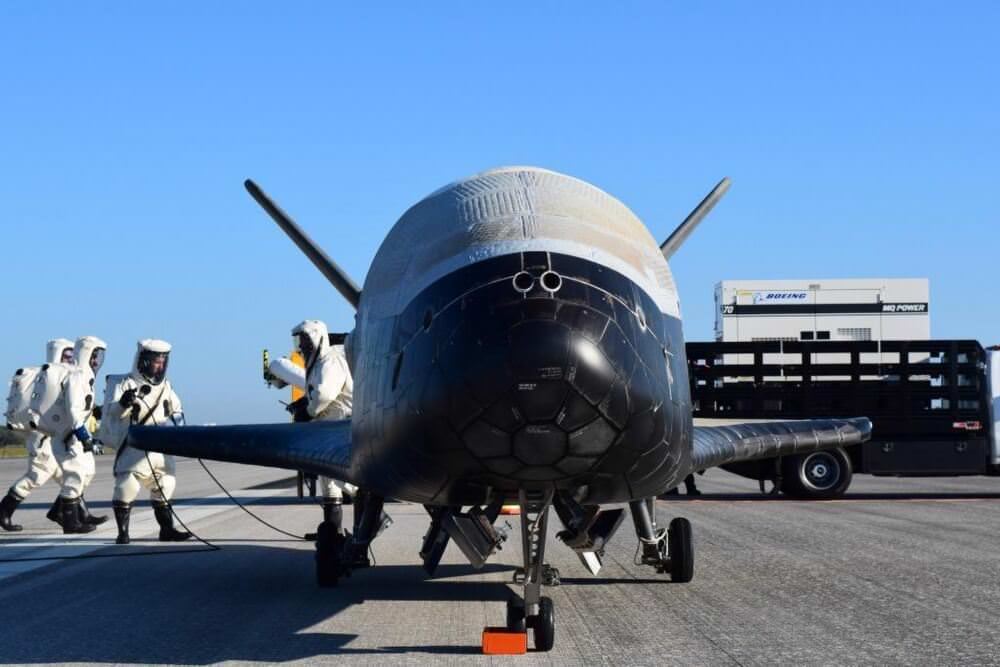
The Air Force’s secretive X-37B space plane landed at the Kennedy Space Center’s orbiter runway on Sunday, May 7, after spending a record 718 days in orbit. This was the fourth flight of the uncrewed, autonomous military project, and was the first landing for an X-37B at KSC.
“The landing of OTV-4 marks another success for the X-37B program and the nation,” said Lt. Col. Ron Fehlen, X-37B program manager. “This mission once again set an on-orbit endurance record and marks the vehicle’s first landing in the state of Florida. We are incredibly pleased with the performance of the space vehicle and are excited about the data gathered to support the scientific and space communities. We are extremely proud of the dedication and hard work by the entire team.”
The mini space shuttle launched on May 20, 2015 on its somewhat clandestine mission. The launch was well publicized (and shown live on a webcast) but the landing came unannounced, except for the sonic boom that heralded its arrival, surprising those living around the space coast area.
The Air Force revealed before the launch that it would carry an experimental electric propulsion thruster to be tested in orbit and an investigation called Materials Exposure and Technology Innovation in Space (METIS), which exposes sample materials to the space environment and builds on more than ten years of similar research on the International Space Station.
Beyond that, however, what the X-37B did in orbit is not known. The Air Force said in a news release is that mini shuttle is “an experimental test program to demonstrate technologies for a reliable, reusable, unmanned space test platform for the U.S. Air Force.” Some experts has said they believe it has intelligence-gathering equipment.

Satellite-tracking enthusiasts were able to monitor the ship’s changing orbital height at various times throughout the mission.
The reusable space plane is designed to be launched like a satellite and land on a runway like an airplane and the NASA space shuttles. The 11,000 pound (4990 kg) OTV space plane was built by Boeing and is about a quarter the size of a NASA space shuttle. It was originally developed by NASA but was transferred to the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in 2004.
Note: In the above video you’ll see a “big” NASA space shuttle sitting near the runway. It is the mockup of a space shuttle that used to be at the entrance of the Kennedy Space Center visitor complex. It is currently being restored.
All four OTV missions launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida and previous missions landed at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The first OTV mission launched on April 22, 2010, and concluded on Dec. 3, 2010, after 224 days in orbit. The second OTV spent 468 days on orbit, and the third mission was 674 days long.
The Air Force said they are preparing to launch the fifth X-37B mission from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, later in 2017.
Sources: Air Force, Spaceflight Now, US Air Force Twitter.