[/caption]
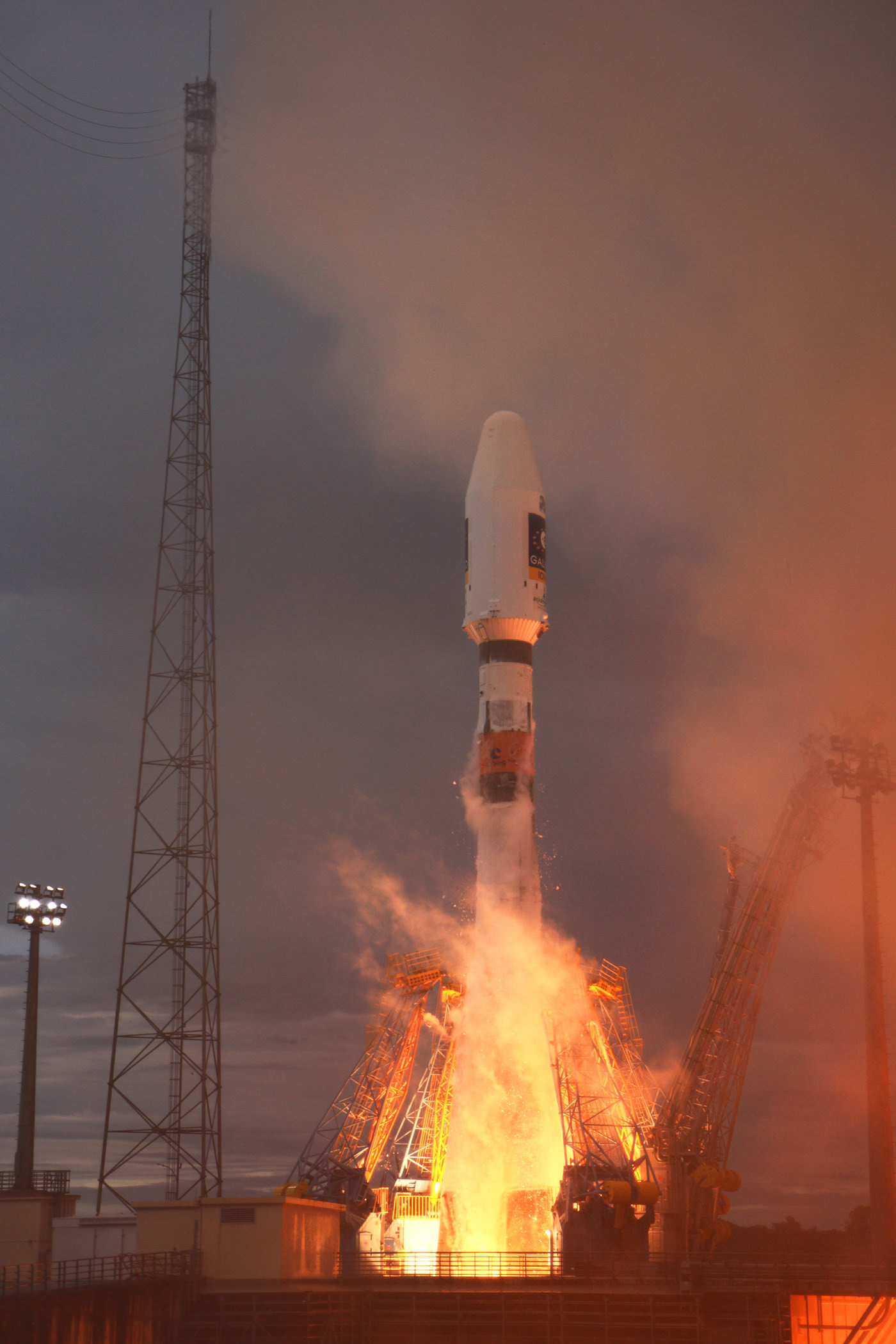
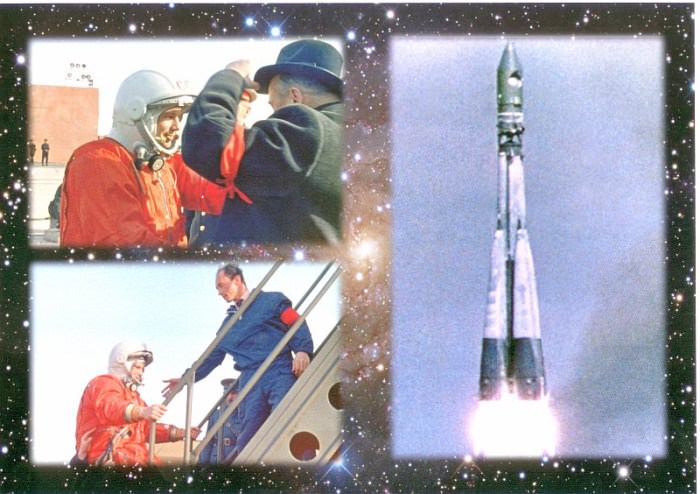
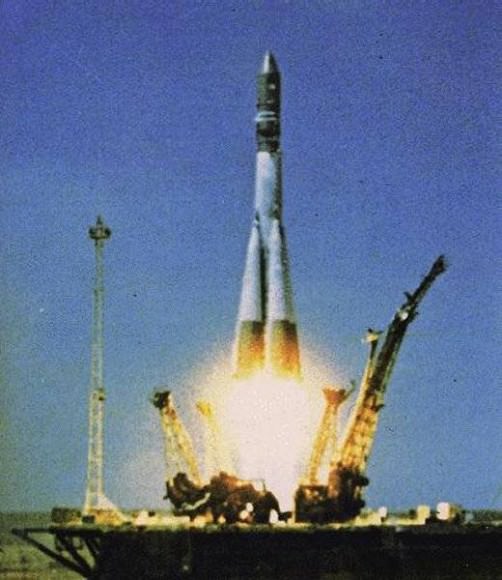
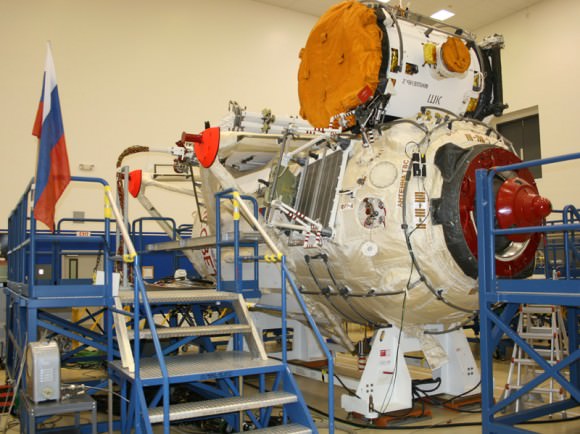
Russia’s legendary Soyuz rocket soared skywards today (Oct.21) on its historic 1st ever blastoff from a new European space base in the equatorial jungles of South America. The history making liftoff of the Soyuz ST-B launcher from French Guiana occurred at exactly 6:30:26 a.m. EST (10:30:26 GMT) and lofted the first two operational satellites of Europe’s new Galileo GPS navigation system.
The flawless liftoff of the Soyuz booster from the ELS pad in French Guiana marked the first time that a Soyuz was launched from outside of the six existing pads in Russia and Kazakhstan. The joint Russian-European project was started back in 2004 and culminated with today’s launch of the Soyuz-VSO1 mission.
“This launch represents a lot for Europe: we have placed in orbit the first two satellites of Galileo, a system that will position our continent as a world-class player in the strategic domain of satellite navigation, a domain with huge economic perspectives,” said Jean-Jacques Dordain, Director General of ESA.

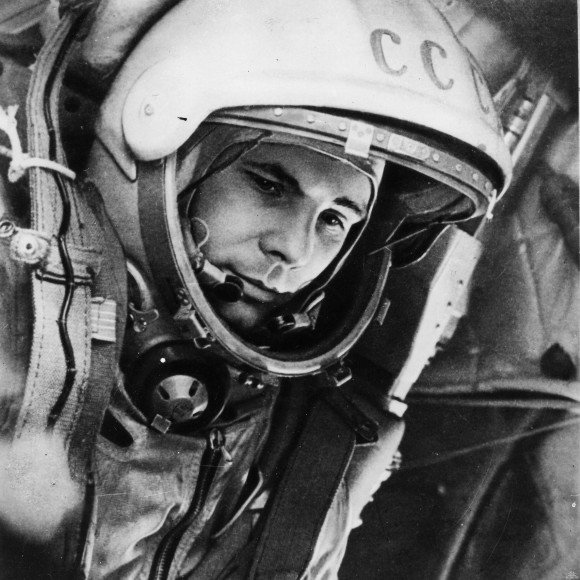
Soyuz lineage dates back to the beginning of the Space Age with the launch of Sputnik-1 in 1957 and the first man in space, Yuri Gagarin, in 1961. Soyuz had flown 1776 times to date.

The launcher is based on the existing Soyuz design with a few changes to accommodate European safety standards and the construction of the ELS launch pad was modeled after the existing pads in Baikonur in Kazakhstan and Plesetsk in Russia. One significant difference is the construction of a 45 meter (170 foot) mobile gantry
A leaky valve delayed the flight by one day.
The duo of 700 kg Galileo satellites were mounted side by side on the Fregat upper stage atop the three stage Soyuz-2 rocket. These two Galileo In-orbit Validation (IOV) model satellites are experimental models that will be used to test the GPS technology.

Two additional Galileo IOV satellites will be launched in 2012 as the initial segment of a 30 strong constellation of satellites in total.
The Galileo satelites will provide pinpoint accuracy to within about 1 meter (3 feet) compared to about 3 meters (10 feet) for the GPS system.
The 4 meter diameter payload fairing jettisoned as planned three minutes into the flight and the first of two firings of the Fregat upper stage was successfully completed after burnout of the lower stages. The second Fregat firing was accomplished about 4 hours after launch and injected the Galileo satellites into orbit some 23,000 km (14,000 miles) miles high.
The Fregat upper stage was designed to reignite and fire up to 20 times. It is fueled with nitrogen tetroxide and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH).

By launching from near the equator (5°N), the Soyuz gains about a 50% performance boost from 1.7 tons to nearly 3 tons to geostationary orbit due to the Earth’s faster spin compared to Baikonur (46°N).
Manned Soyuz missions from South America could be possible at some future date if the political and funding go ahead was approved by ESA and Russia. It is technically possible to reach the ISS from the French Guiana pad and would require the installation of additional ground support equipment.
The next Soyuz launch from South America is set for Dec. 16, 2011. 17 contracts have already been signed for future liftoffs at a rate of 2 to 3 per year.
Read Ken’s continuing features about Soyuz from South America starting here:
Russian Soyuz Poised for 1st Blastoff from Europe’s New South American Spaceport
Read Ken’s features about Russia’s upcoming Phobos-Grunt launch from Baikonur here:
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghou-1 Arrive at Baikonur Launch Site to tight Mars Deadline
Phobos-Grunt: The Mission Poster
Daring Russian Sample Return mission to Martian Moon Phobos aims for November Liftoff