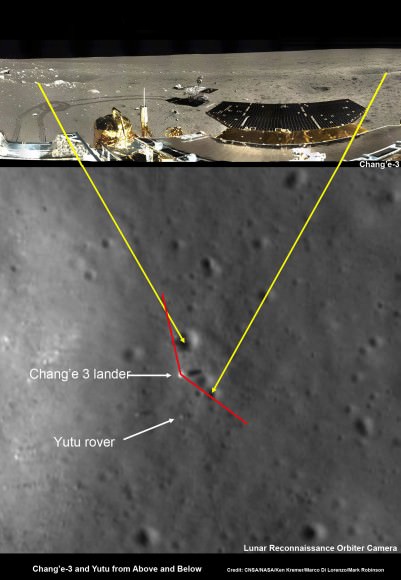
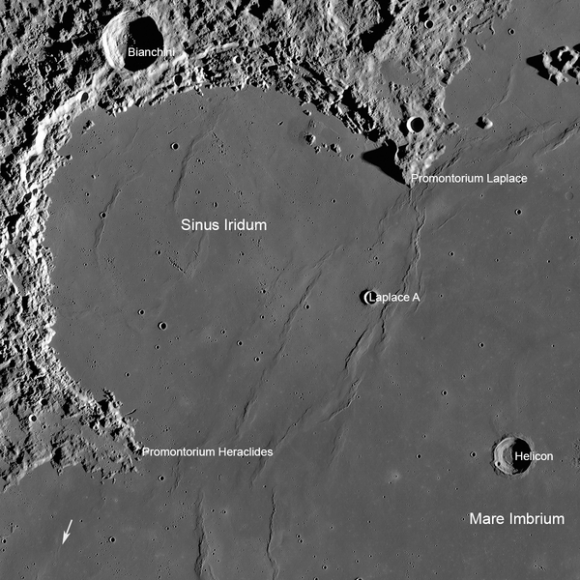
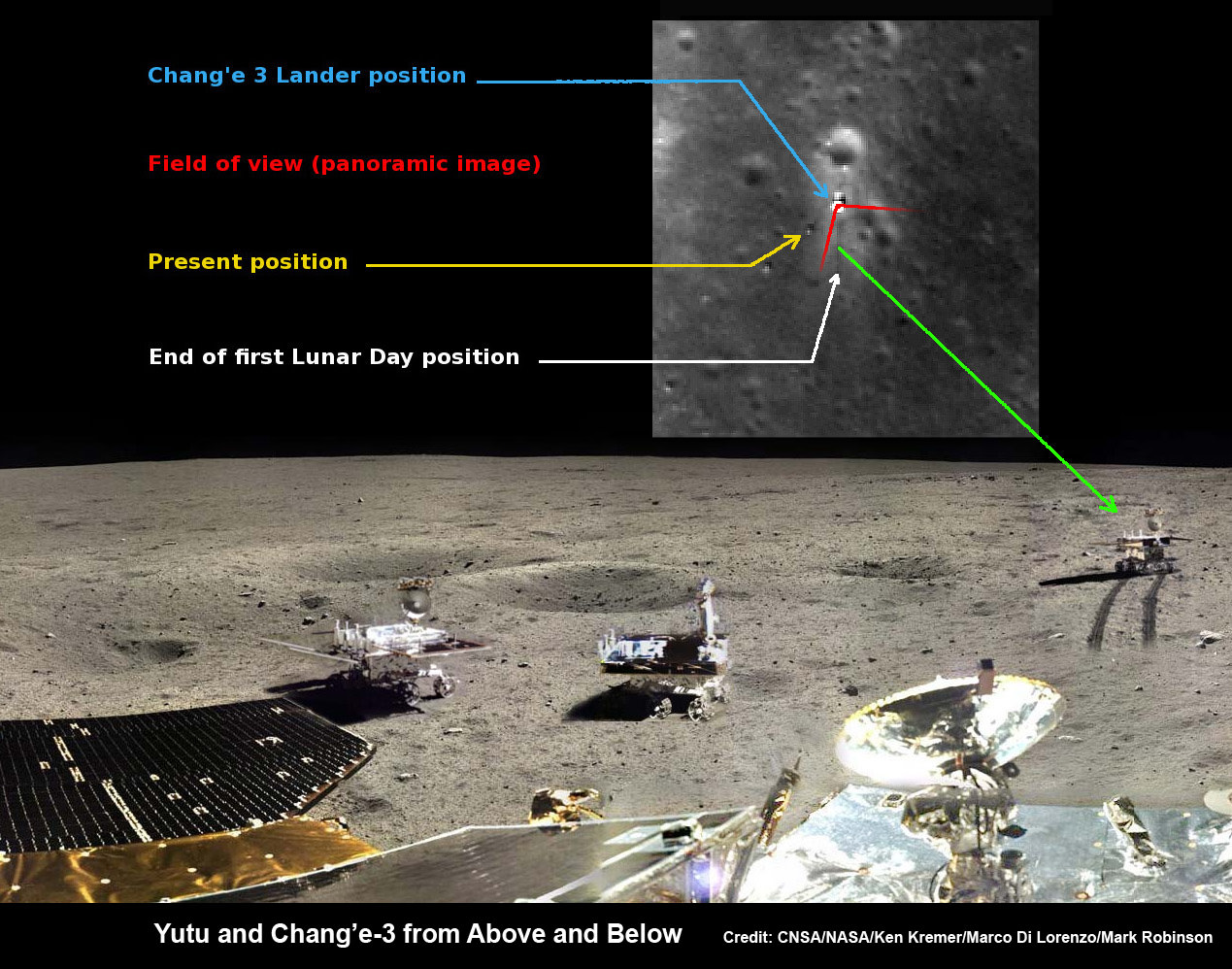
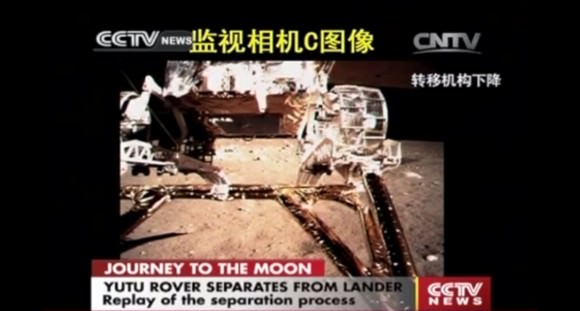
Yutu rover drives around Chang’e-3 lander – from Above And Below
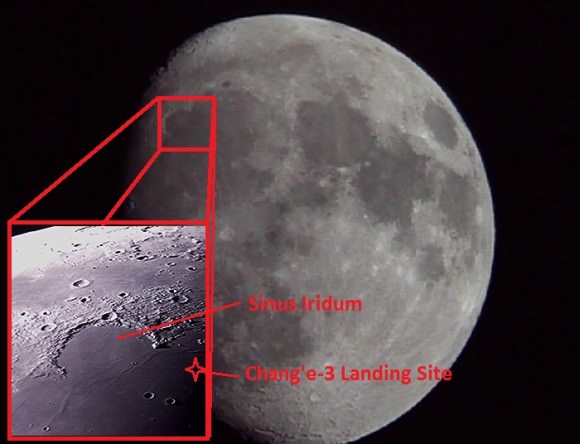
Composite view shows China’s Yutu rover and tracks driving in clockwise direction around Chang’e-3 lander from Above And Below (orbit and surface). The Chang’e-3 timelapse lander color panorama (bottom) and orbital view (top) from NASA’s LRO orbiter shows Yutu rover after it drove down the ramp to the moon’s surface and began driving around the landers right side, passing by craters and heading south on Lunar Day 1. It then moved northwest during Lunar Day 2. Arrows show Yutu’s positions over time.
Credit: CNSA/NASA/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo/Mark Robinson
See below more mosaics and LRO imagery
Story updated[/caption]
The powerful telescopic camera aboard NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has captured spectacular new images detailing the traverse of China’s Yutu moon rover around the landing site during its first two months exploring the Moon’s pockmarked grey terrain.
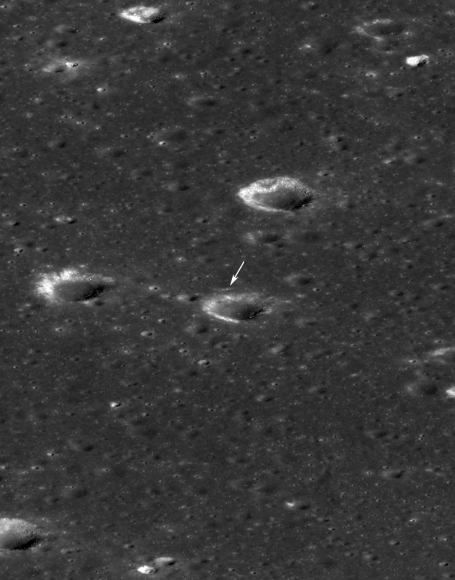
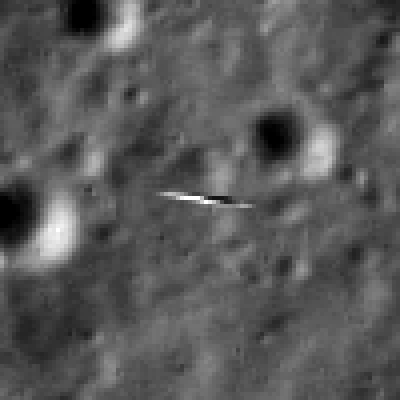
The newly released high resolution LRO images even show Yutu’s tracks cutting into the lunar surface as the world famous Chinese robot drove in a clockwise direction around the Chang’e-3 lander that delivered it to the ground in mid-December 2013.
You can precisely follow Yutu’s movements over time – from ‘above and below’ – in our new composite view (shown above) combining the latest LRO image with our timelapse mosaic showing the rover’s history making path from the touchdown point last December to today’s location.
Yutu is China’s first ever Moon rover and successfully accomplished a soft landing on the Moon on Dec. 14, 2013, piggybacked atop the Chang’e-3 mothership lander.
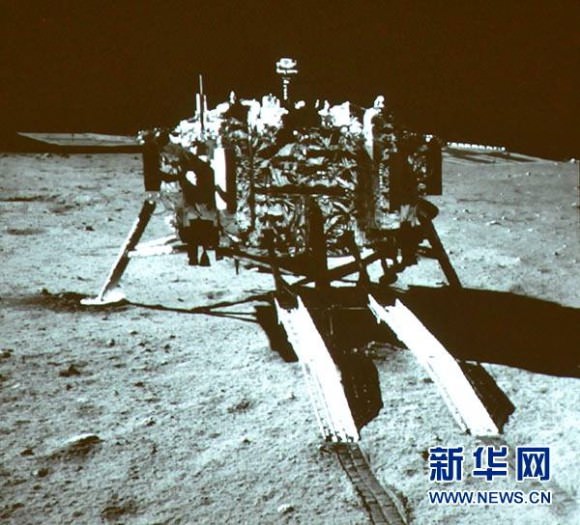
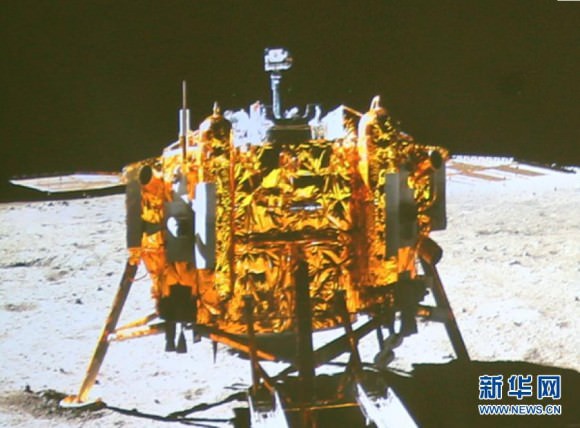
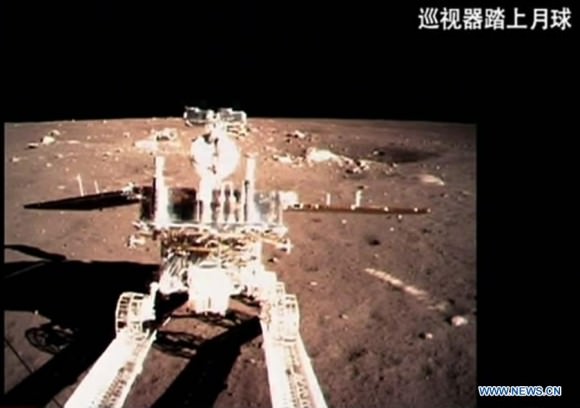
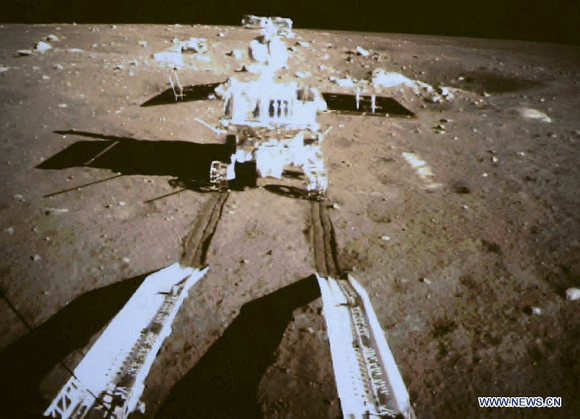
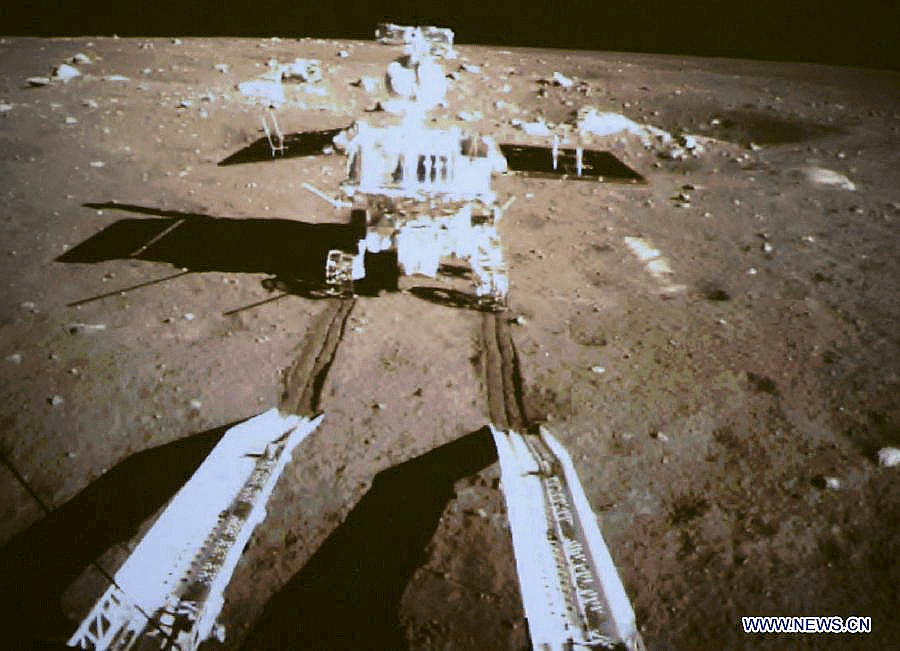
Barely seven hours after touchdown, the six wheeled moon buggy drove down a pair of ramps onto the desolate gray plains of the lunar surface at Mare Imbrium (Sea of Rains) covered by volcanic material.
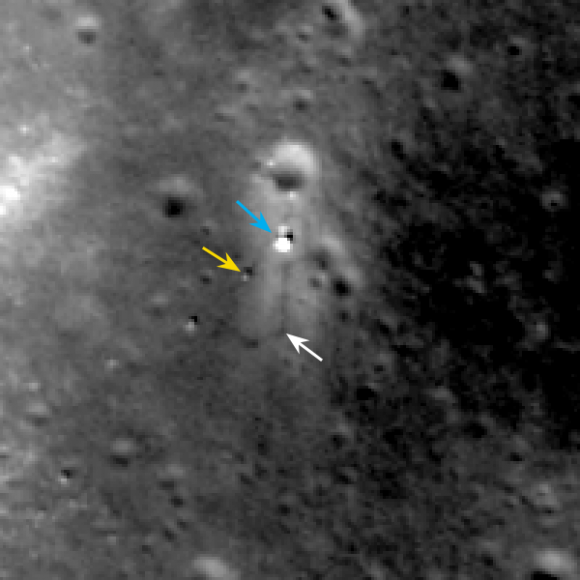
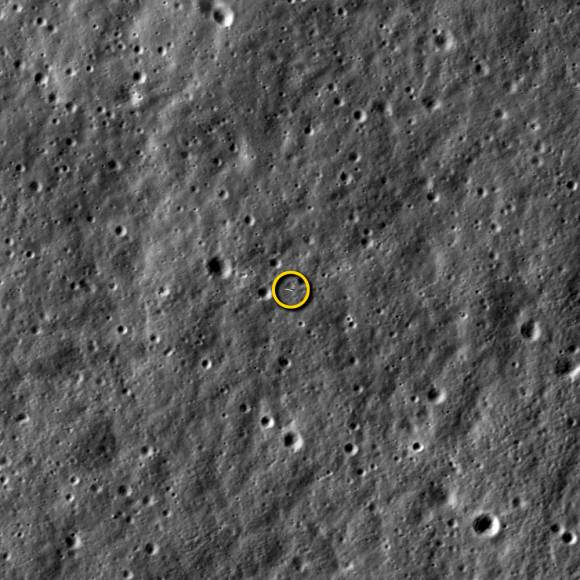
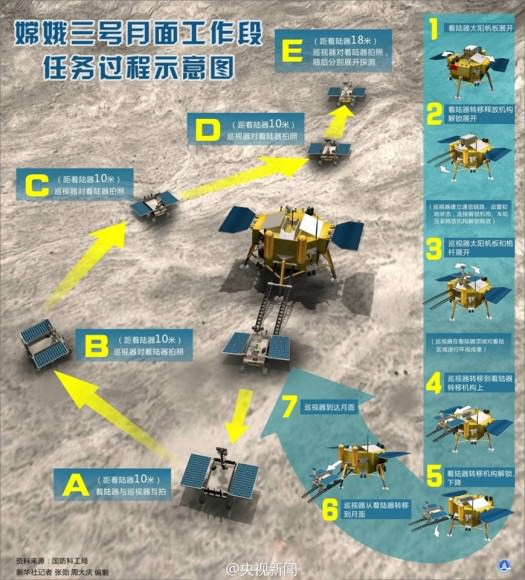
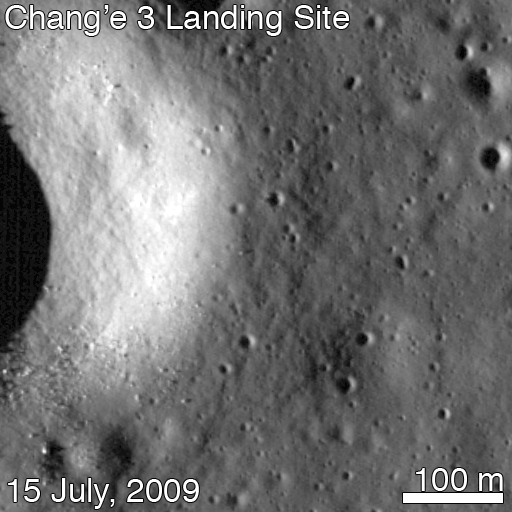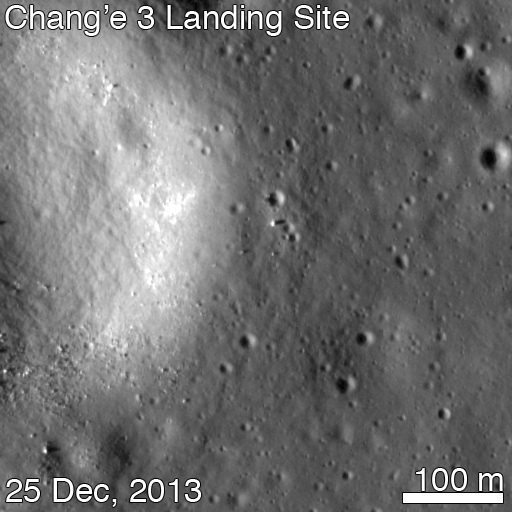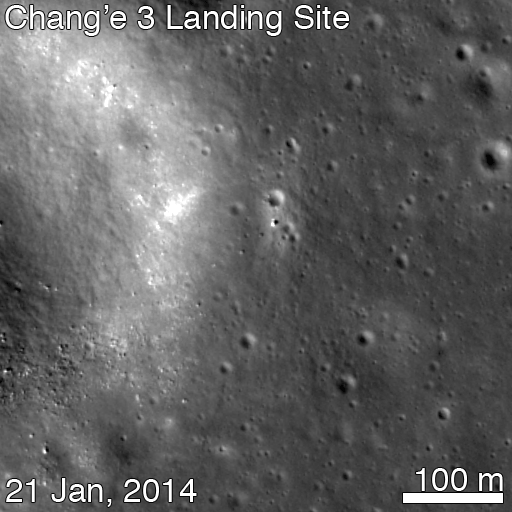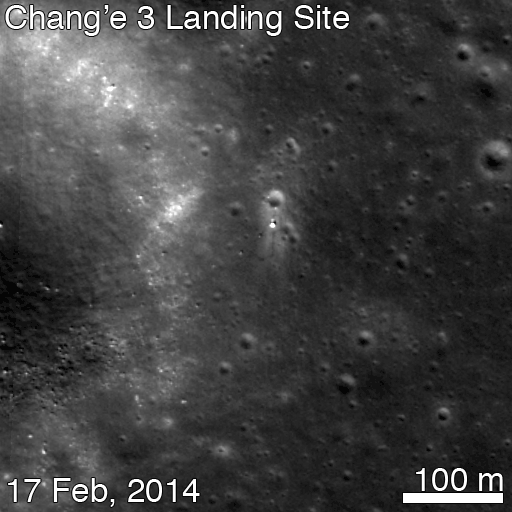
Altogether three images of the rover and lander have been taken to date by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) aboard LRO – specifically the hi res narrow angle camera (NAC).
The LROC NAC images were captured on Dec. 25, 2013, Jan. 21, 2014 and Feb. 17, 2014 as LRO soared overhead.
The four image LRO composite below includes a pre-landing image taken on June 30, 2013.
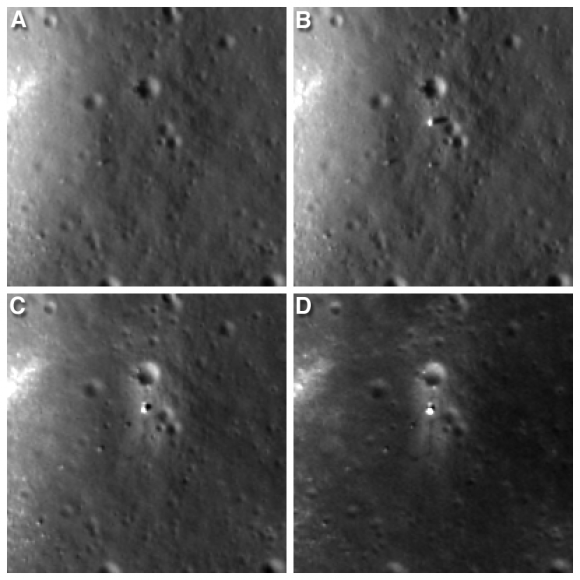

Since the solar incidence angles were different, the local topography and reflectance changes between images showing different levels of details.
“In the case of the Chang’e 3 site, with the sun higher in the sky one can now see the rover Yutu’s tracks (in the February image),” wrote Mark Robinson, Principal Investigator for the LROC camera in an LRO update.
The solar powered rover and lander can only operate during periods of lunar daylight, which last 14 days each.
During each lunar night, they both must power down and enter hibernate mode since there is no sunlight available to generate power and no communications are possible with Earth.
Here is a gif animation from the NASA LRO team combining all four LROC images.
During Lunar Day 1, Yutu drove down the landers ramps and moved around the right side in a clockwise direction.
By the end of the first lunar day, Yutu had driven to a position about 30 meters (100 feet) south of the Chang’e-3 lander, based on the imagery.
See our complete 360 degree timelapse color panorama from Lunar Day 1 herein and at NASA APOD on Feb. 3, 2014 – assembled by Marco Di Lorenzo and Ken Kremer.

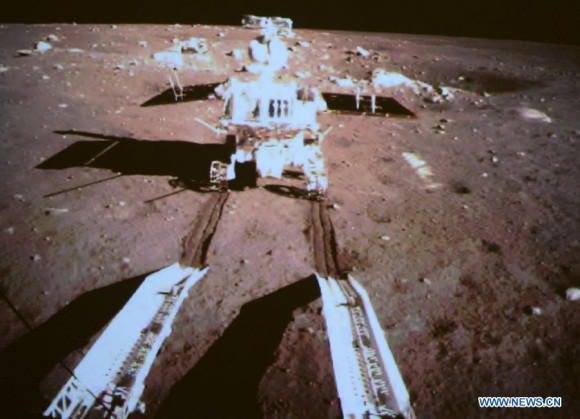
After awakening for Lunar Day 2, Yutu then moved northwest and parked about 17 meters (56 feet) southwest of the lander, according to Robinson.
By comparing the Janaury and February images “it is apparent that Yutu did not move appreciably from the January location,” said Robinson.
At this moment Yutu and the companion Chang’e-3 lander are sleeping through their 3rd Lunar Night.
They entered hibernation mode on Feb. 22 and Feb. 23, 2014 respectively.
Hopefully both probes will awaken from their slumber sometime in the next week when the Moon again basks in daylight glow to begin a 4th day of lunar surface science operations.
“We all wish it would be able to wake up again,” said Ye Peijian, chief scientist of the Chang’e-3 program, according to CCTV, China’s state run broadcaster.
However, the hugely popular ‘Yutu’ rover is still suffering from an inability to maneuver its life giving solar panels. It is also unable to move – as I reported here.
The 140 kg rover is now nearing its planned 3 month long life expectancy on a moon roving expedition to investigate the moon’s surface composition and natural resources.

This newly expanded timelapse composite view shows China’s Yutu moon rover at two positions passing by crater and heading south and away from the Chang’e-3 lunar landing site forever about a week after the Dec. 14, 2013 touchdown at Mare Imbrium. This cropped view was taken from the 360-degree timelapse panorama. See complete 360 degree landing site timelapse panorama herein and APOD Feb. 3, 2014. Chang’e-3 landers extreme ultraviolet (EUV) camera is at right, antenna at left. Credit: CNSA/Chinanews/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo – kenkremer.com. See our complete Yutu timelapse pano at NASA APOD Feb. 3, 2014: http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap140203.htm
China is only the 3rd country in the world to successfully soft land a spacecraft on Earth’s nearest neighbor after the United States and the Soviet Union.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Chang’e-3, Orion, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, LADEE, Mars and more planetary and human spaceflight news. Learn more at Ken’s upcoming presentations at the NEAF astro/space convention on April 12/13.