead Planets

Astronomers have developed a new technique to search for exoplanets – by looking for their crushed up bones in the atmospheres of white dwarfs. And it’s working.
Continue reading “White Dwarf Atmospheres Might Contain the Pulverized Crusts of Their Dead Planets”James Webb Will Look for Signs of Life on Planets Orbiting Dead Stars

Can the galaxy’s dead stars help us in our search for life? A group of researchers from Cornell University thinks so. They say that watching exoplanets transit in front of white dwarfs can tell us a lot about those planets.
It might even reveal signs of life.
Continue reading “James Webb Will Look for Signs of Life on Planets Orbiting Dead Stars”There’s a flash of ultraviolet just as a white dwarf is exploding as a supernova

Astronomers recently spotted a rare type of supernova explosion that was accompanied by a massive flare of ultraviolet radiation. Untangling the mystery of the UV flash could help unravel the mysterious nature of these supernova explosions, and even help us understand the age of the universe.
Continue reading “There’s a flash of ultraviolet just as a white dwarf is exploding as a supernova”A Star had a Partial Supernova and Kicked Itself Into a High-Speed Journey Across the Milky Way
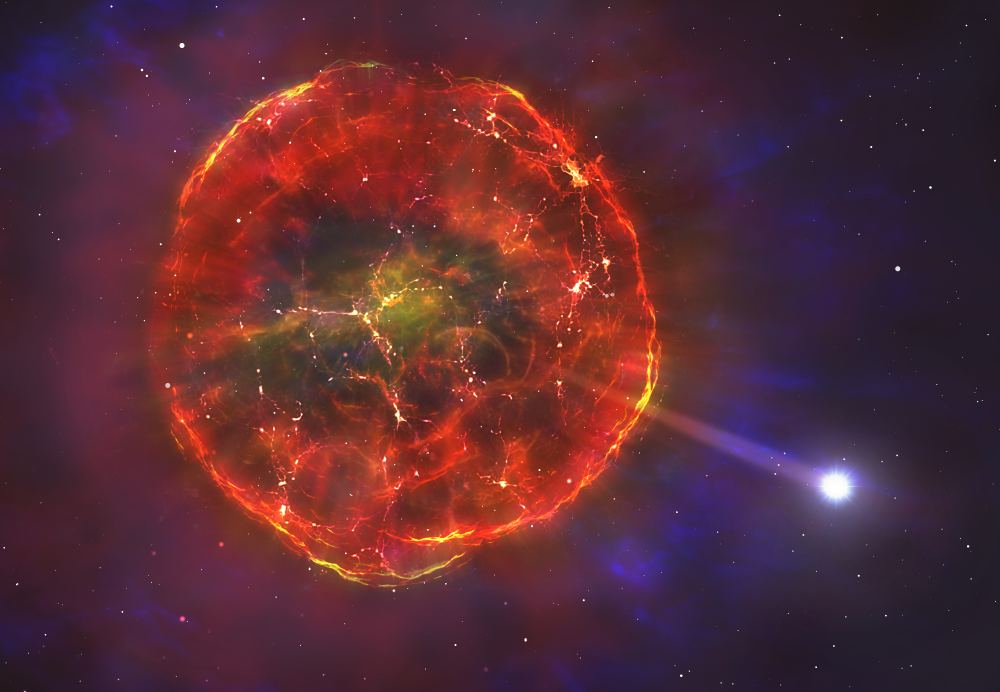
Supernovae are some of the most powerful events in the Universe. They’re extremely energetic, luminous explosions that can light up the sky. Astrophysicists have a pretty good idea how they work, and they’ve organized supernovae into two broad categories: they’re the end state for massive stars that explode near the end of their lives, or they’re white dwarfs that draw gas from a companion which triggers runaway fusion.
Now there might be a third type.
Continue reading “A Star had a Partial Supernova and Kicked Itself Into a High-Speed Journey Across the Milky Way”White dwarfs are a big source of carbon in the Universe

In their nuclear hearts, stars fuse elements heavier than hydrogen, creating the ingredients necessary to make planets, oceans, and people. Tracing the origins of individual elements in the Milky Way has been a challenge, but a new analysis of white dwarf stars reveals that they may be responsible for one of the most essential elements of all: carbon.
Continue reading “White dwarfs are a big source of carbon in the Universe”Astronomers Watch a Nova Go From Start to Finish for the First Time
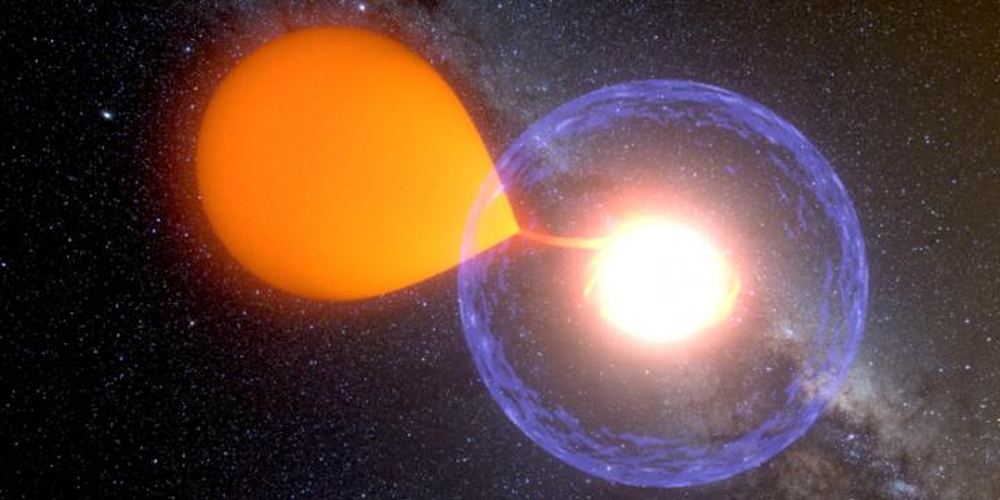
A nova is a dramatic episode in the life of a binary pair of stars. It’s an explosion of bright light that can last weeks or even months. And though they’re not exactly rare—there are about 10 each year in the Milky Way—astronomers have never watched one from start to finish.
Until now.
Continue reading “Astronomers Watch a Nova Go From Start to Finish for the First Time”Astronomers Watched a Star System Die
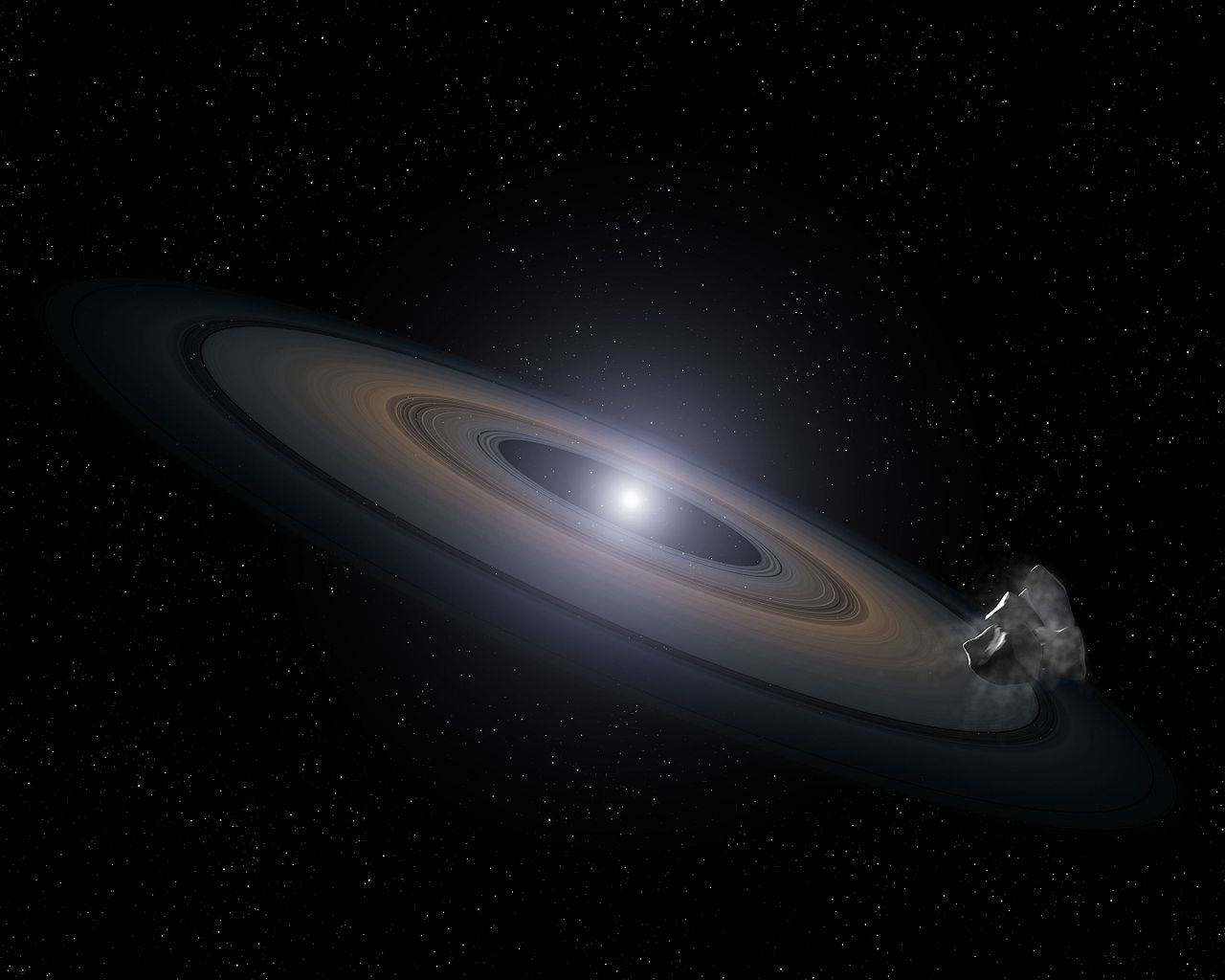

About 570 light years from Earth lies WD 1145+017, a white dwarf star. In many respects it’s a typical white dwarf star. Its mass is about 0.6 solar masses, and its temperature is about 15,900 Kelvin. But five years ago, a team of astronomers wrote a paper on the white dwarf, showing that something unusual was going on.
Continue reading “Astronomers Watched a Star System Die”Two White Dwarfs Merged Together Into a Single “Ultramassive” White Dwarf
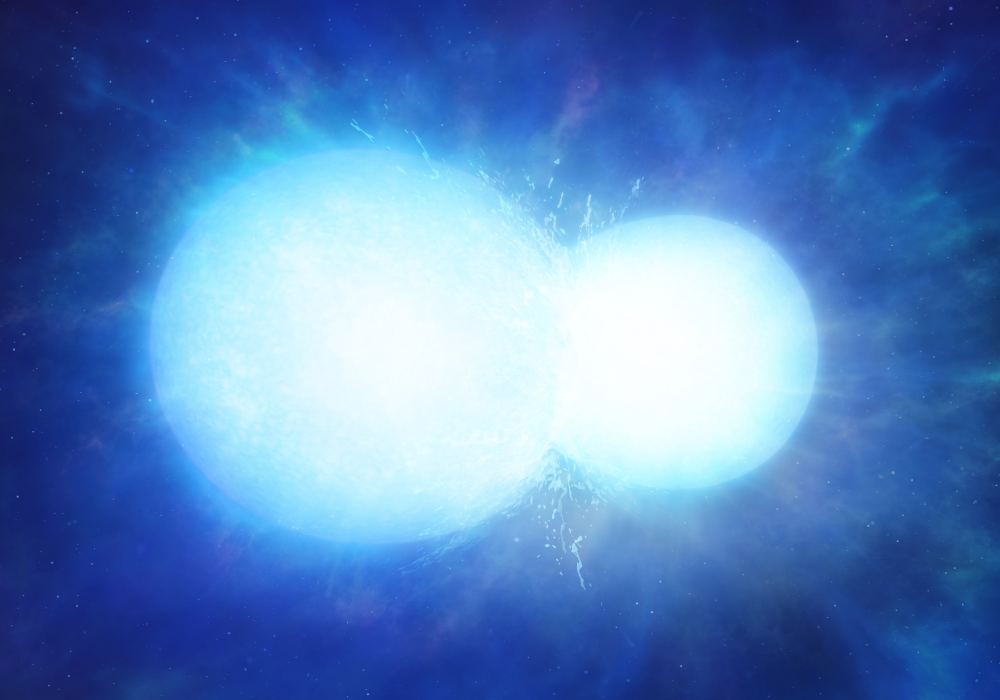

Astronomers have found a white dwarf that was once two white dwarfs. The pair of stars merged into one about 1.3 billion years ago. The resulting star, named WDJ0551+4135, is about 150 light years away.
Continue reading “Two White Dwarfs Merged Together Into a Single “Ultramassive” White Dwarf”
