By Brian Koberlein
March 18, 2025
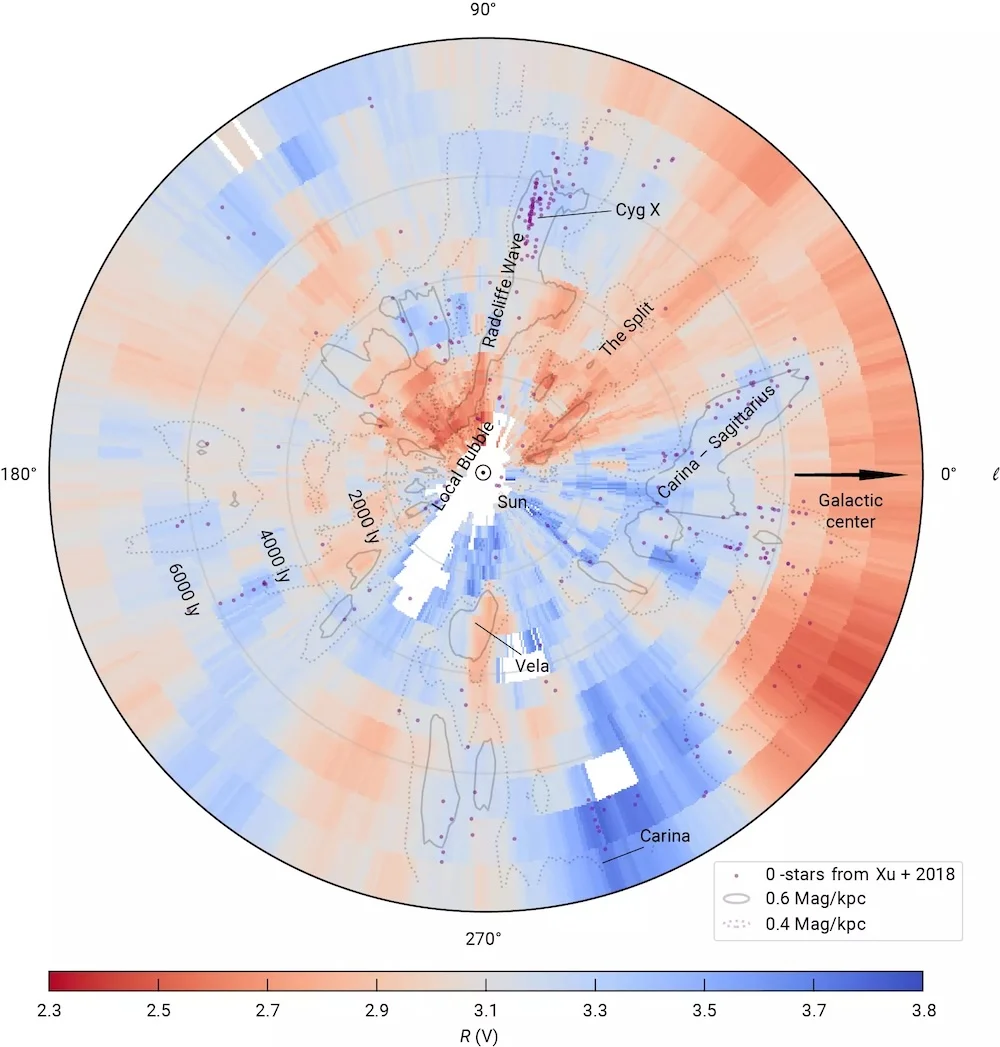
We see the Universe through a glass darkly, or more accurately, through a dusty window. Interstellar dust is scattered throughout the Milky Way, which limits our view depending on where we look. In some directions, the effects of dust are small, but in other regions the view is so dusty it's called the Zone of Avoidance. Dust biases our view of the heavens, but fortunately a new study has created a detailed map of cosmic dust so we can better account for it.
Continue reading
By Evan Gough
March 18, 2025

When massive stars explode as supernovae, they can leave behind neutron stars. Other than black holes, these are the densest objects we know of. However, their masses are difficult to determine. New research is making headway.
In new research published in Nature
Continue reading
By Mark Thompson
March 18, 2025
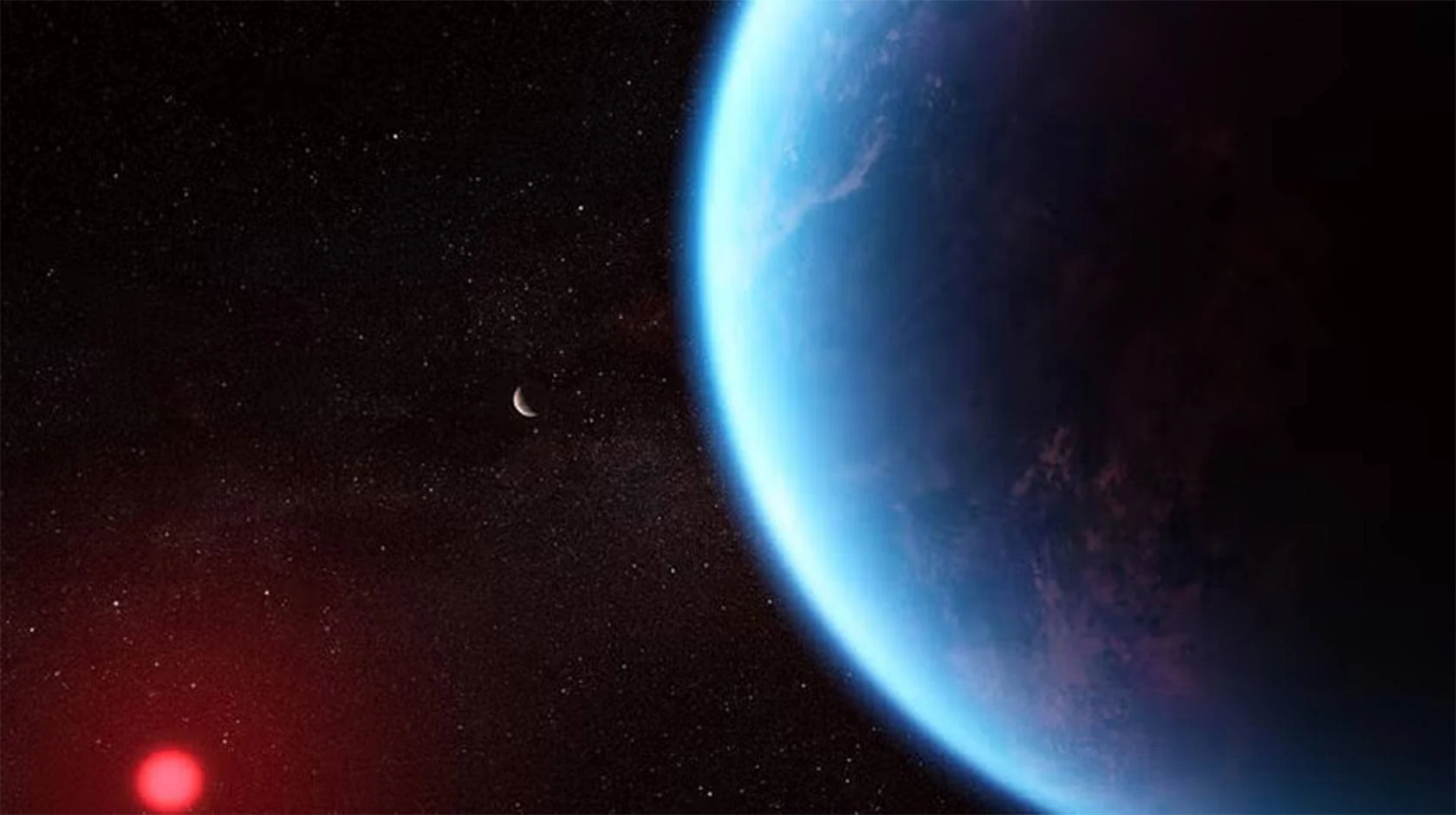

The search for life has become one of the holy grails of science. With the increasing number of exoplanet discoveries, astronomers are hunting for a chemical that can only be present in the atmosphere of a planet with life! A new paper suggests that methyl halides, which contain one carbon and three hydrogen atoms, may just do the trick. Here on Earth they are produced by bacteria, algae, fungi and some plants but not by any abiotic processes (non biological.) There is a hitch, detecting these chemicals is beyond the reach of current telescopes.
Continue reading
By Mark Thompson
March 18, 2025
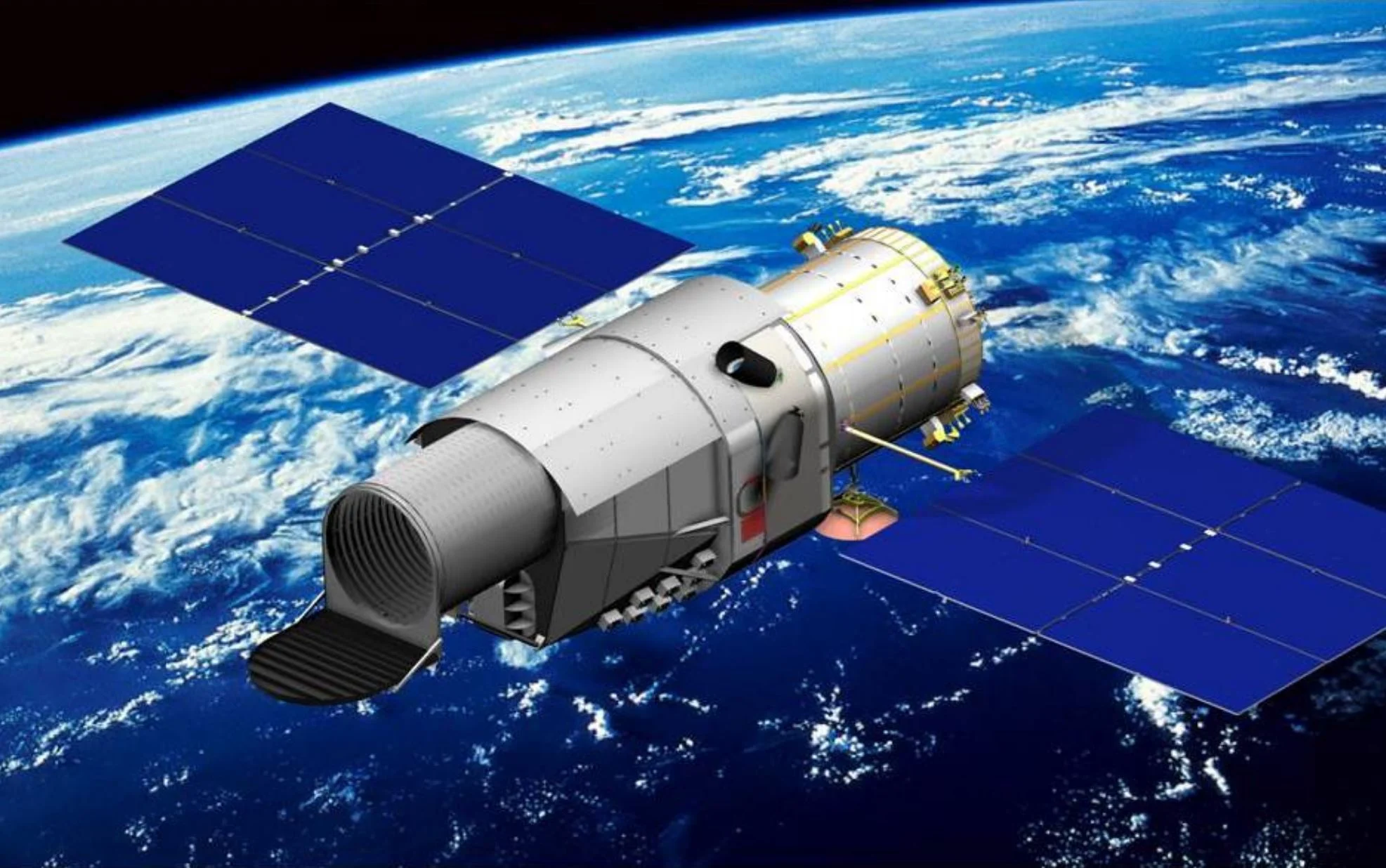

The China Space Station Telescope, scheduled for a 2027 launch, will offer astronomers a fresh view on the cosmos. Though somewhat smaller than Hubble, it features a much wider field of view, giving a wide-field surveys that will map gravitational lensing, galaxy clusters, and cosmic voids. Scientists anticipate it will measure dark energy with 1% precision, differentiate between cold and dark matter models, and evaluate gravitational theories.
Continue reading
By Paul Sutter
March 17, 2025
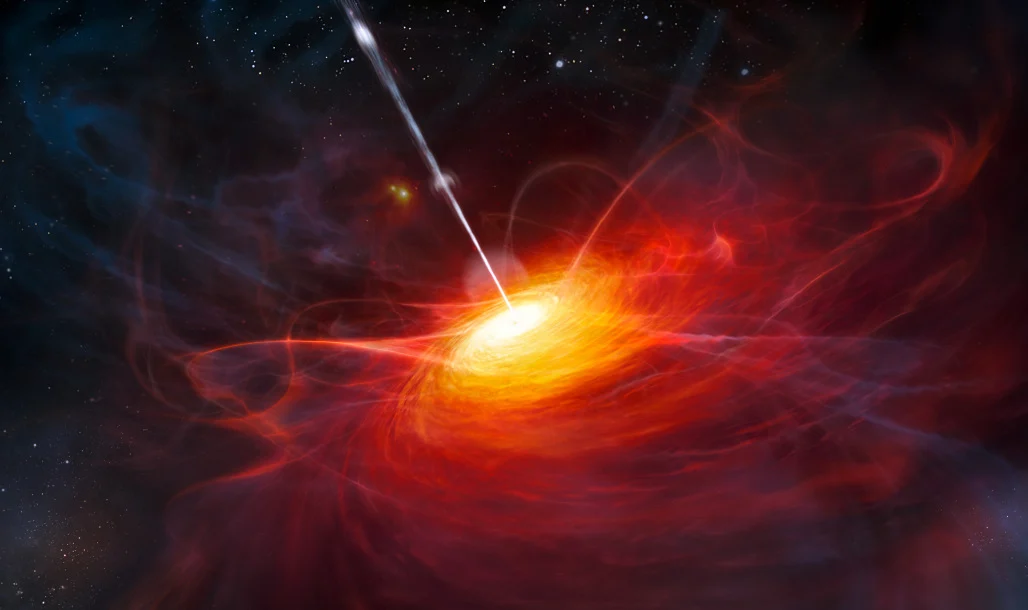
_(52748025943).png)
From far enough away, most supernovas are benign. But the thing you have to watch out for are the X-rays.
Continue reading
By Evan Gough
March 17, 2025
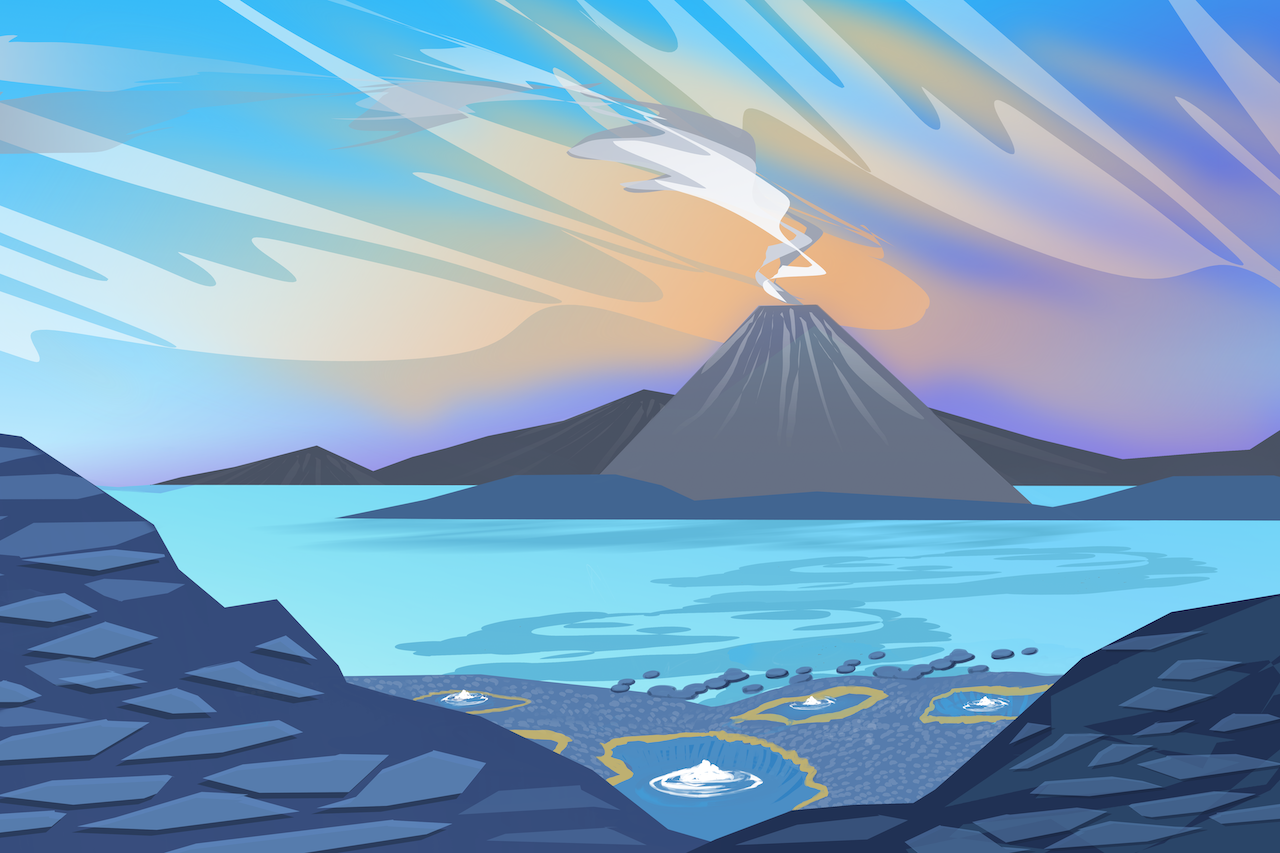

When water is sprayed or splashed, different size microdroplets develop opposite charges. This "microlightning" could've provided the energy needed to synthesize prebiotic molecules necessary for life.
Continue reading
By Andy Tomaswick
March 17, 2025

Helium-3 (He-3) on the Moon's surface has drawn attention for decades. In 1939, a paper first noted the presence of Helium-3 on the Moon. Still, it really came into the collective consciousness of space resource enthusiasts during the 1980s when they realized just how valuable a resource it was and how much the Moon had of it. Now, a new paper from a company called Interlune, a relatively new start-up based out of Seattle, presented a paper at the recent Lunar and Planetary Science Conference that discusses plans to try to mine some of that wealth of material economically.
Continue reading
By Evan Gough
March 17, 2025
_(cropped)-(1).jpg)
Even tipped over onto its side, the Odysseus Lunar Lander was able to do some science. Though a broken leg means it's doomed to spend eternity in an awkward position, its solar panels were able to gather some energy. Enough for its radiotelescope to take observations for about 80 minutes.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today





_(52748025943).png)


_(cropped)-(1).jpg)